
Unter Linux lautet der vollständige Name „GNU Compiler Collection“, was auf Chinesisch „GNU Compiler Suite“ bedeutet. Es handelt sich um einen von GNU entwickelten Compiler für Programmiersprachen. Die gcc-Suite umfasst C-, C++-, Objective-C-, Fortran-, Java-, Ada- und Go-Sprach-Frontends sowie Bibliotheken für diese Sprachen.

Die Betriebsumgebung dieses Tutorials: Linux7.3-System, Dell G3-Computer.
1. Was ist gcc? GCC (GNU Compiler Collection, GNU Compiler Suite) ist ein von GNU entwickelter Programmiersprachen-Compiler, der mehrere Sprachen kompilieren kann. Die GNU-Compiler-Suite umfasst C-, C++-, Objective-C-, Fortran-, Java-, Ada- und Go-Sprach-Frontends sowie Bibliotheken für diese Sprachen (wie libstdc++, libgcj usw.) Am Anfang gcc wurde als C-Sprachcompiler (GNU C Compiler) verwendet und unterstützt jetzt neben der C-Sprache auch C++, Java, Pascal und andere Sprachen. gcc unterstützt mehrere Hardwareplattformen.
2. Funktionen von gcc
gcc ist ein tragbarer Compiler, der mehrere Hardwareplattformen unterstützt. Zum Beispiel ARM, X86 usw.
GCC-Compiler durchläuft hauptsächlich vier Prozesse:
Vorverarbeitung
 Relocation
Relocation
Das Folgende ist ein Bild, um diesen Prozess darzustellen. Achten Sie auf die Suffixänderungen der Dateien während des Prozesses. Dies sind die vier Schritte der GCC-Kompilierung.
4. Gängige gcc-Optionen
Werfen wir einen Blick auf die gebräuchlichen gcc-Optionen
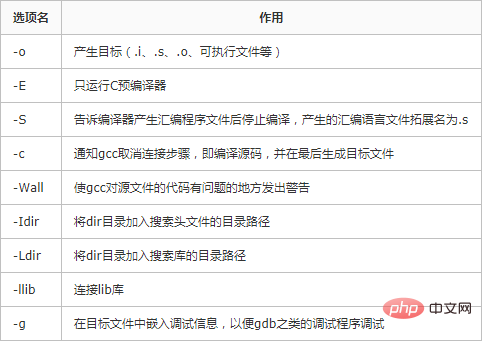 rrree
rrree 使用gcc时可以加上-Wall选项。下面这个例子如果不加上-Wall选项,编译器不会报出任何错误或警告,但是程序的结果却不是预期的:
//bad.c
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("the number is %f ",5); //程序输出了the number is 0.000000,结果错误
return 0;
}使用-Wall选项:
gcc -Wall bad.c -o bad
gcc将输出警告信息:
warning: format ‘%f’ expects argument of type ‘double’, but argument 2 has type ‘int’ [-Wformat=]
printf("the number is %f\n",5);5、gcc编译多个文件
// hello.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include"hello.h"
void printHello()
{
printf("hello world!\n");
}//main.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include"hello.h"
int main()
{
printHello();
return 0;
}//hello.h //仅包含函数声明 #ifndef _HELLO_ #define _HELLO_ void printHello(); #endif
编译这三个文件,可以一次编译:
gcc hello.c main.c -o main 生成可执行文件main
也可以独立编译:
gcc -Wall -c main.c -o main.o gcc -Wall -c hello.c -o hello.o gcc -Wall main.o hello.o -o main
独立编译的好处是,当其中某个模块发送改变时,只需要编译该模块就行,不必重新编译所有文件,这样可以节省编译时间。
6、使用外部库
在使用C语言和其他语言进行程序设计的时候,我们需要头文件来提供对常数的定义和对系统及库函数调用的声明。库文件是一些预先编译好的函数集合,那些函数都是按照可重用原则编写的。它们通常由一组互相关联的可重用原则编写的,它们通常由一组互相关联的用来完成某项常见工作的函数构成。使用库的优点在于:
库又可以分为静态库与动态库:
一般头文件或库文件的位置在:
7、生成静态库
为了生成.a文件,我们需要先生成.o文件。下面这行命令将我们的hello.o打包成静态库libhello.a:
ar rcs libhello.a hello.o
ar是gun归档工具,rcs表示replace and create,如果libhello之前存在,将创建新的libhello.a并将其替换。
然后就可以这样来使用静态库libhello.a
gcc -Wall main.c libhello.a -o main
还有另外一种使用方式:
gcc -Wall -L. main.c -o main -lhello 【lhello 是 libhello的缩写】
其中 -L.表示库文件的位置在当前目录下,由于libhello.a是我们自己生成的,并存放在当前录下下,所以需要加上-L.选项。默认库文件是在系统的目录下进行搜索。同样的,-I.选项用于头文件的搜索。
8、生成共享库
生成一个共享库,名称的规则是libxxx.so。将刚才hello.o生成libhello.so的命令为:
gcc -shared -fPIC hello.o -o libhello.so
生成了共享库之后,可以这样来使用共享库:
gcc -Wall main.o -o main -L. -lhello
该命令与使用静态库的命令相同,但是在共享库与静态库共存的情况下,优先使用共享库。
共享库有时候并不不在当前的目录下,为了让gcc能够找得到共享库,有下面几种方法:
拷贝.so文件到系统共享库路径下,一般指/usr/lib
在~/.bash_profile文件中,配置LD_LIBRARY_PATH变量
配置/etc/ld.so.conf,配置完成后调用ldconfig更新ld.so.cache
其中,shared选项表示生成共享库格式。fPIC表示产生位置无关码(position independent code),位置无关码表示它的运行、加载与内存位置无关,可以在任何内存地址进行加载。
9、库的搜索路径
库的搜索路径遵循几个搜索原则:从左到右搜索-I -l指定的目录,如果在这些目录中找不到,那么gcc会从由环境 变量指定的目录进行查找。头文件的环境变量是C_INCLUDE_PATH,库的环境变量是LIBRARY_PATH.如果还是找不到,那么会从系统指定指定的目录进行搜索。
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonWas ist gcc unter Linux?. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!