
Dieser Artikel vermittelt Ihnen relevantes Wissen über Java, das hauptsächlich die damit verbundenen Probleme der Implementierung einer einfachen Version des Bibliotheksverwaltungssystems organisiert, einschließlich der Analyse der Funktionen des Bibliotheksverwaltungssystems und der Erstellung funktionaler Klassen in IDEA. Werfen wir einen Blick darauf Benutzerbezogene Verarbeitung usw. Ich hoffe, dass es für alle hilfreich ist.

Empfohlene Studie: „Java-Video-Tutorial“
Lassen Sie uns zunächst die Funktionen analysieren, die ein Bibliotheksverwaltungssystem haben sollte, und ein einfaches Framework erstellen.
(1) Anmeldung
Normalerweise können nur zwei Personen das Bibliotheksverwaltungssystem verwenden, einer ist der Schüler und der andere der Bibliothekar
Dies ist die Anmeldeschnittstelle der Online-Bibliothek meiner Schule, über die Schüler nach Büchern suchen können Zugriff über das Internet
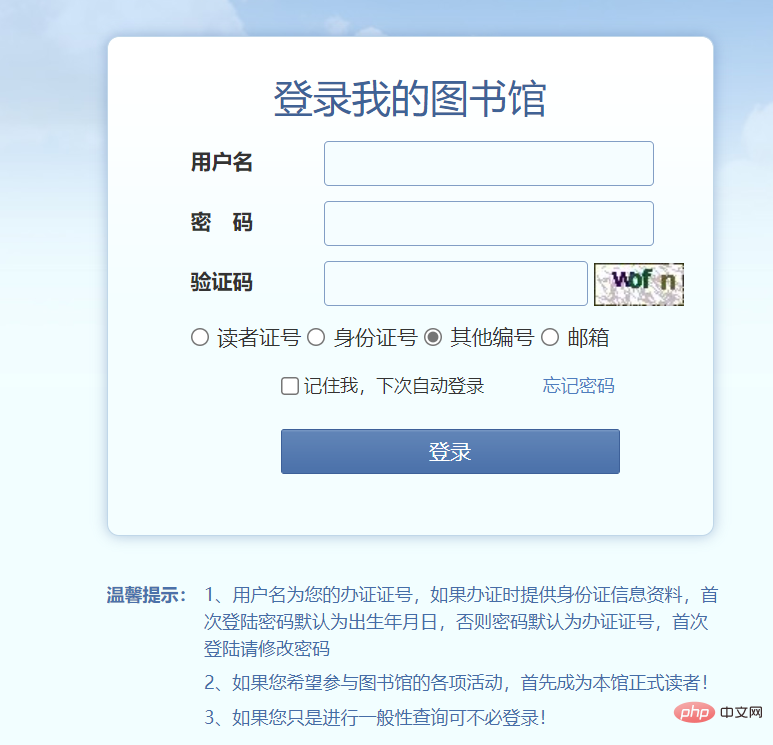
Ich kann die Anmeldeoberfläche des Administrators hier nicht sehen, aber es wird auf jeden Fall ein Fenster geben, in dem sich Administratoren für die Systemwartung anmelden können. Es hängt also vom Benutzer ab, wann er sich anmeldet egal, ob Sie ein normaler Benutzer oder ein Administrator sind. (2) Analysefunktion: Die Funktionen, die ein einfaches Bibliotheksverwaltungssystem haben sollte: -bezogene Informationen
(1) Erstellen Sie eine Buchklasse, um die Attribute des Buches anzuzeigen
Um nach einem Buch zu suchen, sollte ein Buch diese Attribute haben
private String name;//书名 private String author;//作者 private int price;//价格 private String type;//类型 private boolean isBorrowed;//借阅情况
Beachten Sie hier die von der bereitgestellten Steuerzeichen book sind privat und können außerhalb der Klasse nicht aufgerufen werden 
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public boolean isBorrowed() {
return isBorrowed;
}
public void setBorrowed(boolean borrowed) {
isBorrowed = borrowed;
} Dann stellen Sie eine Konstruktormethode für die Eigenschaften des Buches bereit,
Dann stellen Sie eine Konstruktormethode für die Eigenschaften des Buches bereit,
Da es sich um eine Bibliothek handelt und Bücher gespeichert werden sollen, wird ein Array zum Speichern von Büchern eingerichtetund eine Mitgliedsvariable wird bereitgestellt, um die Anzahl der Bücher im aktuellen Bücher-Array in Echtzeit aufzuzeichnenpublic Book(String name, String author, int price, String type) { this.name = name; this.author = author; this.price = price; this.type = type; }Nach dem Login kopieren
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BookList{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
", isBorrowed=" + isBorrowed +
'}';
}Folgendes kann eine Konstruktionsmethode zum Speichern der Bücher darin bereitstellen. Die vorherigen Bücher
//最多存放20本书 private Book[] books = new Book[20];
stellen eine Methode bereit, wenn Sie einen zulässigen Array-Index angeben. Sie finden dieses Buch 
private int usedSize;//实时记录 当前Books这个数组中有多少本书
( 1) Erstellen Sie eine IOperation-Schnittstelle, um die Operationsreferenz auf das Array zu implementierenDenn unabhängig davon, ob es sich um einen Administrator oder einen normalen Benutzer handelt, werden die Operationen an Büchern im Bücherarray der BookList-Klasse ausgeführt.
So kann es eine IOperation-Schnittstelle bereitstellen, um Operationen auf Arrays zu implementieren,
public BookList() {
books[0] = new Book("西游记","吴承恩",25,"小说");
books[1] = new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",26,"小说");
books[2] = new Book("三国演义","罗贯中",27,"小说");
books[3] = new Book("水浒传","施耐庵",28,"小说");
usedSize = 4;//当前有4本书
}(2) Erstellen Sie verschiedene Klassen, um alle Operationen auf Büchern zu implementieren
Zum Beispiel müssen normale Benutzer und Administratoren Bücher anzeigen. Diese Anzeige ist ein Effekt, also schreiben Sie einfach eine Klasse und sowohl normale Benutzer als auch Administratoren können sie aufrufen.
Gemeinsam erstellen Sie einfach diese Kurse,
然后就可以对这些类引用接口了,再重写一下
比如新增图书
public class AddOperation implements IOperation {
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("新增图书!");
}
}也就是对普通用户和管理员进行处理
(1)创建一个user的包,在包中创建一个类
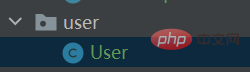
这里只创建一个类,是因为对于普通用户和管理员来说,他们两个都是用户
所以创建一个成员变量,来表示用户
//写protected是后面要继承 protected String name;//用户名
下面提供一个构造方法对其初始化
//提供一个构造方法,用来初始化当前对象name属性
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}(2)在user包中再创建两个类
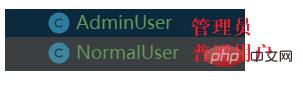
子类NormalUser继承父类User,提供一个构造方法来显示帮助父类进行构造
public class NormalUser extends User{
public NormalUser(String name) {
super(name);
}
}子类AdminUser继承父类User和前面一样
下来就是打印菜单了,根据两个用户所需功能进行打印菜单
先看AdminUser管理员的
public int menu() {
System.out.println("hello " + this.name + "欢迎进入图书管理系统!");
System.out.println("1.查找图书!");
System.out.println("2.新增图书!");
System.out.println("3.删除图书!");
System.out.println("4.显示图书!");
System.out.println("0.退出系统!");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
//因为这个是个菜单,所以要把这个输入的值传出去,才能使用
}再看NormalUser普通用户的
System.out.println("hello " + this.name + "欢迎进入图书管理系统!");
System.out.println("1.查找图书!");
System.out.println("2.借阅图书!");
System.out.println("3.归还图书!");
System.out.println("0.退出系统!");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
//因为这个是个菜单,所以要把这个输入的值传出去,才能使用(3)单独创建一个Main的类,将前面所有整合起来
菜单用户都有了,下面就是要把这些都整合起来,
先准备图书
BookList bookList = new BookList();//准备图书
结下来就是登录了,
先写一个判断你是普通用户还是管理员的方法
public static User login() {
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入你的身份:1:-》管理员.0:-》普通用户");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) {
return new AdminUser(name);
}else {
return new NormalUser(name);
}
}注意观察这段代码,返回类型是User,这是因为不论if中返回是AdminUser还是NormalUser,User作为父类都可以接收,这个过程就发生了向上转型
然后再在main方法中引用这个login()方法,就可以实现选择登录了
//登录-》user这个引用 引用哪个对象看前面if User user = login();
选择完你是哪种用户后,就打印对应功能菜单
但是注意,刚刚把菜单写在了对应子类中去了
如果现在要在父类中访问,是访问不了的,所以就要在父类中也引用出菜单
public abstract class User {
//写protected是后面要继承
protected String name;//用户名
//提供一个构造方法,用来初始化当前对象name属性
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract int menu();
}看代码中,只需将父类写成抽象类,然后在抽象类中,引出抽象方法的菜单,
就可以在Main类中通过父类访问到菜单,这就实现了动态绑定
public static void main(String[] args) {
//开始整合
BookList bookList = new BookList();//准备图书
//登录-》user这个引用 引用哪个对象看前面if
User user = login();
user.menu();//动态绑定
//要想访问子类中的菜单,那就要将父类写成抽象类,
//然后子类重写父类的方法,才可以访问菜单
}
}然后此时代码就可以运行了
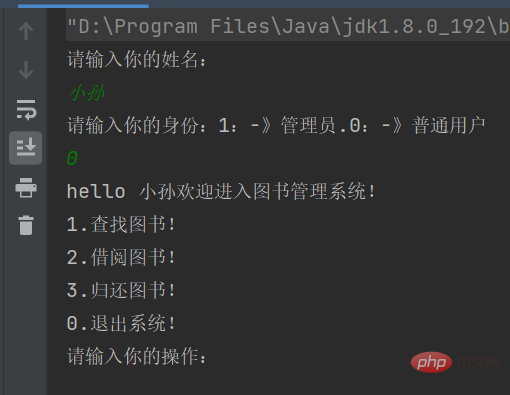
先在User中写一个方法,这个方法的作用是
通过某个用户,访问这个用户对应方法功能的数组下标,然后通过调用work方法,来实现功能
public void doOperation(int choice, BookList bookList) {
this.iOperations[choice].work(bookList);
}然后在mian中,通过选择用户引用这个方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//开始整合
BookList bookList = new BookList();//准备图书
//登录-》user这个引用 引用哪个对象看前面if
User user = login();
int choice = user.menu();//动态绑定
user.doOperation(choice,bookList);
}细节可以看这个图片
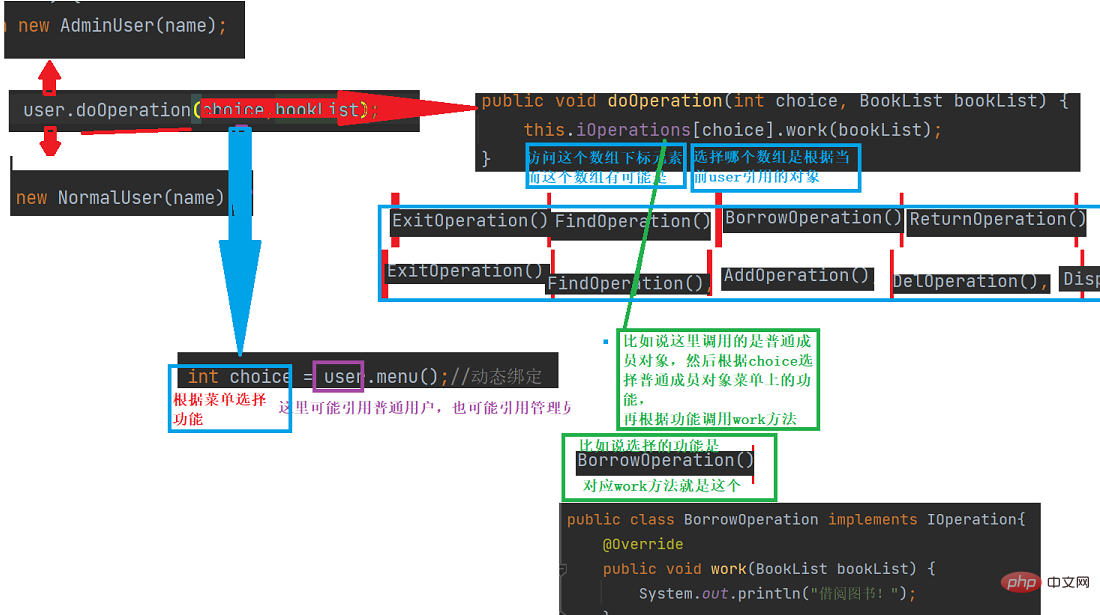
下面来看一下具体细节分析
(1)mian函数先调用
(2)现在user引用,有可能是两个对象
(3)
当引用doOperation时,根据菜单选择来访问数组元素
(4)具体选择哪个用户根据,前面login()中输入的选择对象
(5)根据前面选择需要的功能,调用work方法
比如这个
现在已经整合完成了,就差具体操作功能实现了,先运行代码试试
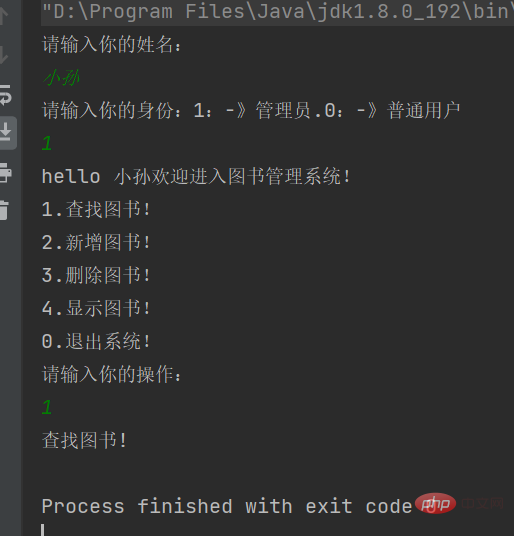
代码成功运行起来了,但是就用了一个功能就结束了,
所以我们可以加一个循环,来使用多个功能
public static void main(String[] args) {
//开始整合
BookList bookList = new BookList();//准备图书
//登录-》user这个引用 引用哪个对象看前面if
User user = login();
while(true){
int choice = user.menu();//动态绑定
user.doOperation(choice,bookList);
}
}(1)新增图书 AppOperation类
新增一本图书我们需要考虑输入这些
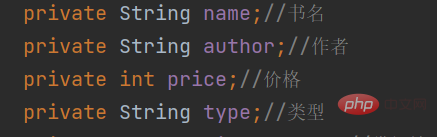
不用考虑isBorrowed 因为默认状态是未被借出的
将这些属性进行输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的作者:");
String author = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的价格:");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入图书的类型:");
String type = scanner.nextLine();然后将这些属性存放到new Book中
Book book = new Book(name,author,price,type);
获取当前下标,然后赋给currentSize,将前面输入的那本书放到数组下标为currentSize中,
然后给 currentSize加1
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize(); bookList.setBooks(currentSize,book); bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize+1);
运行一下,试试看
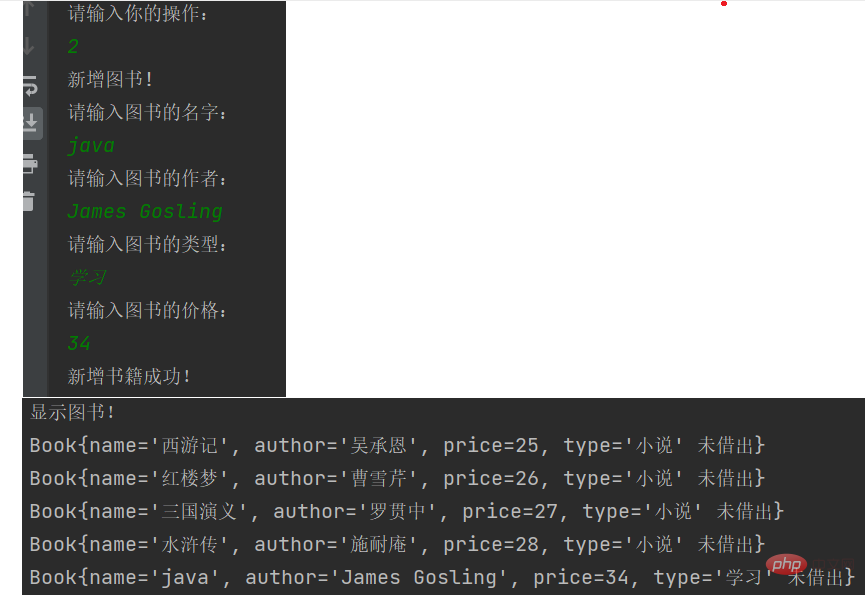
新增图书 AppOperation类的所有代码
public class AddOperation implements IOperation {
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("新增图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的作者:");
String author = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的类型:");
String type = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的价格:");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
Book book = new Book(name,author,price,type);
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
bookList.setBooks(currentSize,book);
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize+1);
System.out.println("新增书籍成功!");
}
}(2)借阅图书 orrowOperation类
先输入要借阅图书的名字
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入借阅图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();通过for循环遍历一遍,然后将遍历的每一本书赋给变量 book ,
再通过equals,来判断book和输入的书的名字是否相同,
如果相同就通过setBorrowed修改此时借阅状态,显示借阅成功
如果不同就显示没有这本书
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
book.setBorrowed(true);
System.out.println("借阅成功!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有这本书!");运行一下,试试看

借阅图书 orrowOperation类的所有代码
public class BorrowOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("借阅图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入借阅图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
book.setBorrowed(true);
System.out.println("借阅成功!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有这本书!");
}
}(3)删除图书 DelOperation类
输入删除图书的名字
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入删除图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();找到图书,然后删除
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
for (int j = i; j < currentSize; j++) {
bookList.getBook(j);
}
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize-1);//不要忘记更新图书种类
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize-1);
System.out.println("删除成功!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有找到要删除的图书!");运行程序,试试看
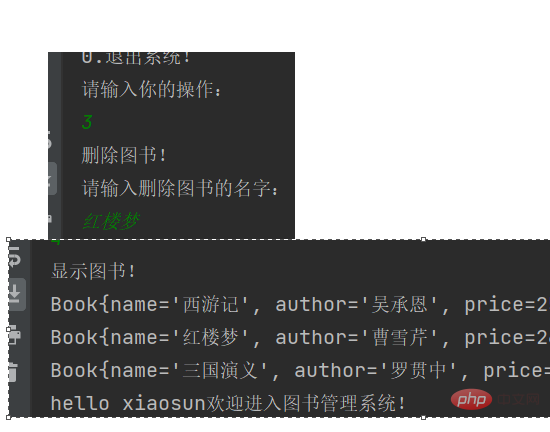
删除图书 DelOperation类的全部代码
public class DelOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("删除图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入删除图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
for (int j = i; j < currentSize; j++) {
bookList.getBook(j);
}
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize-1);//不要忘记更新图书种类
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize-1);
System.out.println("删除成功!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有找到要删除的图书!");
}
}(4)显示图书 DisplayOperation类
将当前有几本书记录下来
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
然后for循环全部遍历一遍就可以了 ,直接看代码吧
public class DisplayOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("显示图书!");
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
System.out.println(bookList.getBook(i));
}
}
}运行结果就是这样

(5)退出系统 ExitOperation类
直接调用状态码exit来退出系统
public class ExitOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
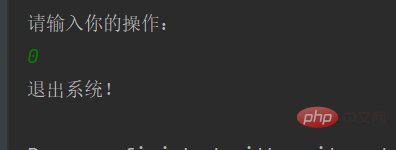
System.out.println("退出系统!");
System.exit(0);
}
}
(6)查找图书 FindOperation类
要查找图书,肯定是先要输入你需要查找书的名字
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();通过for循环遍历一遍,然后将遍历的每一本书赋给变量 book ,
再通过equals,来判断book和输入的书的名字是否相同,
如果相同就打印,并显示找到了,如果不相同,就直接显示没有找到,
但这里有一个问题在前面给每一本书默认都是false,现在打印还是这样,所以要修改一下
在Book类中,修改toString,给借阅状态一个三目运算符,来判断是否借出了
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
((isBorrowed == true)?" 已经借出":" 未借出")+
'}';
}运行一下,试试
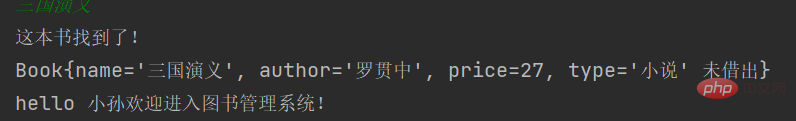 查找图书 FindOperation类的全部代码就是
查找图书 FindOperation类的全部代码就是
public class FindOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("查找图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
System.out.println("这本书找到了!");
System.out.println(book);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("这本书没有找到!");
}
}(7)归还图书 ReturnOperation类
先输入要归还图书的名字
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入归还图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();和前面借阅基本一样,修改一下setBorrowed的状态就可以了
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
book.setBorrowed(false);
System.out.println("归还成功!");
return;
}
}运行代码,试试看
<br>
归还图书 ReturnOperation类的全部代码
public class ReturnOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("归还图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入归还图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
book.setBorrowed(false);
System.out.println("归还成功!");
return;
}
}
}
}推荐学习:《java视频教程》
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonDetailliertes Beispiel für die Implementierung einer einfachen Version des Bibliotheksverwaltungssystems in Java. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!