
Linux hat eine Funktion, um die Zeit zu ermitteln. Häufig verwendete Zeitfunktionen unter Linux: 1. Funktion time() zum Abrufen der aktuellen Uhrzeit; 2. Funktionen „localtime_r“() und localtime() zum Abrufen der aktuellen Ortszeit und des aktuellen Datums; Zeit Zeit.

Die Betriebsumgebung dieses Tutorials: Linux7.3-System, Dell G3-Computer.
Einführung in häufig verwendete Zeitfunktionen:
#include <time.h> time_t time(time_t *t); /* 此函数会返回从公元1970年1月1日的UTC时间从0时0分0秒算起到现在所经过的秒数。 * 如果t 并非空指针的话,此函数也会将返回值存到t指针所指的内存。 */
Beispielcode:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
time_t sec;
sec = time((time_t *)NULL);
printf("%d\n", (int)sec);
return 0;
}Laufergebnisse:
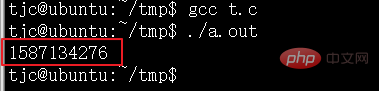
localtime_ r() localtime() ruft die aktuelle Ortszeit und das aktuelle Datum ab
#include <time.h> struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timep); struct tm *localtime_r(const time_t *timep, struct tm *result); /*该函数将有time函数获取的值timep转换真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果由结构tm返回*/ /**需要注意的是localtime函数可以将时间转换本地时间,但是localtime函数不是线程安全的。 多线程应用里面,应该用localtime_r函数替代localtime函数,因为localtime_r是线程安全的**/
Beispielcode:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
time_t tmp;
struct tm *timp;
time(&tmp);
timp = localtime(&tmp);
printf("%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d\n", (1900 + timp->tm_year), ( 1 + timp->tm_mon), timp->tm_mday,
(timp->tm_hour), timp->tm_min, timp->tm_sec);
return 0;
}Ausführungsergebnisse:
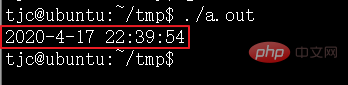
asctime() asctime_r() gibt die Uhrzeit und das Datum im String-Format zurück
#include <time.h> struct tm *gmtime(const time_t *timep); struct tm *gmtime_r(const time_t *timep, struct tm *result); char *asctime(const struct tm *tm); char *asctime_r(const struct tm *tm, char *buf); /* *gmtime是把日期和时间转换为格林威治(GMT)时间的函数。 *将参数time 所指的time_t 结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果由结构tm返回 *asctime 将时间以换为字符串字符串格式返回 */
Beispielcode:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
time_t timp;
time(&timp);
printf("%s\n", asctime(gmtime(&timp)));
return 0;
}Laufergebnisse: (Die von asctime erhaltene Zeichenfolge hat ihr eigenes Zeilenumbruchzeichen)
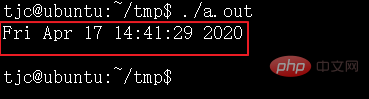
ctime(), ctime_r() stellt die Uhrzeit und das Datum im Zeichenfolgenformat dar
#include <time.h> char *ctime(const time_t *timep); char *ctime_r(const time_t *timep, char *buf); /* *ctime()将参数timep所指的time_t结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法, *然后将结果以字符串形态返回 */
Beispielcode:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(void)
{
time_t tmp;
time(&tmp);
printf("%s\n", ctime(&tmp));
return 0;
}Laufergebnis: (ctimeDie erhaltene Zeichenfolge hat ein Zeilenumbruchzeichen )
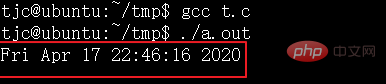
mktime() Wandelt den Wert der Zeitstruktur struct tm in verstrichene Sekunden um
#include <time.h> time_t mktime(struct tm *tm); /* *将时间结构体struct tm的值转化为经过的秒数 */
Beispielcode:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
time_t tmp;
struct tm *timp;
time(&tmp);
timp = localtime(&tmp);
tmp = mktime(timp);
printf("%d\n", (int)tmp);
return 0;
}Laufergebnis:
gettimeofday() Aktuelle Uhrzeit abrufen
#include <sys/time.h>
int gettimeofday(struct timeval *tv, struct timezone *tz);
struct timeval {
time_t tv_sec; /* seconds (秒)*/
suseconds_t tv_usec; /* microseconds(微秒) */
};
struct timezone {
int tz_minuteswest; /* minutes west of Greenwich */
int tz_dsttime; /* type of DST correction */
};
/*
*gettimeofday函数获取当前时间存于tv结构体中,相应的时区信息则存于tz结构体中
*需要注意的是tz是依赖于系统,不同的系统可能存在获取不到的可能,因此通常设置为NULL
*/Beispielcode:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
int main()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
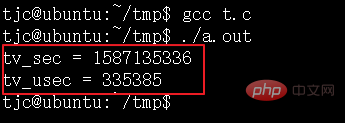
printf("tv_sec = %d\n", (int)tv.tv_sec);
printf("tv_usec = %d\n", (int)tv.tv_usec);
return 0;
}Laufergebnis:
Empfohlenes Lernen: Linux-Video-Tutorial
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonGibt es eine Funktion zum Abrufen der Zeit unter Linux?. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!