
Java ist eine der nützlichsten Programmiersprachen. Es verfügt über eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen wie Architekturerstellung, Lösung von Berechnungen in der Naturwissenschaft, Erstellung von Karten usw. Um diese Aufgaben zu vereinfachen, stellt Java eine java.lang.Math-Klasse oder Mathe-Funktionen in Java bereit, die verschiedene Operationen wie Quadrat- und Exponentialoperationen ausführt , Decke, Logarithmus, Kubik, Bauchmuskeln, Trigonometrie, Quadratwurzel, Boden usw.
WERBUNG Beliebter Kurs in dieser Kategorie JAVA MASTERY - Spezialisierung | 78 Kursreihe | 15 ProbetestsStarten Sie Ihren kostenlosen Softwareentwicklungskurs
Webentwicklung, Programmiersprachen, Softwaretests und andere
Dieser Kurs bietet zwei Felder, die die Grundlagen des Mathematikunterrichts bilden. Sie sind,
Java bietet eine Fülle mathematischer Methoden. Sie können wie folgt klassifiziert werden:
Lassen Sie uns nun einen genaueren Blick darauf werfen.
Zum besseren Verständnis können wir die oben genannten Methoden wie unten gezeigt in einem Java-Programm implementieren:
| Methode | Rückgabewert | Argumente |
Beispiel |
|
abs() |
Absoluter Wert des Arguments. d.h. positiver Wert | long, int, float, double |
int n1 = Math.abs (80) //n1=80 int n2 =Math.abs (-60) //n2=60 |
|
sqrt() |
Die Quadratwurzel des Arguments | doppelt |
double n= Math.sqrt (36.0) // n=6.0 |
|
cbt() |
Kubikwurzel des Arguments | doppelt |
double n= Math.cbrt (8.0) // n=2.0 |
|
max() |
Maximum der beiden im Argument übergebenen Werte | long, int, float, double |
int n=Math.max(15,80) //n=80 |
|
min() |
Minimum der beiden im Argument übergebenen Werte | long, int, float, double |
int n=Math.min(15,80) //n=15 |
|
ceil() |
Rundet den Gleitkommawert auf einen ganzzahligen Wert auf | doppelt | double n=Math.ceil(6.34) //n=7.0 |
| floor() | Rundet den Gleitkommawert auf einen ganzzahligen Wert ab | doppelt |
double n=Math.floor(6.34) //n=6.0 |
|
round() |
Rundet den Float- oder Double-Wert entweder auf oder ab auf einen ganzzahligen Wert | doppelt, schwebend | double n = Math.round(22.445);//n=22.0 double n2 = Math.round(22.545); //n=23,0 |
|
pow() |
Wert des ersten Parameters erhöht auf den zweiten Parameter |
doppelt |
double n= Math.pow(2.0, 3.0) //n=8.0 |
|
zufällig() |
Eine Zufallszahl zwischen 0 und 1 | doppelt | double n= Math.random() //n= 0,2594036953954201 |
|
signum() |
Vorzeichen des übergebenen Parameters.
Wenn positiv, wird 1 angezeigt. Wenn negativ, wird -1 angezeigt. Wenn 0, wird 0 angezeigt |
doppelt, schwebend |
double n = Mathe. signum (22.4);//n=1.0 double n2 = Math. signum (-22,5);//n=-1,0 |
|
addExact() |
Summe der Parameter. Eine Ausnahme wird ausgelöst, wenn das erhaltene Ergebnis einen Long- oder Int-Wert überschreitet. | int, long |
int n= Math.addExact(35, 21)//n=56 |
|
incrementExact() |
Parameter um 1 erhöht. Die Ausnahme wird ausgelöst, wenn das erhaltene Ergebnis den int-Wert überläuft. | int, long |
int n=Mathe. incrementExact(36) //n=37 |
|
subtractExact() |
Unterschied der Parameter. Die Ausnahme wird ausgelöst, wenn das erhaltene Ergebnis den int-Wert überschreitet. | int, long |
int n= Math.subtractExact(36, 11) //n=25 |
|
multiplyExact() |
Summe der Parameter. Eine Ausnahme wird ausgelöst, wenn das erhaltene Ergebnis einen Long- oder Int-Wert überschreitet. | int, long |
int n= Math.multiplyExact(5, 5) //n=25 |
|
decrementExact() |
Parameter um 1 dekrementiert. Die Ausnahme wird ausgelöst, wenn das erhaltene Ergebnis einen Int- oder Long-Wert überläuft. | int, long |
int n=Mathe. decrementExact (36) //n=35 |
|
negateExact() |
Die Negation des Parameters. Die Ausnahme wird ausgelöst, wenn das erhaltene Ergebnis einen Int- oder Long-Wert überschreitet. | int, long |
int n=Mathe. negateExact(36) //n=-36 |
|
copySign() |
Absoluter Wert des ersten Parameters zusammen mit dem im zweiten Parameter angegebenen Vorzeichen | double,float |
double d= Math.copySign(29.3,-17.0) //n=-29.3 |
|
floorDiv() |
Dividieren Sie den ersten Parameter durch den zweiten Parameter und die Bodenoperation wird ausgeführt. | long, int |
int n= Math.floorDiv(25, 3) //n=8 |
|
hypot() |
Berechnen Sie die Summe der Quadrate der Parameter und führen Sie eine Quadratwurzeloperation durch. Ein zwischenzeitlicher Überlauf oder Unterlauf sollte nicht vorhanden sein. | doppelt |
double n=Math.hypot(4,3) //n=5.0 |
|
getExponent() |
unvoreingenommener Exponent. Dieser Exponent wird in Double oder Float | dargestelltint |
double n=Math.getExponent(50.45) //n=5 |
Code:
//Java program to implement basic math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n1 = Math.abs(80);
System.out.println("absolute value of 80 is: "+n1);
int n2 = Math.abs(-60);
System.out.println("absolute value of -60 is: "+n2);
double n3 = Math.sqrt(36.0);
System.out.println("Square root of 36.0 is: "+n3);
double n4 = Math.cbrt(8.0);
System.out.println("cube root 0f 8.0 is: "+n4);
int n5= Math.max(15,80);
System.out.println("max value is: "+n5);
int n6 =Math.min(15,80);
System.out.println("min value is: "+n6);
double n7 = Math.ceil(6.34);
System.out.println("ceil value of 6.34 is "+n7);
double n8 = Math.floor(6.34);
System.out.println("floor value of 6.34 is: "+n8);
double n9 = Math.round(22.445);
System.out.println("round value of 22.445 is: "+n9);
double n10 = Math.round(22.545);
System.out.println("round value of 22.545 is: "+n10);
double n11= Math.pow(2.0, 3.0);
System.out.println("power value is: "+n11);
double n12= Math.random();
System.out.println("random value is: "+n12);
double n13 = Math. signum (22.4);
System.out.println("signum value of 22.4 is: "+n13);
double n14 = Math. signum (-22.5);
System.out.println("signum value of 22.5 is: "+n14);
int n15= Math.addExact(35, 21);
System.out.println("added value is: "+n15);
int n16=Math. incrementExact(36);
System.out.println("increment of 36 is: "+n16);
int n17 = Math.subtractExact(36, 11);
System.out.println("difference is: "+n17);
int n18 = Math.multiplyExact(5, 5);
System.out.println("product is: "+n18);
int n19 =Math. decrementExact (36);
System.out.println("decrement of 36 is: "+n19);
int n20 =Math. negateExact(36);
System.out.println("negation value of 36 is: "+n20);
}
}Output:

Following is the Java program to implement trigonometric math functions mentioned in the table:
|
Method |
Return value | Arguments | Example |
|
sin() |
Sine value of the parameter | double |
double num1 = 60; //Conversion of value to radians double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.sine (value) //output is 0.8660254037844386 |
|
cos() |
Cosine value of the parameter | double |
double num1 = 60; //Conversion of value to radians double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.cos (value) //output is 0.5000000000000001 |
|
tan() |
tangent value of the parameter | double |
double num1 = 60; //Conversion of value to radians double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.tan(value) //output is 1.7320508075688767 |
|
asin() |
Arc Sine value of the parameter. Or Inverse sine value of the parameter | double |
Math.asin(1.0) // 1.5707963267948966 |
|
acos() |
Arc cosine value of the parameter Or Inverse Cosine value of the parameter | double |
Math.acos(1.0) //0.0 |
|
atan() |
Arctangent value of the parameter Or Inverse tangent value of the parameter | double |
Math.atan(6.267) // 1.4125642791467878 |
Code:
//Java program to implement trigonometric math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double num1 = 60;
// Conversion of value to radians
double value = Math.toRadians(num1);
System.out.println("sine value is : "+Math.sin(value));
System.out.println("cosine value is : "+Math.cos(value));
System.out.println("tangent value is : "+Math.tan(value));
double num2 = 1.0;
System.out.println("acosine value is : "+Math.acos(num2));
System.out.println("asine value is : "+Math.asin(num2));
double num3 = 6.267;
System.out.println("atangent value is : "+Math.atan(num3)); <strong>Output:</strong>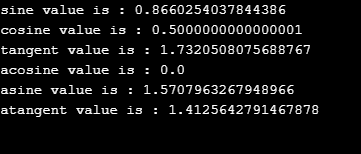
Following is the sample program that implements Logarithmic math methods:
|
Method |
Return Value | Arguments |
Example |
|
expm1() |
Calculate E’s power and minus 1 from it. E is Euler’s number. So here, it is ex-1. | double |
double n = Math.expm1(2.0) // n = 6.38905609893065 |
|
exp() |
E’s power to the given parameter. That is, ex | double |
double n=Math.exp(2.0) //n = 7.38905609893065 |
|
log() |
Natural logarithm of parameter | double |
double n=Math.log(38.9) //n=3.6609942506244004 |
|
log10() |
Base 10 logarithm of parameter | double |
double n = Math.log10(38.9) //n= 1.5899496013257077 |
|
log1p() |
Natural logarithm of the sum of parameter and one. ln(x+1) | double |
double n = Math.log1p(26) //n= 3.295836866004329 |
Code:
//Java program to implement logarithmic math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n1 = Math.expm1(2.0);
double n2 = Math.exp(2.0);
double n3 = Math.log(38.9);
double n4 = Math.log10(38.9);
double n5 = Math.log1p(26);
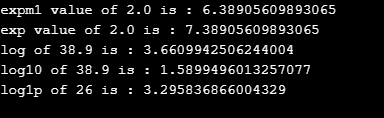
System.out.println("expm1 value of 2.0 is : "+n1);
System.out.println("exp value of 2.0 is : "+n2);
System.out.println("log of 38.9 is : "+n3);
System.out.println("log10 of 38.9 is : "+n4);
System.out.println("log1p of 26 is : "+n5);
}}Output:
Following is the Java program to implement hyperbolic math functions mentioned in the table:
|
Method |
Return value | Arguments |
Example |
|
sinh() |
Hyperbolic Sine value of the parameter. i.e (ex – e -x)/2 Here, E is the Euler’s number. | double |
double num1=Math.sinh (30) //output is 5.343237290762231E12 |
|
cosh() |
Hyperbolic Cosine value of the parameter. i.e. (ex + e -x)/2 Here, E is the Euler’s number. | double |
double num1 = Math.cosh (60.0) //output is 5.710036949078421E25 |
|
tanh() |
Hyperbolic tangent value of the parameter | double |
double num1= Math.tanh (60.0) //output is 1.0 |
Code:
//Java program to implement HYPERBOLIC math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n1 = Math.sinh (30);
double n2 = Math.cosh (60.0);
double n3 = Math.tanh (60.0);
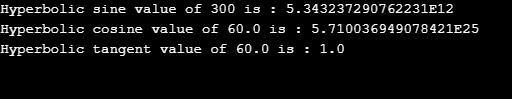
System.out.println("Hyperbolic sine value of 300 is : "+n1);
System.out.println("Hyperbolic cosine value of 60.0 is : "+n2);
System.out.println("Hyperbolic tangent value of 60.0 is : "+n3);
}
}Output:
| Method | Return Value | Arguments | Example |
| toRadians() | Degree angle converts to radian angle | double |
double n = Math.toRadians(180.0) //n= 3.141592653589793 |
| toDegrees() | Radian angle converts to Degree angle | double |
double n = Math. toDegrees (Math.PI) //n=180.0 |
Now, let us see a sample program to demonstrate Angular Math methods.
Code:
//Java program to implement Angular math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n1 = Math.toRadians(180.0);
double n2 = Math. toDegrees (Math.PI);
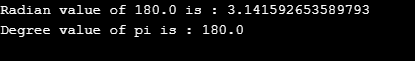
System.out.println("Radian value of 180.0 is : "+n1);
System.out.println("Degree value of pi is : "+n2);
}
}Output:
Java offers a wide variety of math functions to perform different tasks such as scientific calculations, architecture designing, structure designing, building maps, etc. This document discusses several basic, trigonometric, logarithmic and angular math functions in detail with sample programs and examples.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonMathematische Funktionen in Java. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!




