HTML block element
First of all, we need to know that HTML elements are defined as block-level elements or inline elements. So what is a block-level element and what is an inline element:
Block-level element (block) characteristics: It always occupies an exclusive line, which means it starts on a new line, and subsequent elements must also start on a new line. Display; width, height, padding and margin can all be controlled; just like the previously used < h1>, < p>, < ul>, < ; table> label.
Inline element (inline) characteristics: On the same line as adjacent inline elements; width (width), height (height), top/bottom of padding (padding-top/padding-bottom) ) and the top/bottom (margin-top/margin-bottom) of the outer margin cannot be changed, which is the size of the text or pictures inside; the previously used < b>, < td>, < a>, < img> tag.
Here we first introduce two tags, the < div> tag and the < span> tag.
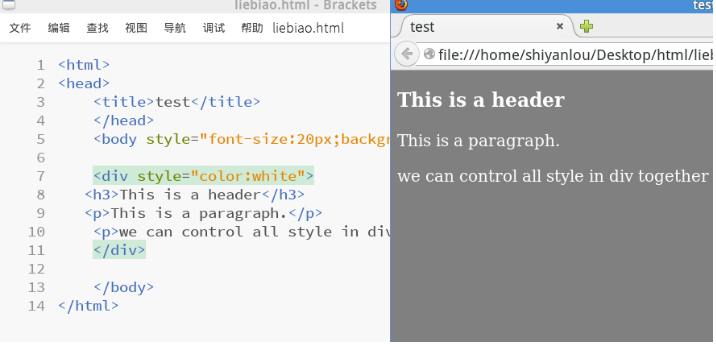
< div> is used to define a division or section (division/section) in the document and has no specific meaning. It is a container that can be used to combine other HTML elements. The
If used with CSS, the

![Front-end Vue3 actual combat [handwritten vue project]](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/068/639b12e98e0b5441.png)
![APIPOST tutorial [Popularization of technical concepts related to network communication]](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/068/63996f34c6c94370.png)










