PHP MySQL insert data
We have learned about creating databases and data tables before, so this section will tell you about adding data to the table:
The following are some syntax rules:
· SQL query statements in PHP Quotes must be used
· String values in SQL query statements must be quoted
· Numeric values do not require quotes
· NULL values do not require quotes
INSERT INTO statement is usually used to add new records to a MySQL table
Syntax
INSERTINTOtable_name (column1, column2, column3,...)VALUES(value1, value2, value3,...)
table_name: The name of the table we want to insert data into.
column1,column2: The fields in the table, such as id firstname
value1,value2: are the data we want to insert
Note
1. It is not necessary to specify the field name column..., but the order after the values should be consistent with the sorting of the table fields. insert into user(username,sex) values('Liu Qi',1);
2. Fields with default values do not need to be written, and they will be default values.
3. If there is a default value or a nullable field and you do not want to pass in a specific value, you can write null.
To learn more about SQL, check out our SQL tutorials.
Let us illustrate it with an example:
Examples
In the previous few In the chapter we have created the table "MyGuests" with the following fields: "id", "firstname", "lastname", "email" and "reg_date". Now, let's start filling the table with data.
Note: If the column is set to AUTO_INCREMENT (such as the "id" column) or TIMESTAMP (such as the "reg_date" column), we do not need to specify the value in the SQL query statement; MySQL will Automatically add a value to the column.
AUTO_INCREMENT means to add data by yourself
" . mysqli_error($conn); } mysqli_close($conn); ?>
Program running result:
New record insertion is successful
Let us open PHPadmin and see if there is any data we added:
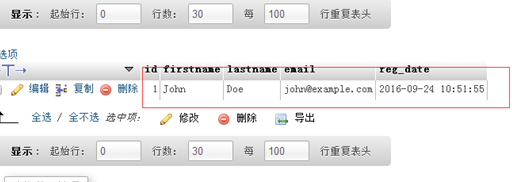
You can see that we have inserted the data into our data table

![Front-end Vue3 actual combat [handwritten vue project]](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/068/639b12e98e0b5441.png)
![APIPOST tutorial [Popularization of technical concepts related to network communication]](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/068/63996f34c6c94370.png)










