Common functions and constants in php files
Constants for file operations
The following constant is the most commonly used. Is a constant that is the delimiter of the file directory.
Let’s take a look at the format:
| Platform | Separator |
|---|---|
| windows | \ |
| unix-like | / |
The path format of windows is d:\xxx\xxx Note: windows supports d:/xxx/xxx
The path format of linux is /home/xxx/xxx Note: If \home\xxx\xxx is on linux It's wrong
So when you enable escaping and the like, the escape character \ is the same as d:\xxx\xxx if used together. When judging, if there are two \, convert it into one \ and replace the \ with / to split the path, so that the paths on Linux or Windows can remain unified.
We will use a constant:
DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR
Let’s write a small example to define the path of the current file:
SinceFILEis a predefined constant of PHP, it cannot be changed. If necessary,FILEcan also adapt to the operating system.
Then don’t useFILE, you can use custom constants and processFILEas follows:
file Pointer operation function
rewind (resource handle)
Function: The pointer returns to the beginning
fseek ( resource handle, int offset [, int from_where])
Function: Move the file pointer backward by the specified character
In the previous reading, we found that fread reads data of the specified length. Read the content of the specified length. The next time you read it, start from the original position and then read backward.
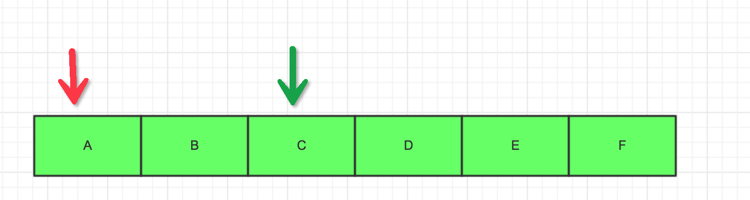
As shown in the picture above, we can imagine:
1. When the file is first opened, the red icon is read
2 .The false color of the file is read from A to C
3. The next time you open it, you can start reading from the green arrow of C.
We write a batch of files in the demo.txt file:
abcdeefghijklk
opqrst
uvwxyz
12345678
We can start experimenting once.
'; echo fread($fp,10); echo '
'; //文件指针向后移动10个字符 echo fseek($fp,10); echo '
'; //再看看文件中输出的是什么 echo fread($fp,10); echo '
'; fclose($fp); ?>
In the above example, you will find that fseek will move as many bytes as the specified length. And rewind returns to the beginning of the file every time.
How to move to the end? We can count the number of bytes. Move directly to the back during fseek.
Let’s talk about filesize statistics bytes.
filesize Detect the size of the file
Other functions for operating files
In fact, there are some other functions for operating files , read file
| Function name | Function |
|---|---|
| Read the entire file Into an array | |
| Read a line from the file pointer, read to the end and return false | |
| Read a character from the file pointer and return false after reading to the end | |
| Truncate the file to the given length |
abcdeefghijklkopqrst
uvwxyz
12345678
File time function
| Function description | |
|---|---|
| File creation time | |
| File modification time | |
| File last access time |

![Front-end Vue3 actual combat [handwritten vue project]](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/068/639b12e98e0b5441.png)
![APIPOST tutorial [Popularization of technical concepts related to network communication]](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/068/63996f34c6c94370.png)










