Correction status:qualified
Teacher's comments:作业依旧完成的很好,很认真,继续加油



概括:当出现样式层叠时(使用不同的选择器但是匹配到的是同一个元素且设置的是同一个样式属性)由选择器的权重或者在样式表中的位置决定
选择器的权重的值由四个独立的部分 a,b,c,d 组成。进行复合选择器的权重计算时四个部分是独立的,不会出现进位。在比较大小时按从 a-b-c-d 的顺序依次进行比较,高位相同才需要比较低位。
| 选择器 | 权重 | 权重等级 |
|---|---|---|
| !important | 无穷大 | 0 |
| style 行内属性 | 1,0,0,0 | 1 |
| id 选择器 | 0,1,0,0 | 2 |
| class 类选择器 | 0,0,1,0 | 3 |
| 标签,伪元素选择器 | 0,0,0,1 | 4 |
通配符选择器* |
0,0,0,0 | 5 |
| 继承的样式 | 没有权重 | 6 |
通配符选择器使用*来定义,用来匹配所以的元素,他的权重是0,0,0,0 常用于清楚浏览器默认样式
/* 通配符选择器,可以匹配所有的元素 */*{padding:0;margin:0;box-sizing:border-box;list-style:none;}
标签选择器是指用html标签名字elementName作为选择器,为页面中的某一类标签指定统一的CSS样式,他的权重是0,0,0,1,
/* 标签选择器,为所以的li标签元素设置color颜色 */li{color:aqua;}
类选择器使用className来定义,如果想要差异性选择不同的标签,可以使用类选择器,可以把某一些标签元素共同拥有的样式放到同一个类中。这样这些元素可以添加这个公共的类,然后也可以添加自己独有的类。
/* 这三个元素具有相同的颜色属性,所以将他们放同一个类中 */.item{color:aqua;}/*background-color属性是第一个元素独有的样式,所以可以将他设置为一个独有的类 */.first{background-color:red;}
class="nav"> item1item2item3class="list"> class="item first">list1 class="item">list2 class="item last">list3 item4item5item6item7item8item9
id选择器用idName来定义,id选择器一般用于选择页面唯一的元素,他的权重是0,1,0,0
/* 为id为paw的元素设置宽度样式 */#paw{width:50px;}
for="paw">密码:type="password"name=""id="paw">
| 语法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| E:nth-child() | 匹配的元素在括号内定义。 |
| E:first-child | 匹配的元素是其父元素的第一个子元素 |
| E:nth-last-child() | 从最后一个元素往前数。数几个括号定义 |
| E:last-child | 匹配的元素是其父元素的最后一个子元素 |
结构伪类选择器
结构伪类选择器用于选择具有某些特定特征的一类元素的选择器,他们的这些特征和 html 结构(在 html 中的位置)有关。他们的权重是 0,0,1,0(同类选择器)。
E:nth-child()示例
/* nth-child 匹配子级的第几个元素,括号内定义 */.nav>.list:nth-child(3){color:aqua;}

E:nth-last-child()示例
/* nth-last-child 从最后一个元素往前数,括号内定义 */.nav>.list:nth-last-child(4){color:blue-;}

E:first-child示例
/* :first-child 匹配第一个子级元素 */.nav>:first-child{color:brown-;}

E:last-child示例
/* last-child匹配最后一个元素 */.nav>:last-child{color:blueviolet;}

E:nth-child()/E:last-child()括号计算公式=a*n + b
/*a= 0,1,2,3,...n= 0,1,2,3,...b= 从0开始...an + b =a*n +b*//* 偶数 even =2n奇数 odd =2n+1 */
示例1
/* 获取前五个 a=-1 反向 */.nav>:nth-child(-n+5){color:blueviolet;}

示例2
/* 获取后五个 */.nav>:nth-last-child(-n+5){color:blueviolet;}

示例3
/* 获取双数 */.nav>:nth-last-child(2n){color:blueviolet;}

ps:双数可以用
even表示
示例4
/* 获取单数 */.nav>:nth-last-child(2n+1){color:blueviolet;}

ps:双数可以用
odd表示
| 语法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| :hover | 鼠标悬停 |
| :enabled | 有效控件 |
| :disabled | 禁用控件 |
| :checked | 选中控件 |
| :focus | 焦点控件 |
| :not() | 过滤掉某些元素 |
| :empty() | 空,匹配的元素必须没有子元素 |
| :invalid | 根据输入类型匹配有非法输入值的元素 |
| :link | 用来选择未被访问过的链接 |
| :visited | 选择已经被访问过的链接 |
| :active | 选择鼠标按下的链接 |
hover鼠标悬停 示例
/* hover 鼠标悬停 */.nav>.list:nth-child(3):hover{background-color:aquamarine;color:beige;}
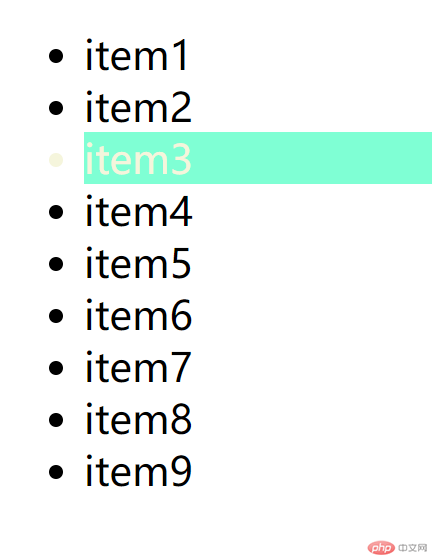
ps:需要注意的是这四个伪类的书写顺序:
:link 和 :visited 必须写在 :hover 和 :active前面,否则 :hover 和 :active 的样式将被覆盖(层叠)掉。
:hover 必须写在 :active 的前面,否则点击样式会被鼠标覆盖样式层叠(点击元素必然是在鼠标覆盖元素的情况下发生)。
平时使用时按照需求按照上面的顺序书写。
:hover 和 :active 不只对 a 元素有效,也可以应用于其他元素。
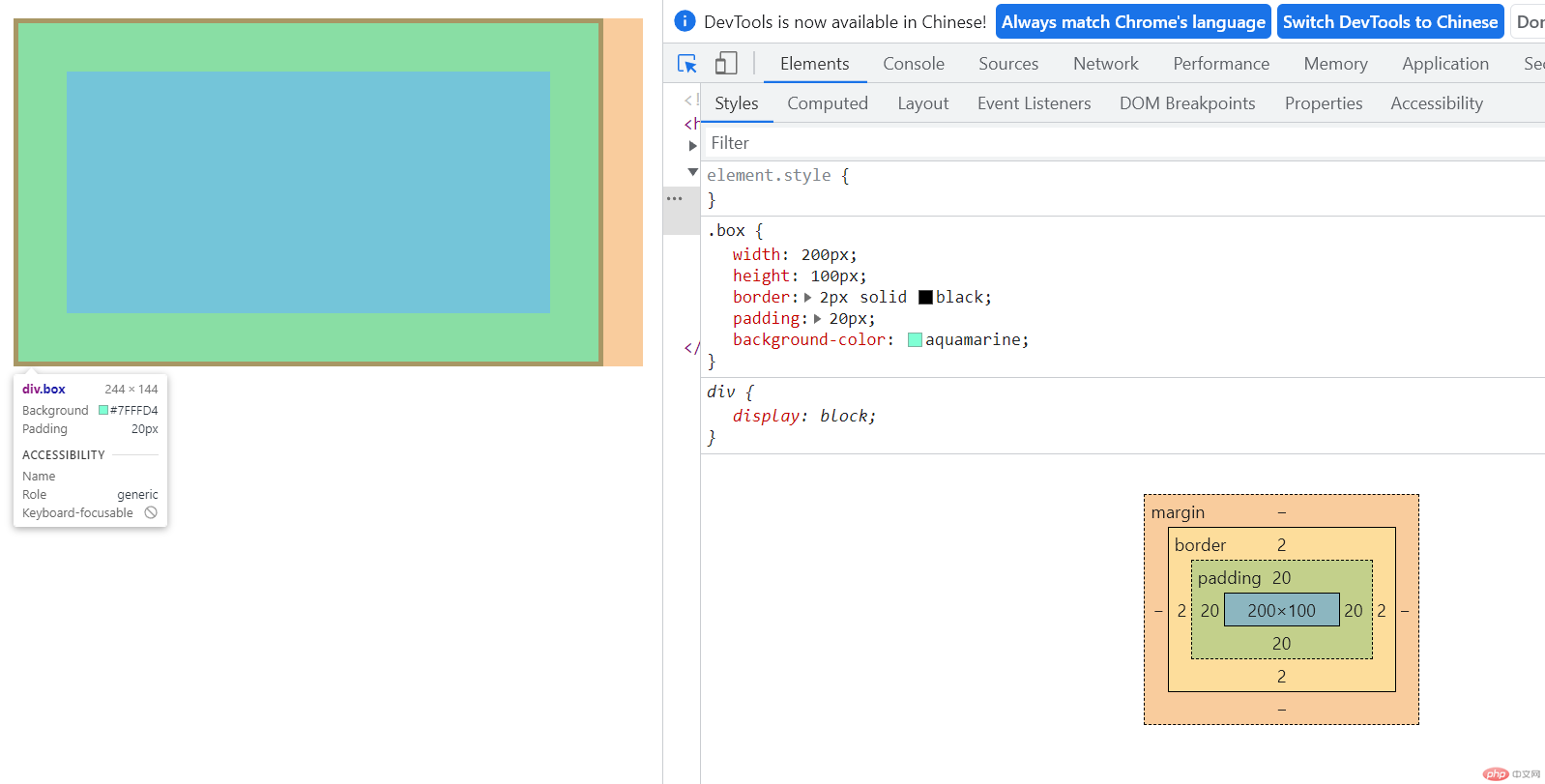
外边距(不计入盒子实际宽度)
(1). 标准盒子模型=content(内容)+border(边框)+padding(内边距)
class="box">
.box{width:200px;height:100px;border:2pxsolid black;padding:20px;background-color:aquamarine;}
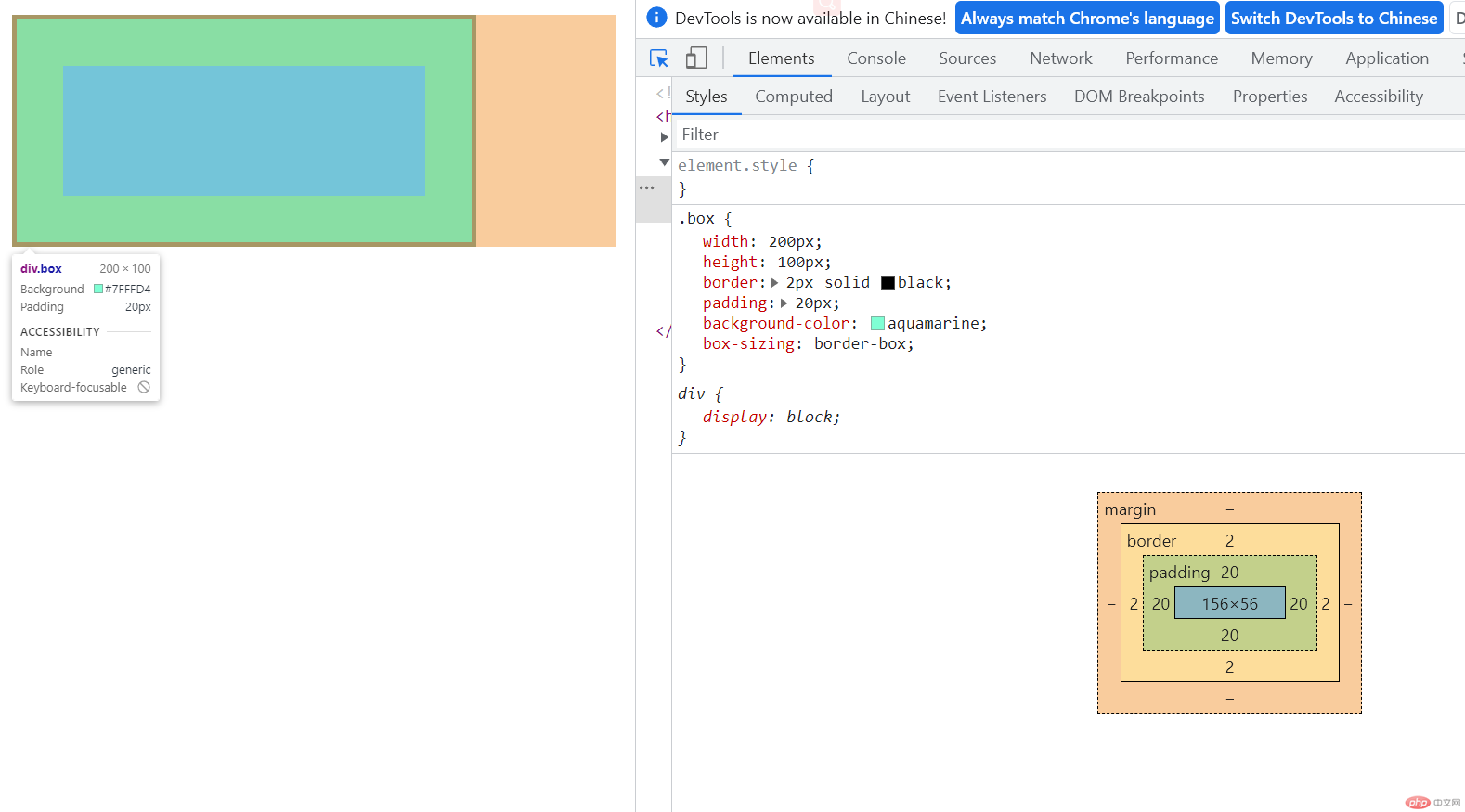
(2). 怪异盒子模型=content(内容)(已经包含了 padding 和 border)
class="box">
.box{width:200px;height:100px;border:2pxsolid black;padding:20px;background-color:aquamarine;box-sizing:border-box;}
默认值box-sizing: content-box;width=200 + border22(左右) +padding2020(左右) =244px
怪异盒子模型box-sizing: border-box;内容区content 已经包含了内边距padding和边框border