a.是个二叉树(每个节点最多有两个子节点)
b.对于这棵树中的节点的节点值
左子树中的所有节点值 < 根节点 < 右子树的所有节点值
二分搜索树中一般不考虑值相等的情况(元素不重复)JDK中的搜索树就不存在相同的值(TreeMap-key)
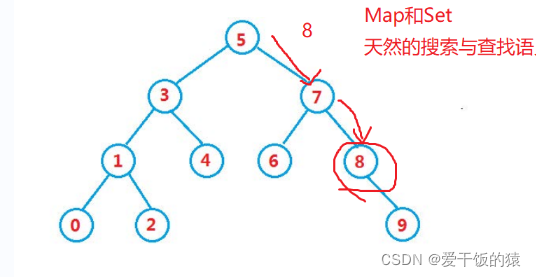
最大特点:也是判断是否是搜索树的方法
对该树进行中序遍历,就可以得到一个升序集合0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
在一个有序区间上进行二分查找的时间复杂度? logn不断将集合/2/2 / 2 ==1为止logN
logN =》联想到"树"
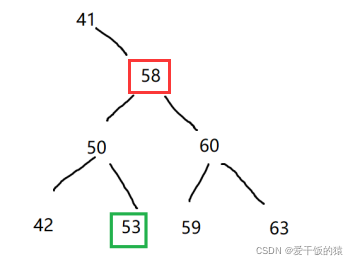
当删除58时,此节点左右子树都不为空
Hibbard Deletion 1962
在BST中删除一个左右子树都存在的节点
找到当前以58为根节点的前驱或者后继节点作为删除后的新节点
前驱:在以58为根的BST中最后一个小于58的节点->53
后继:在以58为根的BST中第一个大于58的节点->59
当我们使用后继节点时,先连removeMin(root.right),在连root.left
TreeNode successor = findMin(root.right); successor.right = removeMin(root.right); successor.left = root.left;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 基于整型的
* 普通的二分搜索树
*/
public class BST {
private class TreeNode{
private int val;
private TreeNode left;
private TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
private int size;
private TreeNode root;
/**
* 向以root为根的BST中插入一个新的结点val
* @param val
*/
public void add(int val){
root = add(root,val);
}
private TreeNode add(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null){
//创建一个新节点
TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(val);
size++;
return newNode;
}
//左子树插入
if(val < root.val){
root.left = add(root.left,val);
}
//右子树插入
if(val > root.val){
root.right = add(root.right,val);
}
return root;
}
/**
* 判断当前以root为根的BST中是否包含了val
* @param val
* @return
*/
public boolean contains(int val){
return contains(root,val);
}
private boolean contains(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null){
return false;
}
if(val == root.val){
//找到了
return true;
}else if(val < root.val){
//递归左子树查找
return contains(root.left,val);
}else{
//递归右子树查找
return contains(root.right,val);
}
}
/**
* 找到最小值
* @return
*/
public int findMin(){
//判空
if(root == null){
//抛出一个空指针异常
throw new NoSuchElementException("root is empty! cannot find min");
}
TreeNode minNode = findMin(root);
return minNode.val;
}
private TreeNode findMin(TreeNode root) {
//当此节点左子树为空,说明此节点是最小值
if(root.left == null){
return root;
}
//递归访问左子树
return findMin(root.left);
}
/**
* 找到最大值
* @return
*/
public int findMax(){
//判空
if(root == null){
throw new NoSuchElementException("root is empty! cannot find max");
}
TreeNode maxNode = findMax(root);
return maxNode.val;
}
private TreeNode findMax(TreeNode root) {
//当此节点右子树为空,说明此节点是最大值
if(root.right == null){
return root;
}
//递归访问右子树
return findMax(root.right);
}
/**
* 在当前BST中删除最小值节点,返回删除的最小值
* @return
*/
public int removeMin(){
int min =findMin();
root = removeMin(root);
return min;
}
private TreeNode removeMin(TreeNode root) {
if(root.left == null){
TreeNode right = root.right;
//找到最小值,删除节点
root = root.left = null;
size--;
return right;
}
root.left = removeMin(root.left);
return root;
}
/**
* 在当前BST中删除最大值节点,返回删除的最大值
* @return
*/
public int removeMax(){
int max = findMax();
root = removeMax(root);
return max;
}
//在当前以root为根的BST中删除最小值所在的节点,返回删除后的树根
private TreeNode removeMax(TreeNode root) {
if(root.right == null){
TreeNode right = root.right;
//找到最大值,删除节点
root = root.right = null;
size--;
return right;
}
root.right = findMax(root.right);
return root;
}
/**
* 在当前以root为根节点的BST中删除值为val的节点
* 返回删除后的新的根节点
* @return
*/
public void removeValue(int value){
root = removeValue(root,value);
}
private TreeNode removeValue(TreeNode root, int value) {
if(root == null){
throw new NoSuchElementException("root is empty! cannot find remove");
}else if(value < root.val){
root.left = removeValue(root.left,value);
return root;
}else if(value > root.val){
root.right = removeValue(root.right,value);
return root;
}else {
//此时value == root.value
if(root.left == null){
//删除最小数
TreeNode right = root.right;
root = root.right = null;
size--;
return right;
}
if(root.right == null){
//删除最大数
TreeNode left = root.left;
root = root.left =null;
size--;
return left;
}
//找到当前该删除节点的前驱或者后继节点作为删除后的新节点
//当我们使用后继节点时,先连removeMin(root.right),在连root.left
TreeNode successor = findMin(root.right);
successor.right = removeMin(root.right);
successor.left = root.left;
return successor;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
generateBSTString(root,0,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
//直观打印,可以看到树的深度
private void generateBSTString(TreeNode root, int height, StringBuilder sb) {
if(root == null){
sb.append(generateHeightString(height)).append("NULL\n");
return;
}
sb.append(generateHeightString(height)).append(root.val).append("\n");
generateBSTString(root.left,height+1,sb);
generateBSTString(root.right,height+1,sb);
}
private String generateHeightString(int height) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
sb.append("--");
}
return sb.toString();
}
}以上是Java如何实现二分搜索树的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




