在C#中多态性的定义是:同一操作作用于不同类的实例,不同的类进行不同的解释,最后产生不同的执行结果。换句话说也就是 一个接口,多个功能。
C# 支持2种形式的多态性: 编译时的多态性、运行时的多态性
编译时的多态性:
编译时的多态性是通过重载来实现的
方法重载
您可以在同一个范围内对相同的函数名有多个定义。函数的定义必须彼此不同,可以是参数列表中的参数类型不同,也可以是参数个数不同。不能重载只有返回类型不同的函数声明。写个例子
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{
class exchange //定义一个exchange类
{//方法实现交换两参数数据
public void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}",a,b);
}
public void swap(string a, string b)
{
string temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", a, b);
}
}
class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
exchange exch = new exchange();
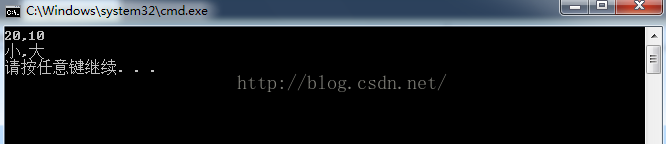
exch.swap(10, 20); //调用 swap(int a,int b)方法
exch.swap("大", "小"); //调用 swap(string a,string b)方法
}
}
}结果:
操作符重载
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{
class student //定义student类
{
private int Chinese;
private int Math;
public void value(int a, int b) //定义一个赋值的方法,以后学了构造方法就不这么麻烦了
{
Chinese = a;
Math = b;
}
public static student operator + (student a, student b) //运算符重载,实现相加功能
{
student stu = new student();
stu.Chinese = a.Chinese + b.Chinese;
stu.Math = a.Math + b.Math;
return stu;
}
public int getChinese() //获取Chinese 的方法
{
return Chinese;
}
public int getMath() //获取Math 的方法
{
return Math;
}
}
class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
student a = new student();
student b = new student();
a.value(70,80);
b.value(40, 50);
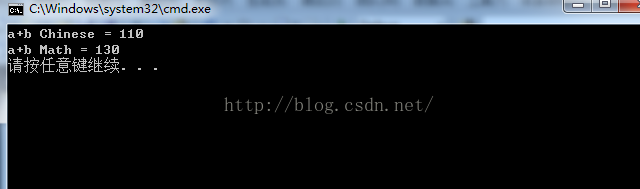
student stu = a + b; //70+40, 80+50
Console.WriteLine("a+b Chinese = {0}\na+b Math = {1}", stu.getChinese(), stu.getMath());
}
}
}结果:
运行时的多态性:
运行时的多态是指直到系统运行时,才根据实际情况决定实现何种操作,C#中运行时的多态通过抽象类或虚方法来实现的。
抽象类和抽象方法
C# 允许您使用关键字 abstract 创建抽象类或抽象方法,当一个派生类继承自该抽象类时,实现即完成。抽象类包含抽象方法,抽象方法可被派生类实现。派生类具有更专业的功能。抽象类不能够被实例化,
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{//创建抽象类和抽象方法
abstract class score
{
public abstract int Add();
}
//创建子类
class student : score
{
private int Chinese = 80;
private int Math = 90;
public override int Add() //关键字 override 实例方法
{
int sum=Chinese+Math;
return sum;
}
}
class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
student stu = new student();
Console.WriteLine(stu.Add() ); //结果 170
}
}
}虚方法
虚方法是使用关键字 virtual 声明的。虚方法可以在不同的继承类中有不同的实现。对虚方法的调用是在运行时发生的。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{
class score
{
protected int Chinese = 80;
protected int Math = 90;
public virtual int Add() //定义一个虚方法
{
int sum = Chinese + Math;
return sum;
}
}
//定义子类,实现方法
class student : score
{
public override int Add() //关键字 override 实例方法,实现相减操作
{
int sub = Math - Chinese ;
return sub;
}
}
class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
student stu = new student();
Console.WriteLine(stu.Add() ); //结果 10
}
}
}我们可以看出运行时真正调用的方法并不是虚方法,而是override 实例后的方法
以上就是 C#学习日记23---多态性 之 运算符重载、方法重载、抽象类、虚方法的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(m.sbmmt.com)!




