了解冒泡排序算法:分步指南
图片来源:medium
排序是数据结构和算法中最重要的部分之一。排序算法有很多种,这是最简单的算法之一:冒泡排序。
排序算法是计算机科学的基础,而冒泡排序是最简单、最直观的排序算法之一。这篇文章将探讨冒泡排序的工作原理,分析其时间复杂度,并演练 JavaScript 实现。
在本系列中,我将分享使用 Javascript 的完整排序算法数据结构和算法,并从冒泡排序开始。如果您喜欢并希望我通过示例分享完整的排序算法,请喜欢并关注我。它激励我为你们创建和准备内容。
什么是冒泡排序?
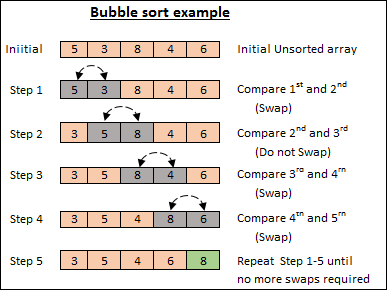
冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法,它重复遍历列表,比较相邻元素(下一个元素),如果顺序错误则交换它们。重复此过程直到列表排序完毕。该算法因其较小的元素“冒泡”到列表顶部而得名。
JavaScript 实现:
让我们深入代码看看冒泡排序是如何在 JavaScript 中实现的:
// By default ascending order
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of an array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop runs n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
for (let j = 0; j > len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if the first element greater than to the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array; // return the sorted array;
}
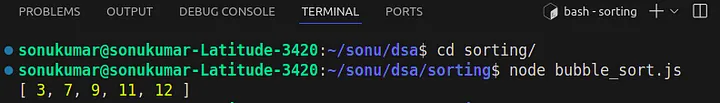
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
输出
按降序排序:
// Descending order
function bubble_sort_descending_order(array) {
const len = array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if first element greter than next element,
if (array[j] < array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort_descending_order(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [ 12, 11, 9, 7, 3 ]
输出:

已经添加了注释并解释了上面的每一行代码。但我也会详细解释,以帮助您理解完整的流程和代码。
工作原理:
- 初始化:我们首先确定数组的长度,这有助于控制迭代次数。
- 外循环:该循环运行 n-1 次,其中 n 是数组的长度。每次迭代都会确保下一个最大元素被放置在正确的位置。
- 内循环:对于外循环的每一次循环,内循环都会比较相邻元素,如果它们无序,则交换它们。内部循环的范围随着每次传递而减小,因为最大的元素已经排序在数组的末尾。
- 交换:如果一个元素大于下一个元素,则使用临时变量交换它们。
- 返回:最后返回排序后的数组。
优化版本:
// By default ascending order
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of an array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop runs n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
for (let j = 0; j > len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if the first element greater than to the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array; // return the sorted array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
说明:
- for (令 i = 0; i
- 让 isSwapped = false 布尔变量 isSwapped 被初始化为 false。该变量用于跟踪在内部循环的当前传递期间是否交换了任何元素。如果没有发生交换,则数组已经排序,算法可以提前终止。
- for (令 j = 0; j
- if (数组[j] > 数组[j 1]) { 此条件检查当前元素是否大于下一个元素。如果为 true,则需要进行交换才能正确排序元素。
// Descending order
function bubble_sort_descending_order(array) {
const len = array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if first element greter than next element,
if (array[j] < array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort_descending_order(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [ 12, 11, 9, 7, 3 ]
- 这些行使用临时变量 temp 执行元素 array[j] 和 array[j 1] 的交换。交换后,isSwapped 设置为 true,表示发生了交换。
// optimized version:
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of the array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop run n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
let isSwapped = false;
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
//check if the first element is greater than the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
isSwapped = true;
}
}
//If no element swap by inner loop then break;
if (isSwapped === false) {
break;
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
- 内部循环完成后,此条件检查 isSwapped 是否仍然为 false。如果没有进行交换,则数组已经排序,并且可以使用break提前退出外循环。
- 最后返回排序后的数组。
时间复杂度
在最坏和平均情况下,冒泡排序的时间复杂度为 (O(n²)),其中 (n) 是数组中元素的数量。这是因为每个元素都会与其他元素进行比较。在最好的情况下,当数组已经排序时,如果添加优化以在不需要交换时停止算法,时间复杂度可以是 (O(n))。
在最好的情况下,当数组已经排序时,由于 isSwapped 优化,算法可以提前终止,导致时间复杂度为 (O(n))。
总体而言,由于其二次时间复杂度,冒泡排序对于大型数据集效率不高,但它对于小型数组很有用,或者作为理解排序算法的教育工具。
结论
冒泡排序由于其简单性而成为一种用于教育目的的优秀算法。然而,由于其二次时间复杂度,它不适合大型数据集。尽管冒泡排序效率低下,但理解冒泡排序为学习更高级的排序算法奠定了基础。
以上是了解冒泡排序算法:分步指南的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 Vercel SPA路由与资源加载:解决深层URL访问问题
Aug 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
Vercel SPA路由与资源加载:解决深层URL访问问题
Aug 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
本文旨在解决在Vercel上部署单页应用(SPA)时,深层URL刷新或直接访问导致页面资源加载失败的问题。核心在于理解Vercel的路由重写机制与浏览器解析相对路径的差异。通过配置vercel.json实现所有路径重定向至index.html,并修正HTML中静态资源的引用方式,将相对路径改为绝对路径,确保应用在任何URL下都能正确加载所有资源。
 Vercel 单页应用 (SPA) 部署指南:解决深度 URL 资产加载问题
Aug 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Vercel 单页应用 (SPA) 部署指南:解决深度 URL 资产加载问题
Aug 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
本教程旨在解决 Vercel 上部署单页应用 (SPA) 时,在访问多层级 URL(如 /projects/home)时遇到的资产(CSS、JS、图片等)加载失败问题。核心在于理解 Vercel 的路由重写机制与 HTML 中相对/绝对路径的差异。通过正确配置 vercel.json 确保所有非文件请求重定向至 index.html,并修正 HTML 中资产引用为绝对路径,从而实现 SPA 在任意深度 URL 下的稳定运行。
 Qwik:用于即时加载Web应用程序的可重新框架
Aug 15, 2025 am 08:25 AM
Qwik:用于即时加载Web应用程序的可重新框架
Aug 15, 2025 am 08:25 AM
Qwikachievesinstantloadingbydefaultthroughresumability,nothydration:1)TheserverrendersHTMLwithserializedstateandpre-mappedeventlisteners;2)Norehydrationisneeded,enablingimmediateinteractivity;3)JavaScriptloadson-demand,onlywhenuserinteractionoccurs;4
 js添加元素到数组的开始
Aug 14, 2025 am 11:51 AM
js添加元素到数组的开始
Aug 14, 2025 am 11:51 AM
在JavaScript中,向数组开头添加元素最常用的方法是使用unshift()方法;1.使用unshift()会直接修改原数组,可添加一个或多个元素,返回添加后的数组新长度;2.若不想修改原数组,推荐使用扩展运算符(如[newElement,...arr])创建新数组;3.也可使用concat()方法,将新元素数组与原数组合并,返回新数组且不改变原数组;综上,修改原数组时用unshift(),保持原数组不变时推荐扩展运算符。
 如何使用JavaScript懒负载图像
Aug 14, 2025 pm 06:43 PM
如何使用JavaScript懒负载图像
Aug 14, 2025 pm 06:43 PM
Usetheloading="lazy"attributefornativelazyloadinginmodernbrowserswithoutJavaScript.2.Formorecontrolorolderbrowsersupport,implementlazyloadingwiththeIntersectionObserverAPIbysettingdata-srcfortheactualimageURLandusingaplaceholderinsrc.3.Obse
 深入解析JavaScript XSS防御函数的常见漏洞与改进策略
Aug 14, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
深入解析JavaScript XSS防御函数的常见漏洞与改进策略
Aug 14, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
本文深入探讨了自定义JavaScript XSS防御函数中常见的安全漏洞,特别是字符转义不完整和基于关键字的过滤易被绕过的问题。通过分析一个示例函数,揭示了引号、反引号等关键字符未处理的风险,以及代码混淆技术如何规避简单关键词检测。文章强调了上下文敏感转义的重要性,并建议采用成熟的库和多层防御策略,以构建更健壮的安全防护。
 如何使用JavaScript中的DOM访问和修改HTML元素
Aug 16, 2025 am 11:25 AM
如何使用JavaScript中的DOM访问和修改HTML元素
Aug 16, 2025 am 11:25 AM
toaccessandModifyHtmlelementsIsjavaScript,firstSelectThelementIsedmethodslikedocument.getElementbyId,document.querySelector,ordocument.queryselector.clearselectorall,thenAlterItsContent,thenAlteritScontent,attributes,artibutes,orstyles,orstyles; orstyles; orstyles;
 优化jQuery弹窗中动态外部链接跳转的事件处理
Sep 01, 2025 am 11:48 AM
优化jQuery弹窗中动态外部链接跳转的事件处理
Sep 01, 2025 am 11:48 AM
本文旨在解决jQuery弹窗中外部链接重定向按钮重复绑定事件处理器导致跳转错误的问题。当用户连续点击多个外部链接时,弹窗中的跳转按钮可能始终指向首次点击的链接。核心解决方案是利用off('click')方法在每次绑定新事件前解除旧的事件处理器,确保跳转行为始终指向最新的目标URL,从而实现准确且可控的链接重定向。







