Java 中的层次继承是 Java 中的继承类型之一。继承是面向对象编程系统(oops)的重要特征之一。继承是一种机制,其中一个类继承或获取其他类的所有属性和行为。继承属性和行为的类称为父类、超类或基类,继承属性和行为的类称为子类或派生类。在层次继承中,多个子类继承单个类,或者单个类被多个子类继承。 Java 中继承的使用是为了代码的可重用性和动态多态性(方法重写)。
借助下图我们可以更清楚地理解层次继承。
广告 该类别中的热门课程 JAVA 掌握 - 专业化 | 78 课程系列 | 15 次模拟测试
如上例图所示,ClassB 和 ClassC 继承同一个或单个类 ClassA。因此 ClassA 的变量和方法在 ClassB 和 ClassC 两个类中都被重用。上图表明,多个子类具有相同的父类,因此这种继承方式称为层次继承。
Java 中单继承的语法:
class Subclassname1 extends Superclassname
{
// variables and methods
}
Java 中层次继承的语法:
class Subclassname1 extends Superclassname
{
// variables and methods
}
class Subclassname2 extends Superclassname
{
// variables and methods
}“扩展”的意思是增加功能。 extends关键字表示继承;也就是说,我们正在创建一个从现有类派生的新类。
以下是不同的示例:
Java 中从超类继承变量的层次继承示例。接下来,我们通过以下示例编写 Java 代码来理解层次继承,从超类继承变量。
代码:
package P1;
class Employee{
float salary = 40000;
}
class PermanentEmp extends Employee{
double hike = 0.5;
}
class TemporaryEmp extends Employee{
double hike = 0.35;
}
public class HerInheritanceDemo
{
public static void main(String args[]){
PermanentEmp p = new PermanentEmp();
TemporaryEmp t = new TemporaryEmp();
// All objects of inherited classes can access the variable of class Employee
System.out.println("Permanent Employee salary is :" +p.salary);
System.out.println("Hike for Permanent Employee is:" +p.hike);
System.out.println("Temporary Employee salary is :" +t.salary);
System.out.println("Hike for Temporary Employee is :" +t.hike);
}
}输出:

如上面的代码,PermanentEmp 类和 TemporaryEmp 类是子类,Employee 是超类,这些子类的对象都在访问超类的变量,这体现了 Java 中的层次继承概念或特性。
Java 中层次继承的示例,从超类继承方法。接下来,我们通过以下示例编写 Java 代码,以便更清楚地理解 Java 中的这一点。
代码:
package P1;
class Employee{
float salary = 40000;
void dispSalary()
{
System.<em><i>out</i></em>.println("The Employee salary is :" +salary);
}
}
class PermanentEmp extends Employee{
double hike = 0.5;
void incrementSalary()
{
System.out.println("The Permanent Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary+(salary * hike)));
}
}
class TemporaryEmp extends Employee{
double hike = 0.35;
void incrementSalary()
{
System.out.println("The Temporary Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary+(salary * hike)));
}
}
public class HerInheritanceDemo
{
public static void main(String args[]){
PermanentEmp p = new PermanentEmp();
TemporaryEmp t = new TemporaryEmp();
// All objects of inherited classes can access the method of class Employee
p.dispSalary();
p.incrementSalary();
t.dispSalary();
t.incrementSalary();
}
}输出:

如上面的代码,PermanentEmp 类和 TemporaryEmp 类是子类,Employee 是超类,这些子类的对象都调用超类的方法,这体现了 Java 中的层次继承概念或特性。
例如使用 super 关键字调用超类的方法。接下来,我们重写上面的 Java 代码,通过以下示例更清楚地了解 super 关键字的作用。
代码:
package P1;
class Employee{
float salary = 40000;
void dispSalary()
{
System.out.println("The Employee salary is :" +salary);
}
}
class PermanentEmp extends Employee{
double hike = 0.5;
void incrementSalary()
{
super.dispSalary();
System.out.println("The Permanent Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary+(salary * hike)) );
}
}
class TemporaryEmp extends Employee{
double hike = 0.35;
void incrementSalary()
{
super.dispSalary();
System.out.println("The Temporary Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary+(salary * hike)) );
}
}
public class HerInheritanceDemo
{
public static void main(String args[]){
PermanentEmp p = new PermanentEmp();
TemporaryEmp t = new TemporaryEmp();
// All objects of inherited classes can access the variable of class Employee
p.incrementSalary();
t.incrementSalary();
}
}输出:
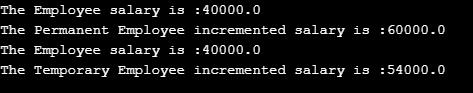
如上面的代码,PermanentEmp 类和 TemporaryEmp 类是子类,Employee 是超类,在子类方法中,调用超类方法,并以 super 关键字为前缀。 super关键字是Java中的引用变量,用于引用父类对象的变量和方法。在main方法中,子类的对象调用自己的方法,这再次体现了Java中的概念或特性。
继承是一种特性,其中一个类继承另一个类的所有属性和行为。 Java 中的继承类型之一是 Java 中的层次继承。在层次继承中,多个类从单个类继承属性和方法。
以上是Java中的层次继承的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




