Java a été lancé pour la première fois par Sun Microsystems en 1995. Le développement de Java a commencé au début des années 1990, dirigé par James Gosling et son équipe. Le langage s'appelait à l'origine « Oak », mais a ensuite été renommé « Java » en hommage à un type de café.
Java a été créé pour répondre au besoin d'un langage de programmation indépendant de la plate-forme pouvant être utilisé pour créer des logiciels pouvant s'exécuter sur n'importe quel appareil, quel que soit le matériel ou le système d'exploitation sous-jacent. L'objectif principal était de permettre aux développeurs de « écrire une fois, exécuter n'importe où », ce qui signifie que le code écrit en Java pouvait s'exécuter sur n'importe quelle plate-forme prenant en charge la machine virtuelle Java (JVM).
La conception de Java s'est concentrée sur la simplicité, la portabilité et la sécurité, ce qui le rend adapté à un large éventail d'applications, du développement Web aux logiciels d'entreprise. Il a rapidement gagné en popularité en raison de sa polyvalence et de sa capacité à créer des applications robustes et performantes sur différentes plates-formes.
Étant l'un des langages les plus utilisés aujourd'hui dans le développement de logiciels, et l'ayant étudié pendant longtemps, j'ai rassemblé ici quelques questions et réponses sur le monde merveilleux de Java.
Détesté par beaucoup, mais aimé par d'autres.

Questions
1. Quelle est la différence entre JDK et JRE ?
Le JDK (Java Development kit) est utilisé par les développeurs pour créer des applications Java et comprend les outils, bibliothèques et compilateurs nécessaires. Le JRE (Java Runtime Environment) est utilisé par les utilisateurs finaux pour exécuter des applications Java et fournit l'environnement d'exécution et les bibliothèques de classes essentielles, mais n'inclut pas d'outils de développement.
2. Quels sont les avantages de l'utilisation de Java ?
Voici les avantages de l'utilisation de Java :
Portabilité :Le code Java peut être exécuté sur n'importe quelle plate-forme dotée d'une machine virtuelle Java (JVM).
Sécurité :Java dispose d'un modèle de sécurité intégré qui aide à protéger les utilisateurs contre les codes malveillants.
Orienté objet :Java est un langage de programmation orienté objet, qui facilite la création de code modulaire et réutilisable.
Robuste :Java est un langage robuste conçu pour être fiable et efficace.
Largement utilisé :Java est un langage largement utilisé qui dispose d'une large communauté de développeurs et de ressources d'assistance.
3. Quels sont les différents composants de la Plateforme Java ?
La plateforme Java est un environnement logiciel qui fournit un moyen standard de développer et d'exécuter des applications Java. Il se compose des éléments suivants :
Machine virtuelle Java (JVM).
Environnement d'exécution Java (JRE).
Kit de développement Java (JDK).
4. Quels sont les différents types de données Java ?
Il existe deux types de types de données en Java : les types de données primitifs et les types de données non primitifs.
Types de données primitifs
Types de données non primitifs
5. Quels sont les différents types d'instructions de contrôle Java ?
Il existe trois types d'instructions de contrôle en Java :
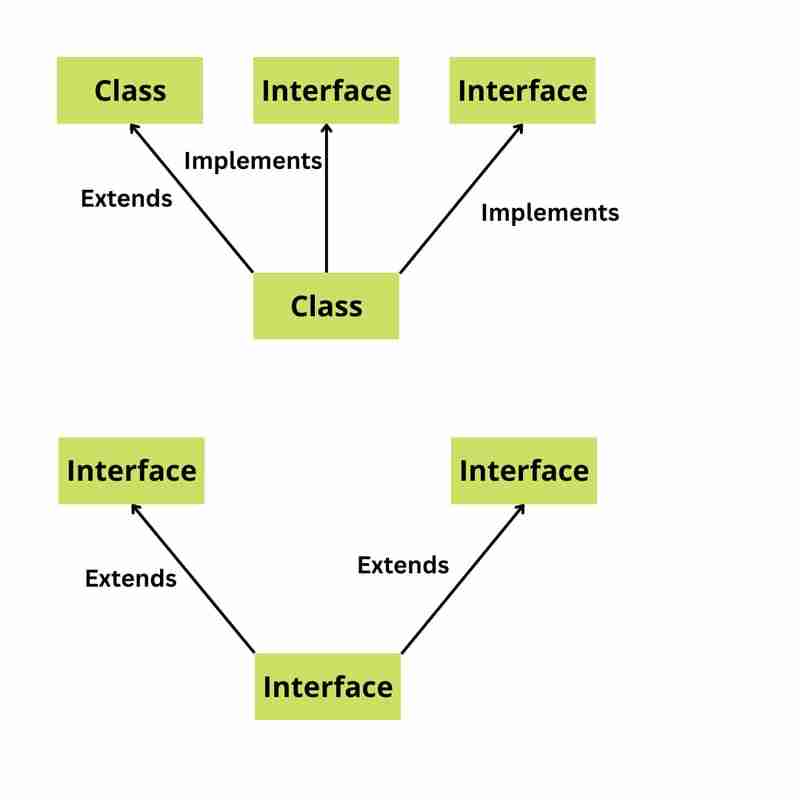
6. Quels sont les différents types de classes Java et d'interfaces Java ?
Il existe deux principaux types de classes Java :
Les classes normalessont le type de classe le plus courant en Java. Ils peuvent avoir des champs, des méthodes et des constructeurs.
Les classes abstraitessont des classes qui ne peuvent pas être instanciées. Ils ne peuvent être utilisés que comme classe de base pour d'autres classes.
Il existe également deux principaux types d'interfaces Java :
Les interfaces normalessont une collection de méthodes abstraites. Une classe peut implémenter une interface, héritant ainsi des méthodes abstraites de l'interface.
Maker interfacessont des interfaces qui ne contiennent aucune méthode. Ils sont utilisés pour indiquer qu'une classe a une certaine propriété ou un certain comportement.
7. Quels sont les différents types de bibliothèques Java et de frameworks Java ?
Une bibliothèque Java est une collection de classes et d'interfaces Java réutilisables.
** Java 库的一些示例:**
雷雷java 框架是可重用的 Java 类、接口和提供特定功能的代码的集合。
Java 库的一些示例:
8. Java 工具有哪些不同类型?
Java中有两种类型的线程:用户线程和守护线程。
用户线程是由用户或应用程序创建的线程。它们是高优先级线程,JVM 将等待任何用户线程完成其任务,然后再终止它。
守护线程是为了向用户线程提供服务而创建的线程。它们是低优先级线程,仅在用户线程运行时才需要。一旦所有用户线程完成执行,即使还有守护线程仍在运行,JVM也会终止。
9. Java 网络有哪些不同类型?
Java 网络有两种主要类型:
客户端-服务器网络是一种网络类型,其中有客户端应用程序向服务器应用程序请求服务。然后服务器应用程序向客户端应用程序提供服务。
点对点网络是一种网络类型,其中两个或多个应用程序无需服务器即可直接相互通信。
10.过程式编程和面向对象编程有什么区别?
过程式编程是一种自上而下的编程方法,其中程序分为一系列函数,每个函数执行特定的任务。
另一方面,OOP 是一种自下而上的编程方法,其中程序被划分为对象,每个对象代表一个现实世界的实体。
11。 OOP的核心概念是什么?
OOP 的核心概念是:
抽象:抽象是向用户隐藏对象实现细节的过程。这允许用户。这使得用户可以专注于对象的功能,而不必担心它是如何工作的。
12。重载和覆盖有什么区别?
重载是指可以有多个同名但参数不同的方法。
重写是指子类中的方法与超类中的方法具有相同签名的能力。
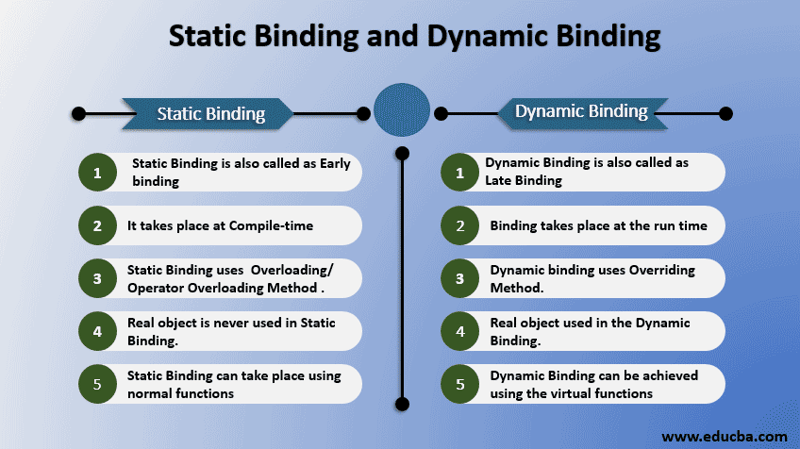
13。静态绑定和动态绑定有什么区别?
静态绑定和动态绑定是面向对象编程(OOP)中解决函数调用的两种不同方式。
-静态绑定:当编译器在编译时确定要调用的方法时发生。这是 OOP 中最常见的绑定类型,它用于静态方法和非虚拟方法。
-动态绑定:直到运行时才确定要调用的方法时发生。这用于虚拟方法,允许多态性。
14。为什么Java不支持多重继承?
Java 不支持多重继承,因为它会导致许多问题,包括:
15。 Java中什么时候使用接口和抽象类?
抽象类和接口都用于在面向对象编程中实现抽象。
抽象类与普通类类似,不同之处在于它们可以包含抽象方法,即没有主体的方法。抽象类无法实例化。
Interfaces are a kind of code contract, which must be implemented by a concrete class. Interfaces cannot have state, whereas the abstract class can have state whith instance variables.
16. What are the challenges of using OOP in Java?
There are some challenges associated with using OOP in Java.
These challenges include:
Complexity:OOP can make code more complex, especially when dealing with large and complex systems.
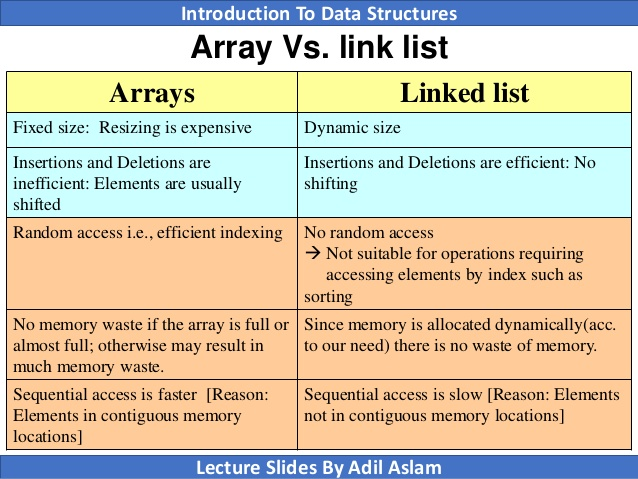
17. What is the difference between an array and a linked list?
In general, arrays are good choice for data structures where the data is accessed frequently and the order of the data is important.
Linked lists are a good choice for data structures where the data is inserted or deleted frequently and the order of the data is not important.
18. Explain the concept of a hash table.
A hash table is a data structure that maps keys to values. It is a very efficient data structure for storing and retrieving data, as it can access data in constant time.
put(key, value):This method stores the key-value pair in the hash table.
get(key):This method returns the value associated with the key.
remove(key):This method removes the key-value pair from the hash table.
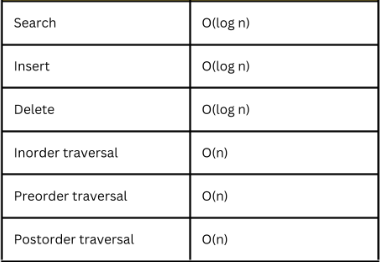
19. What is the time complexity of various operations in a binary search tree (BST)?
The time complexity of various operations in a binary search tree (BST) depends on the height of the tree. The height of a BST is the number of nodes on the longest path from the root node to a leaf node.
The following table shows the time complexity of various operations in a BST:
Operation---------------Time complexity
20. Describe the difference between breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS) algorithms.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between BFS and DFS:
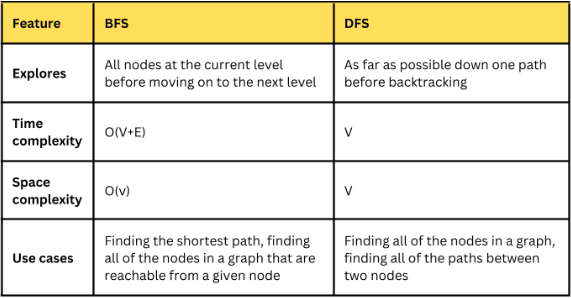
21. Explain the concept of a priority queue and provide an example of its application.
A priority queue is a data structure that stores elements along with their associated priorities. It allows efficient retrieval of the element with the highest (or lowest) priority. The priority determines the order in which elements are processed or accessed.
22. Explain the concept of dynamic programming and provide an example problem where it can be applied.
Dynamic programming is a problem-solving technique that involves breaking down complex problems into smaller, overlapping subproblems and solving them in a bottom-up manner.
23. How does a HashSet work internally in Java?
A HashSet internally uses a HashMap to store its elements. When you add an element to a HashSet, it is first hashed using the hashCode() method.
The hash code is then used to find the corresponding bucket in the HashMap. If the bucket is not empty, the element is compared to the other elements in the bucket using the equals() method. If the element is equal to any of the other elements in the bucket, it is not added to the HashSet.
24. What is the time complexity of various operations in a hash table?
The time complexity of various operations in a hash table depends on the hash function used and the number of elements in the hash table. In general, the time complexity of the following operations is:
25. What is multithreading, and why is it important in Java?
Multithreading is a programming concept that allows multiple tasks to be executed concurrently. In Java, multithreading is implemented using the thread class. A thread object represents a single thread of execution.
多线程在 Java 中如此重要的原因有很多。
一些最重要的原因包括:
26。如何在 Java 中创建线程?
Java中创建线程有两种方式:
27。进程和线程有什么区别?
进程是正在执行的程序。它有自己的内存空间、自己的堆栈和自己的一组资源。
线程是一个轻量级的进程,它与同一进程中的其他线程共享相同的内存空间和资源。
进程和线程之间的一些关键区别:
- 进程彼此独立。
- 进程比线程重。
- 进程比线程更难创建和管理。
28。 Java 中的同步是如何工作的?解释同步方法和块的概念。
Java中的同步是一种允许多线程安全访问共享资源的机制。当一个线程在某个资源上同步时,它是唯一可以访问该资源的线程。
这可以防止竞争条件,即两个或多个线程尝试同时访问同一资源的情况。
Java中有两种同步方式:
同步方法:
同步方法是一种一次只能由一个线程执行的方法。要将方法声明为同步,需要使用synchronized关键字。
同步区块
同步块是一次只能由一个线程执行的代码块。要将代码块声明为同步,您需要使用synchronized关键字并指定该代码块同步的对象。
29。什么是死锁,如何避免?
死锁是两个或多个线程相互等待完成的情况。当两个线程都尝试获取同一资源上的锁时,就会发生这种情况。
为了避免死锁,我们可以这样做:
30。 Java 中 volatile 关键字的用途是什么?
volatile 关键字用于确保所有线程看到变量的相同值,即使该值被另一个线程更改。
31。解释线程调度上下文中抢占式调度和时间切片之间的区别。
抢占式调度是指操作系统可以强行从CPU中移除一个线程并将其交给另一个线程。时间分片是指为每个线程分配一定的时间在 CPU 上运行。
主要区别在于,在抢占式调度中,操作系统可以随时中断线程,而在时间切片中,线程只有在用完分配的时间时才会被中断。
32。 Java 中的异常是什么,为什么异常处理很重要?
在Java中,异常是在程序执行过程中发生的破坏正常指令流的事件。它是一个在运行时抛出的对象。
以下是异常处理的一些好处:
33。 Java是如何处理异常的。
Java 通过使用一种称为异常传播的机制来处理异常。当抛出异常时,它会在调用堆栈中向上传播,直到被捕获。如果没有捕获异常,程序就会崩溃。
34。描述 try-catch-finally 块及其在异常处理中的用途。
try-catch-finally 块是一种 Java 语法,可以让你优雅地处理异常。它由三部分组成:
以下是使用 try-catch-finally 块的一些好处:
35。 Java 中的 throw 和 throws 关键字有什么区别?
Java 中的 throw 和 throws 关键字用于处理异常。
36。如何在 Java 中创建自定义异常?
要在Java中创建自定义异常,您需要创建一个扩展Exception类的类。自定义异常类可以有自己的构造函数、方法和字段。
参考资料:https://medium.com/@spinjosovsky/practical-comparison- Between-depth-first-search-dfs-vs-breadth-first-serch-bfs-bf360240cf72
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/
https://www.algotutor.io/campus-program
以上是Java基础问题的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




