TreeMap is a class of Java Collection Framework that implements NavigableMap Interface. It stores the elements of the map in a tree structure and provides an efficient alternative to store the key-value pairs in sorted . Intern, TreeMap-sally a. black tree, which is a self-balancing binary search tree. A TreeMap must implement the Comparable Interface or a custom Comparator so that it can maintain the sorting order of its elements otherwise, we will encounterClass .書. to explain how TreeMap works internally in Java.
要理解TreeMap的內部工作原理,有必要對紅黑樹演算法有一個概述,因為TreeMap使用它來儲存元素。
紅黑樹是一種自平衡的二元搜尋樹,其屬性如下所述:
每個節點包含一個額外的位,由紅色或黑色表示。這些顏色用於確保樹保持平衡。
The color of root node is always black.
一個紅色節點不能有另一個與其鄰居相同顏色的節點
從根節點到空節點,所有路徑上的黑色節點數量必須相同
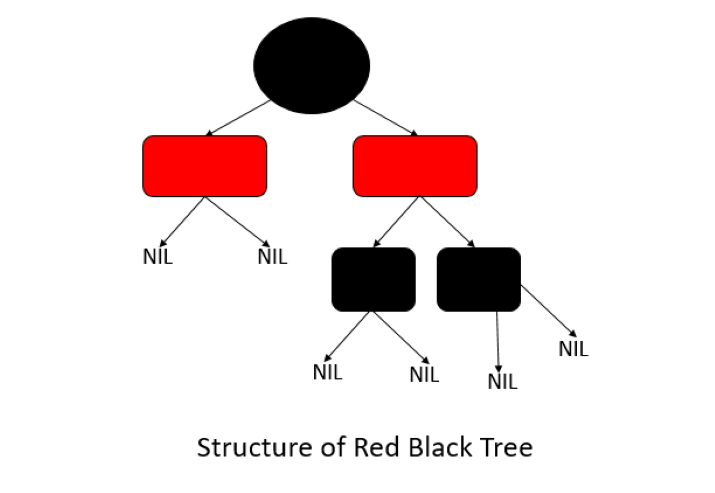
#Now, let's see the structure of TreeMap:
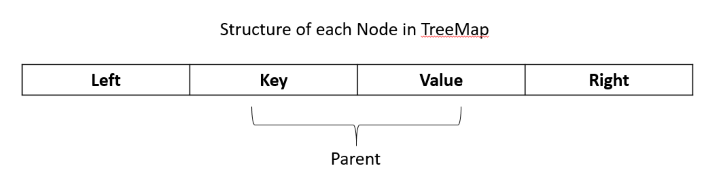
#If we add an element to the TreeMap, it will add the first entry in the first place. From the second element, it will check whether the key of current entry is greater or smaller than the whether the key of current entry is greater or smaller than the previous ent . The key value will be added to the left and the ones with greater value will be added to the right of Parent entry.
To use the TreeMap collection in our program, we first need to create an instance of the TreeMap class. For that Java provides the following constructors:
TreeMap():它將建立一個空的TreeMap集合
TreeMap(Map mapInstance): 我們可以使用另一個映射中的項目來建立一個樹映射
TreeMap(Comparator comparatorInstance):它允許我們建立一個空的樹映射,透過使用比較器進行排序。
TreeMap(SortedMap sortedmapInstance): We can also create a tree map with the entries from a sorted map.
Let's discuss a few examples to have a better understanding of the above discussed points.
在以下範例中,我們將建立一個空的TreeMap,然後使用'put()'方法將一些元素儲存到其中。我們將使用for-each循環列印其詳細資訊。結果將按照排序順序顯示。
import java.util.*;
public class Example1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// creating a TreeMap
TreeMap<String, Integer> TrMap = new TreeMap<>();
// Adding elements in the map
TrMap.put("Kurti", 4000);
TrMap.put("Shirt", 3000);
TrMap.put("TShirt", 1500);
TrMap.put("Watch", 2000);
TrMap.put("Perfume", 2500);
// printing the details of map
System.out.println("Elements of the map: ");
// iterating through the map
for (String unKey : TrMap.keySet()) {
// printing details of each node
System.out.println("Item: " + unKey + ", Price: " +
TrMap.get(unKey));
}
String frstKey = TrMap.firstKey(); // accessing first key
String lstKey = TrMap.lastKey(); // accessing last key
System.out.println("Accessing name of first key in Map: " +
frstKey);
System.out.println("Accessing name of last key in Map: " +
lstKey);
}
}
Elements of the map: Item: Kurti, Price: 4000 Item: Perfume, Price: 2500 Item: Shirt, Price: 3000 Item: TShirt, Price: 1500 Item: Watch, Price: 2000 Accessing name of first key in Map: Kurti Accessing name of last key in Map: Watch
我們在開始這篇文章時定義了TreeMap,並在下一節中討論了它的內部運作原理。 TreeMap使用紅黑樹來儲存其元素,這是一種能夠自我平衡的二元搜尋樹。此外,我們也討論了一個範例來說明TreeMap的工作原理。
以上是Java中TreeMap的內部運作原理的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




