要對方法的參數進行校驗,最簡單暴力的寫法是這個樣子:
public static void utilA(String a,BigDecimal b){
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(a)){
System.out.println("a不可为空");
return;
}
if (b == null){
System.out.println("b不可为空");
return;
}
if (b.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) != 1){
System.out.println("b的取值范围不正确");
return;
}
System.out.println("do something");
}這樣做從功能角度來說一點問題也沒有。
但是從程式碼的長期維護性上來說,程式碼復用率低,校驗規則一旦多起來很難維護,而且怎麼看怎麼顯得笨拙,對於有一點追求的工程師來說,這麼一大坨還挺難接受的。
雖然有一些諸如 Preconditions(com.google) 的解決方案,但很難適應所有的場景,用起來也沒到非常得心應有的地步。
Spring官方推薦的,語義清晰的優雅的方法級別校驗(入參校驗、返回值校驗)
Spring官方在SpringBoot文檔中,關於參數校驗(Validation)給出的解決方案是這樣的:
@Service
@Validated
public class MyBean {
public Archive findByCodeAndAuthor(@Size(min = 8, max = 10) String code,
Author author) {
...
}
}Spring Boot 官網文檔《37. Validation》
也就是說,使用JSR-303 規範,直接利用註解進行參數校驗。
(JSR-303 是JAVA EE 6 中的一個子規範,稱為Bean Validation,官方參考實作是Hibernate Validator)
#2.2.1.註解簡介
對於簡單型別參數(非Bean),直接在參數前,使用註解新增約束規則。註解如下圖:
@AssertTrue / @AssertFalse
驗證適用欄位:boolean
註解說明:驗證值是否為true / false
@DecimalMax / @DecimalMin
驗證適用欄位:BigDecimal,BigInteger,String,byte,short,int,long
#註解:驗證值是否小於或等於指定的小數值,要注意小數存在精確度問題
@Digits
驗證適用欄位:BigDecimal,BigInteger,String,byte,short,int ,long
註解說明:驗證值的數字構成是否合法
屬性說明:integer:指定整數部分的數字的位數。 fraction: 指定小數部分的數字的位數。
@Future / @Past
驗證適用欄位:Date,Calendar
註解說明:驗證值是否在目前時間之後/ 之前
屬性說明:公共
@Max / @Min
#驗證適用欄位:BigDecimal,BigInteger,String,byte,short,int,long
註解說明:驗證值是否小於或等於指定的整數值
屬性說明:公共
注意事項:建議使用在Stirng,Integer類型,不建議使用在int類型上,因為表單提交的值為「」時無法轉換為int
@NotNull / @Null
驗證適用欄位:引用資料型別
註解說明:驗證值是否為非空/ 空
屬性說明:公共
#@NotBlank 檢查約束字串是不是Null還有被Trim的長度是否大於0,只對字串,且會去掉前後空格.
@NotEmpty 檢查約束元素是否為Null或是EMPTY.
##@NotBlank 與@NotEmpty 的區別:空格(" ")對於NotEmpty 是合法的,而NotBlank 會拋出校驗異常@Pattern
驗證適用欄位:String#註解說明:驗證值是否配備正規表示式屬性說明:regexp:正規表示式flags: 指定Pattern.Flag 的數組,表示正規表示式的相關選項。@Size
驗證適用欄位:String,Collection,Map,陣列#註解說明:驗證值是否滿足長度需求屬性說明:max:指定最大長度,min:指定最小長度。@Length(min=, max=):專門套用至String類型
##@Valid##驗證適用字段:遞歸的對關聯物件進行校驗
註解說明:如果關聯物件是集合或陣列,那麼對其中的元素進行遞歸校驗,如果是一個map,則對其中的值部分進行校驗(是否進行遞歸驗證)屬性說明:無@Range(min=, max=)
被指定的元素必須在適當的範圍內#@CreditCardNumber
信用卡驗證@URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=)
2.2.2使用
#1.引入依賴
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate.validator/hibernate-validator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.1.5.Final</version>
</dependency>import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotEmpty;
/**
* @Author: wangxia
* @Date: 2021/10/20 16:30
*/
public class TestPerson {
@NotEmpty(message = "用户名不能为空")
private String username;
@Min(value = 0,message = "年龄不能小于0岁")
@Max(value =150,message = "年龄不能大于150岁")
private int age;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}@RequestMapping("/")
@RestController
public class TestValidatController {
@PostMapping("/testValid")
public String testValid(@Validated @RequestBody TestPerson testPerson){
return "测试成功";
}
}@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class MethodArgumentNotValidHandel {
@ExceptionHandler(value=MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public JSONObject MethodArgumentNotValidHandler(HttpServletRequest request,
MethodArgumentNotValidException exception) throws Exception
{
JSONObject result=new JSONObject();
result.put("code","fail");
JSONObject errorMsg=new JSONObject();
for (FieldError error : exception.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
errorMsg.put(error.getField(),error.getDefaultMessage());
}
result.put("msg",errorMsg);
return result;
}
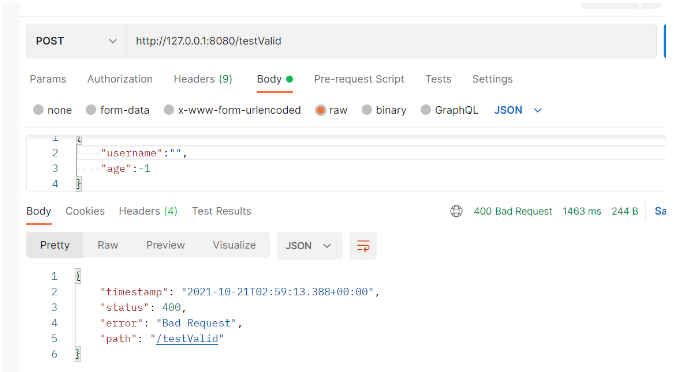
}#未新增優雅捕獲的例外提示: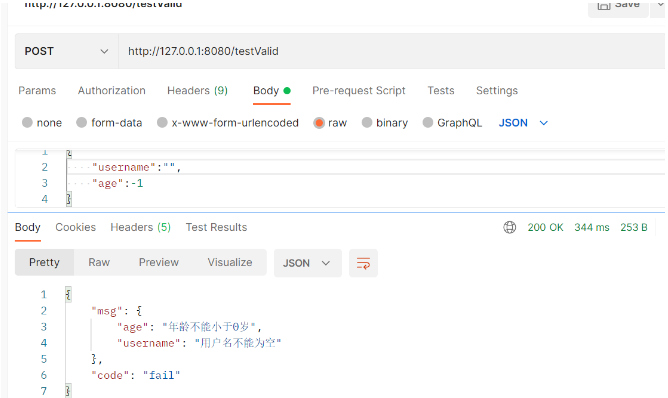
以上是Java如何實現優雅的參數校驗的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




