本篇文章為大家帶來了關於java的相關知識,其中主要整理了10種排序演算法實例的相關問題,包括了冒泡排序、選擇排序、插入排序等等內容,下面一起來看一下,希望對大家有幫助。

推薦學習:《java影片教學》
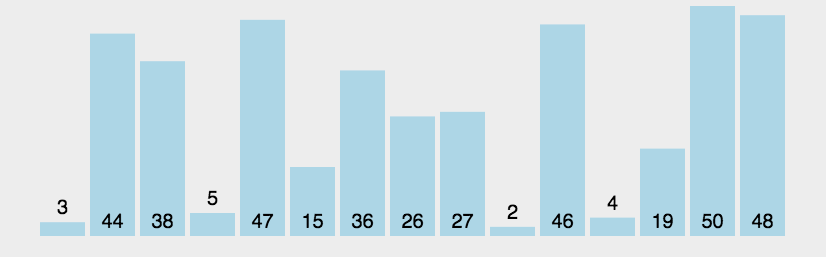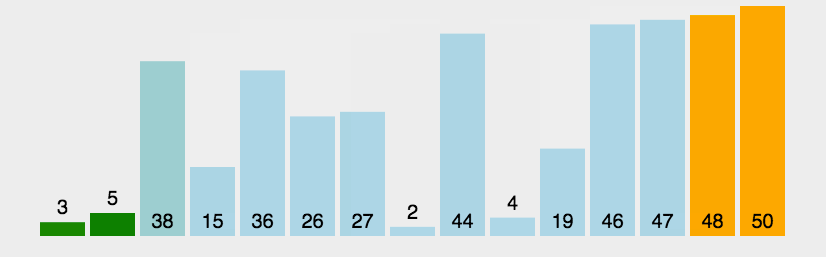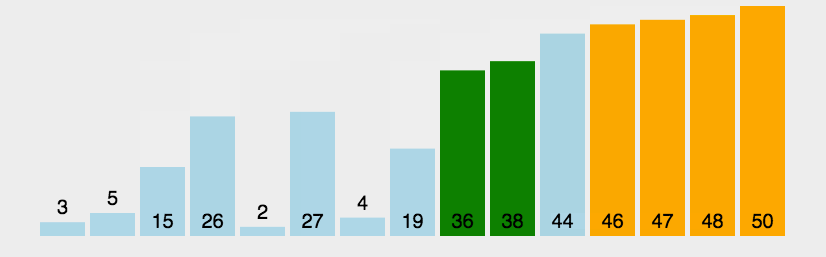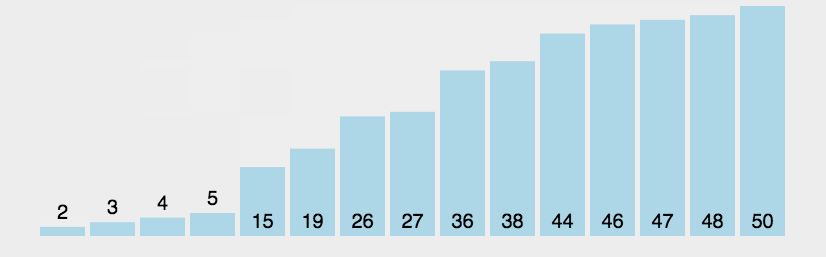
import java.util.Arrays;//冒泡排序public class BubbleSort_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
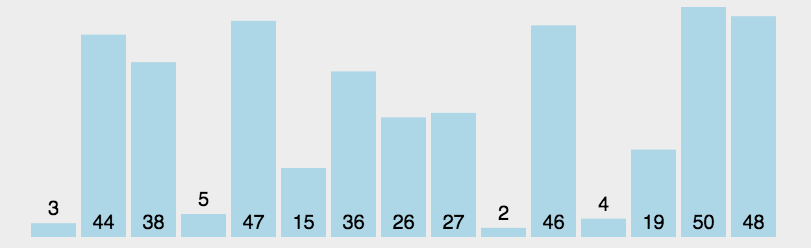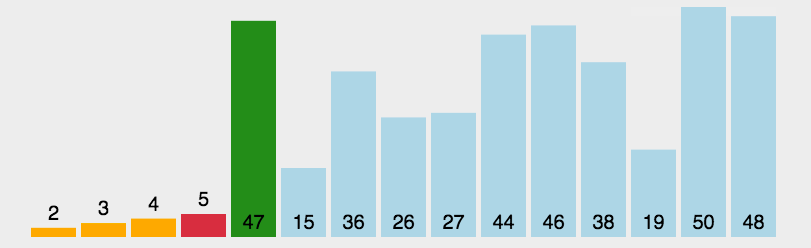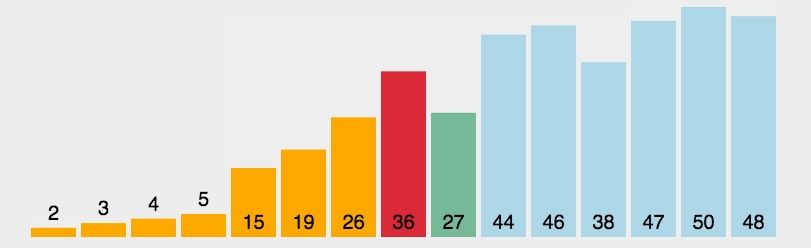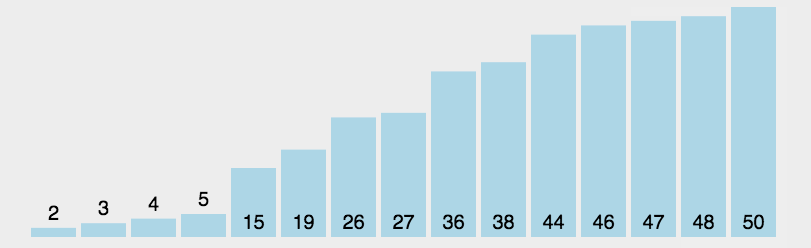
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
//记录比较次数
int count=0;
//i=0,第一轮比较
for (int i = 0; i a[j+1]) {
int temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
}
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
System.out.println("一共比较了:"+count+"次");//一共比较了:105次
}}冒泡排序的最佳化1:
import java.util.Arrays;public class BubbleSort1_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
int count=0;
for (int i = 0; i a[j+1]) {
int temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
flag=false;
}
count++;
}
if (flag) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));// [2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
System.out.println("一共比较了:"+count+"次");//一共比较了:95次
}}
import java.util.Arrays;//选择排序:先定义一个记录最小元素的下标,然后循环一次后面的,找到最小的元素,最后将他放到前面排序好的序列。public class SelectSort_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
for (int i = 0; i <h2>3.插入排序(Insert Sort)</h2><p><img src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/b3f75638c97a493ecae2237fc6ea0427-2.gif" alt="java的10種排序演算法實例"></p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">import java.util.Arrays;//插入排序:定义一个待插入的数,再定义一个待插入数的前一个数的下标,然后拿待插入数与前面的数组一一比较,最后交换。public class InsertSort_03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
for (int i = 0; i =0 && insertValue <a a insertindex-- system.out.println><h2>4.希爾排序(Shell Sort)</h2>
<p><img src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/b3f75638c97a493ecae2237fc6ea0427-3.gif" alt="java的10種排序演算法實例"></p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">import java.util.Arrays;//希尔排序:插入排序的升级public class ShellSort_04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
int count=0;//比较次数
for (int gap=a.length / 2; gap > 0; gap = gap / 2) {
//将整个数组分为若干个子数组
for (int i = gap; i =0; j=j-gap) {
//交换元素
if (a[j]>a[j+gap]) {
int temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+gap];
a[j+gap]=temp;
count++;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);//16
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}}參考這篇部落格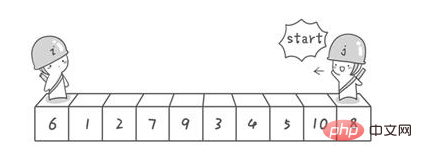
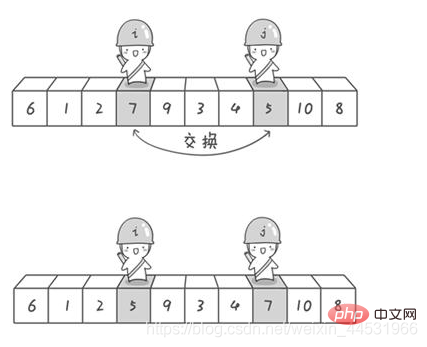
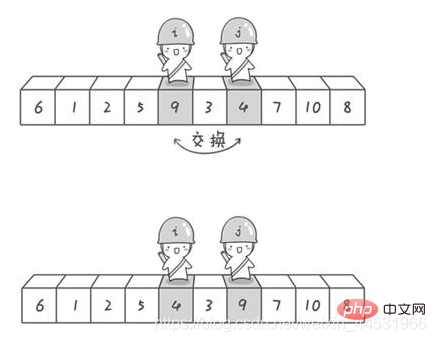
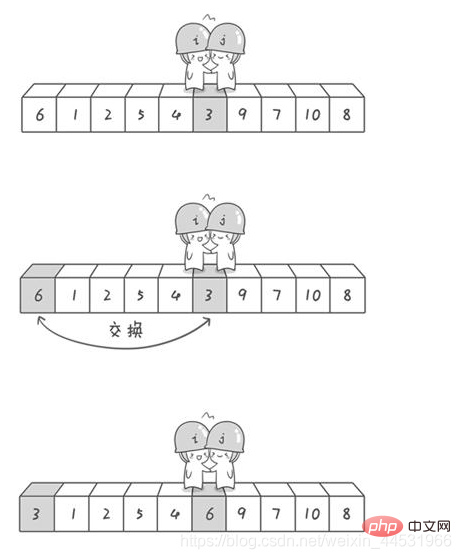
import java.util.Arrays;//快速排序:冒泡排序的升华版public class QuickSort_05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int a[]={50,1,12,2};
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
quicksort(a,0,a.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void quicksort(int[] a, int low, int high) {
int i,j;
if (low>high) {
return;
}
i=low;
j=high;
int temp=a[low];//基准位,low=length时,会报异常,java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 4 ,所以必须在if判断后面,就跳出方法。
while(i<j while j-->=a[i] && i<j i if int a quicksort><h2>6.歸併排序(Merge Sort)</h2>
<p><img src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/77209169484aede4f22c59b944a61b0c-8.gif" alt="java的10種排序演算法實例"></p>
<p><img src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/77209169484aede4f22c59b944a61b0c-9.png" alt="java的10種排序演算法實例"></p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">import java.util.Arrays;//归并排序public class MergeSort_06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
//int a[]={5,2,4,7,1,3,2,2};
int temp[]=new int[a.length];
mergesort(a,0,a.length-1,temp);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void mergesort(int[] a, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
//分解
if (left<right int mergesort merge private while if temp t i j a templeft><h2>7.堆排序(Heap Sort)</h2>
<p>#堆排序<br> 第一步:建構初始堆buildHeap, 使用sink(arr,i, length)調整堆頂的值;<br> 第二步:將堆頂元素下沉目的是將最大的元素浮到堆頂來,然後使用sink (arr, 0,length)調整;<br> 堆排序圖解:連結<br><img src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/77209169484aede4f22c59b944a61b0c-10.gif" alt="java的10種排序演算法實例">##</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">public class Heap_Sort_07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
//构建堆
buildHeap(arr,length);
for ( int i = length - 1; i > 0; i-- ) {
//将堆顶元素与末位元素调换
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
//数组长度-1 隐藏堆尾元素
length--;
//将堆顶元素下沉 目的是将最大的元素浮到堆顶来
sink(arr, 0,length);
}
}
private static void buildHeap(int[] arr, int length) {
for (int i = length / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
sink(arr,i, length);
}
}
private static void sink(int[] arr, int index, int length) {
int leftChild = 2 * index + 1;//左子节点下标
int rightChild = 2 * index + 2;//右子节点下标
int present = index;//要调整的节点下标
//下沉左边
if (leftChild arr[present]) {
present = leftChild;
}
//下沉右边
if (rightChild arr[present]) {
present = rightChild;
}
//如果下标不相等 证明调换过了
if (present != index) {
//交换值
int temp = arr[index];
arr[index] = arr[present];
arr[present] = temp;
//继续下沉
sink(arr, present, length);
}
}} 演算法的步驟如下:
##
import java.util.Arrays;public class CountSort_08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = { 4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1 };
// 找到数组中最大的值 ---> max:8
int max = findMaxElement(array);
int[] sortedArr = countingSort(array, max + 1);
System.out.println("计数排序后的数组: " + Arrays.toString(sortedArr));
}
private static int findMaxElement(int[] array) {
int max = array[0];
for (int val : array) {
if (val > max)
max = val;
}
return max;
}
private static int[] countingSort(int[] array, int range) { //range:8+1
int[] output = new int[array.length];
int[] count = new int[range];
//初始化: count1数组
for (int i = 0; i <img src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/ffad9e606e345031463e4d10b7c44bcc-11.png" alt="java的10種排序演算法實例">9.桶排序( Bucket Sort)<h2>參考連結</h2><p>桶排序可以看成是計數排序的升級版,它將要排的數據分到多個有序的桶裡,每個桶裡的數據再單獨排序,再把每個桶的資料依序取出,即可完成排序。 </p> 桶排序:將值為i的元素放入i號桶,最後依序將桶裡的元素倒出來。 <p><br>桶排序序思路:<br></p>public class BucketSort_09 {
public static void sort(int[] arr){
//最大最小值
int max = arr[0];
int min = arr[0];
int length = arr.length;
for(int i=1; i<length> max) {
max = arr[i];
} else if(arr[i] > bucketList = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i ());
}
//每个桶的存数区间
float section = (float) diff / (float) (length - 1);
//数据入桶
for(int i = 0; i arrayList : bucketList){
for(int value : arrayList){
arr[index] = value;
index++;
}
}
}}</length>我们假设有一个待排序数组[53,3,542,748,14,214],那么如何使用基数排序对其进行排序呢?
首先我们有这样的十个一维数组,在基数排序中也叫桶。用桶排序实现。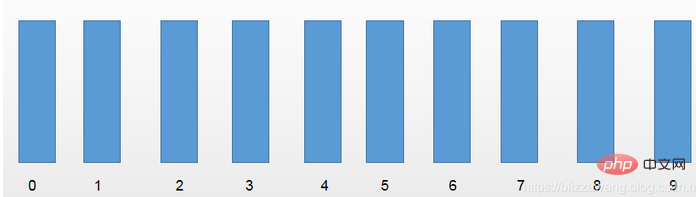 第一轮,以元素的个位数进行区分:[542,53,3,14,214,748]
第一轮,以元素的个位数进行区分:[542,53,3,14,214,748]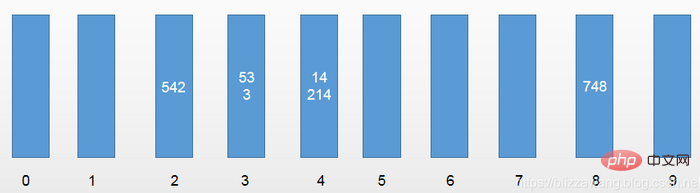 第二轮,以元素的十位数进行区分:[3,14,214,542,748,53]
第二轮,以元素的十位数进行区分:[3,14,214,542,748,53]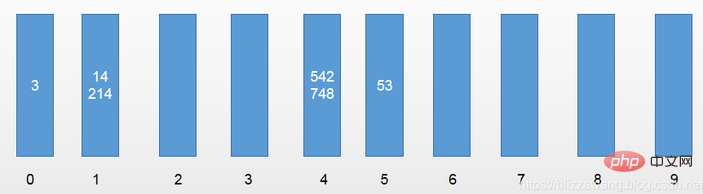 第三轮,以元素的百位数进行区分:[3,14,53,214,542,748]
第三轮,以元素的百位数进行区分:[3,14,53,214,542,748]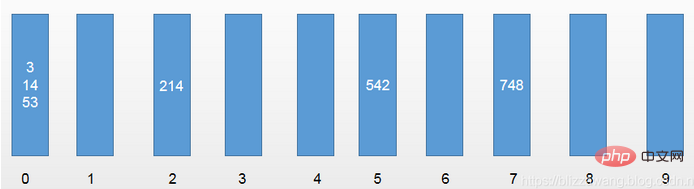
import java.util.Arrays;public class RaixSort_10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 53, 3, 542, 748, 14, 214 };
// 得到数组中最大的数
int max = arr[0];// 假设第一个数就是数组中的最大数
for (int i = 1; i max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
// 得到最大数是几位数
// 通过拼接一个空串将其变为字符串进而求得字符串的长度,即为位数
int maxLength = (max + "").length();
// 定义一个二维数组,模拟桶,每个桶就是一个一维数组
// 为了防止放入数据的时候桶溢出,我们应该尽量将桶的容量设置得大一些
int[][] bucket = new int[10][arr.length];
// 记录每个桶中实际存放的元素个数
// 定义一个一维数组来记录每个桶中每次放入的元素个数
int[] bucketElementCounts = new int[10];
// 通过变量n帮助取出元素位数上的数
for (int i = 0, n = 1; i <p><em>基数排序是用空间换时间的经典算法,当数据足够多时,达到几千万级别时内存空间可能不够用了,发生堆内存溢出</em></p><p><img src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/a246d223e83788646627bce4ca8e0ab1-17.png" alt="java的10種排序演算法實例"></p><p>推荐学习:《<a href="//m.sbmmt.com/course/list/36.html" target="_blank">java视频教程</a>》</p>以上是java的10種排序演算法實例的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!



