在本文中,我們將使用 Scikit-Learn 來示範完整的機器學習專案工作流程。我們將建立一個模型,根據各種特徵(例如收入中位數、房屋年齡和平均房間數量)來預測加州的房價。該專案將指導您完成流程的每個步驟,包括資料載入、探索、模型訓練、評估和結果視覺化。無論您是想要了解基礎知識的初學者,還是想要複習知識的經驗豐富的從業者,本文都將為機器學習技術的實際應用提供寶貴的見解。
加州房地產市場以其獨特的特徵和定價動態而聞名。在這個專案中,我們的目標是開發一種機器學習模型來根據各種特徵預測房價。我們將使用加州住房資料集,其中包括各種屬性,例如收入中位數、房屋年齡、平均房間等。
在本節中,我們將匯入資料操作、視覺化和建立機器學習模型所需的函式庫。
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
我們將載入加州住房資料集並建立一個 DataFrame 來組織資料。目標變量,即房價,將作為新列添加。
# Load the California Housing dataset california = fetch_california_housing() df = pd.DataFrame(california.data, columns=california.feature_names) df['PRICE'] = california.target
為了保持分析的可管理性,我們將從資料集中隨機選擇 700 個樣本進行研究。
# Randomly Selecting 700 Samples df_sample = df.sample(n=700, random_state=42)
本節將提供資料集的概述,顯示前五行以了解資料的特徵和結構。
# Overview of the data
print("First five rows of the dataset:")
print(df_sample.head())
First five rows of the dataset:
MedInc HouseAge AveRooms AveBedrms Population AveOccup Latitude \
20046 1.6812 25.0 4.192201 1.022284 1392.0 3.877437 36.06
3024 2.5313 30.0 5.039384 1.193493 1565.0 2.679795 35.14
15663 3.4801 52.0 3.977155 1.185877 1310.0 1.360332 37.80
20484 5.7376 17.0 6.163636 1.020202 1705.0 3.444444 34.28
9814 3.7250 34.0 5.492991 1.028037 1063.0 2.483645 36.62
Longitude PRICE
20046 -119.01 0.47700
3024 -119.46 0.45800
15663 -122.44 5.00001
20484 -118.72 2.18600
9814 -121.93 2.78000
print(df_sample.info())
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> Index: 700 entries, 20046 to 5350 Data columns (total 9 columns): # Column Non-Null Count Dtype --- ------ -------------- ----- 0 MedInc 700 non-null float64 1 HouseAge 700 non-null float64 2 AveRooms 700 non-null float64 3 AveBedrms 700 non-null float64 4 Population 700 non-null float64 5 AveOccup 700 non-null float64 6 Latitude 700 non-null float64 7 Longitude 700 non-null float64 8 PRICE 700 non-null float64 dtypes: float64(9) memory usage: 54.7 KB
print(df_sample.describe())
MedInc HouseAge AveRooms AveBedrms Population \
count 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000
mean 3.937653 28.855714 5.404192 1.079266 1387.422857
std 2.085831 12.353313 1.848898 0.236318 1027.873659
min 0.852700 2.000000 2.096692 0.500000 8.000000
25% 2.576350 18.000000 4.397751 1.005934 781.000000
50% 3.480000 30.000000 5.145295 1.047086 1159.500000
75% 4.794625 37.000000 6.098061 1.098656 1666.500000
max 15.000100 52.000000 36.075472 5.273585 8652.000000
AveOccup Latitude Longitude PRICE
count 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000
mean 2.939913 35.498243 -119.439729 2.082073
std 0.745525 2.123689 1.956998 1.157855
min 1.312994 32.590000 -124.150000 0.458000
25% 2.457560 33.930000 -121.497500 1.218500
50% 2.834524 34.190000 -118.420000 1.799000
75% 3.326869 37.592500 -118.007500 2.665500
max 7.200000 41.790000 -114.590000 5.000010
我們將資料集分為特徵(X)和目標變數(y),然後將其分為訓練集和測試集,用於模型訓練和評估。
# Splitting the dataset into Train and Test sets
X = df_sample.drop('PRICE', axis=1) # Features
y = df_sample['PRICE'] # Target variable
# Split the dataset into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
在本節中,我們將使用訓練資料建立和訓練線性迴歸模型,以了解特徵與房價之間的關係。
# Creating and training the Linear Regression model lr = LinearRegression() lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
我們將對測試集進行預測,並計算均方誤差 (MSE) 和 R 平方值來評估模型的效能。
# Making predictions on the test set
y_pred = lr.predict(X_test)
# Calculating Mean Squared Error
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"\nLinear Regression Mean Squared Error: {mse}")
Linear Regression Mean Squared Error: 0.3699851092128846
在這裡,我們將建立一個 DataFrame 來比較實際房價與模型產生的預測價格。
# Displaying Actual vs Predicted Values
results = pd.DataFrame({'Actual Prices': y_test.values, 'Predicted Prices': y_pred})
print("\nActual vs Predicted:")
print(results)
Actual vs Predicted:
Actual Prices Predicted Prices
0 0.87500 0.887202
1 1.19400 2.445412
2 5.00001 6.249122
3 2.78700 2.743305
4 1.99300 2.794774
.. ... ...
135 1.62100 2.246041
136 3.52500 2.626354
137 1.91700 1.899090
138 2.27900 2.731436
139 1.73400 2.017134
[140 rows x
2 columns]
在最後一部分,我們將使用散點圖視覺化實際房價和預測房價之間的關係,以直觀地評估模型的性能。
# Visualizing the Results
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.scatter(y_test, y_pred, color='blue')
plt.xlabel('Actual Prices')
plt.ylabel('Predicted Prices')
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted House Prices')
# Draw the ideal line
plt.plot([0, 6], [0, 6], color='red', linestyle='--')
# Set limits to minimize empty space
plt.xlim(y_test.min() - 1, y_test.max() + 1)
plt.ylim(y_test.min() - 1, y_test.max() + 1)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
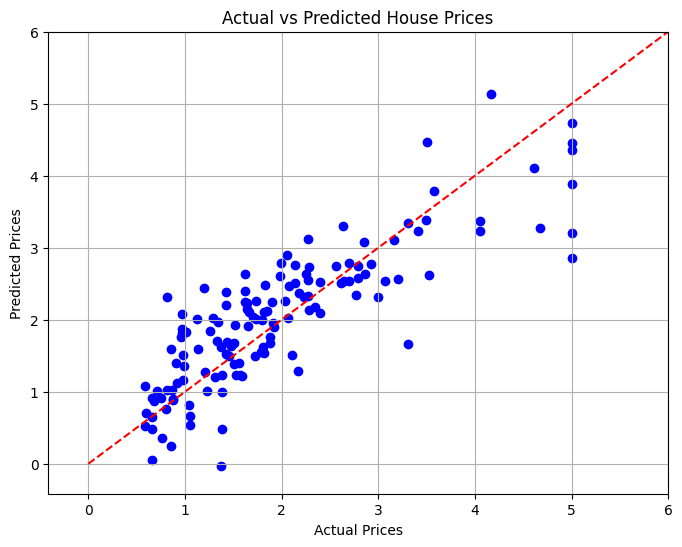
在這個專案中,我們開發了一個線性迴歸模型來根據各種特徵預測加州的房價。計算均方誤差來評估模型的性能,從而提供預測準確性的定量測量。透過視覺化,我們能夠看到我們的模型相對於實際值的表現如何。
該專案展示了機器學習在房地產分析中的強大功能,可以作為更先進的預測建模技術的基礎。
以上是使用 Scikit-Learn 完成機器學習工作流程:預測加州房價的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




