使用 Google Apps 腳本和 Leaflet.js 建立互動式 XY 圖像圖
Google 地圖有大量用於在地圖上繪製點的功能,但是如果您想在圖像上繪製點怎麼辦?這些 XY 影像繪圖通常用於樓層地圖、工作現場檢查,甚至是遊戲。
在本指南中,我將向您展示如何使用 Leaflet.js 和 Google Apps 腳本建立具有可拖曳點的互動式地圖。我們將涵蓋從設定地圖到整合 Google 試算表中的資料以及將其部署為網頁應用程式的所有內容。
本指南將涵蓋:
在 Google Apps 腳本 HTML 服務中設定 Leaflet.js
使用 Google 表格中的資料顯示標記
移動標記時更新表格行
從地圖建立新標記並儲存到表格
從網路應用程式中刪除標記
在 Google Apps 腳本 HTML 服務中設定 Leaflet.js
Leaflet.js 是最受歡迎的開源地圖庫之一。它重量輕,易於使用,並且有很好的文件。它們支援大量不同的地圖類型,包括“CRS.Simple”或坐標參考系統,它允許您提供背景圖像。
Google 試算表設定
先建立一個名為map_pin 的工作表,其架構如下:
| id | title | x | y |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | test1 | 10 | 30 |
| 2 | test2 | 50 | 80 |
Then open Apps Script from the Extensions menu.
Creating HTML File
First, we'll start with the basic example from the Leaflet docs, just to get the library working. You can see the full example in their quick start guide, here.
Add a new HTML File named Index, and set the content to:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Quick Start - Leaflet</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://unpkg.com/leaflet@1.9.3/dist/leaflet.css" />
<style>
#map {
height: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="map"></div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/leaflet@1.9.3/dist/leaflet.js"></script>
<script>
var map = L.map('map').setView([40.73, -73.99], 13);
L.tileLayer('https://{s}.tile.openstreetmap.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png', {
maxZoom: 19,
attribution: '© OpenStreetMap'
}).addTo(map);
var marker = L.marker([40.73, -73.99]).addTo(map)
.bindPopup('Test Popup Message')
.openPopup();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Then update the Code.gs file with:
function doGet() {
const html = HtmlService.createHtmlOutputFromFile('Index')
.setTitle('Map with Draggable Points')
.setXFrameOptionsMode(HtmlService.XFrameOptionsMode.ALLOWALL);
return html;
}
Save, and then click Deploy, and publish as a web app. Then open the link for the new deployment and you should see Leaflet.js displaying a map on New York.
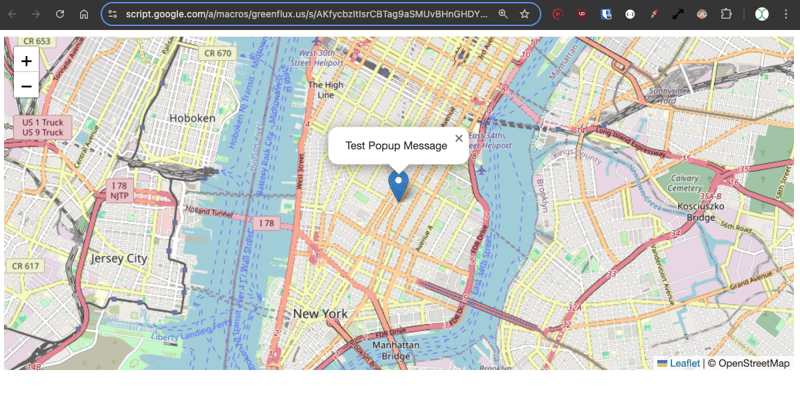
Ok, that's the regular map example using Leaflet. Now on to the CRS.Simple map type, which allows supplying a background image.
Update the HTML with this example from the Leaflet Tutorials.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CRS Simple Example - Leaflet</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://unpkg.com/leaflet@1.9.3/dist/leaflet.css" />
<style>
#map {
height: 400px;
width: 600px;
}
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="map"></div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/leaflet@1.9.3/dist/leaflet.js"></script>
<script>
// Set up the map with a simple CRS (no geographic projection)
var map = L.map('map', {
crs: L.CRS.Simple,
minZoom: -1,
maxZoom: 4
});
// Define the dimensions of the image
var bounds = [[0, 0], [1000, 1000]];
var image = L.imageOverlay('https://leafletjs.com/examples/crs-simple/uqm_map_full.png', bounds).addTo(map);
// Set the initial view of the map to show the whole image
map.fitBounds(bounds);
// Optional: Add a marker or other elements to the map
var marker = L.marker([500, 500]).addTo(map)
.bindPopup('Center of the image')
.openPopup();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Here we are supplying an image of 1000 x 1000 pixels, then setting the center marker at 500, 500.
Click Save, then Deploy>Test Deployments, to see the new map type. You should now have a map with a background image and a marker plotted in the center.
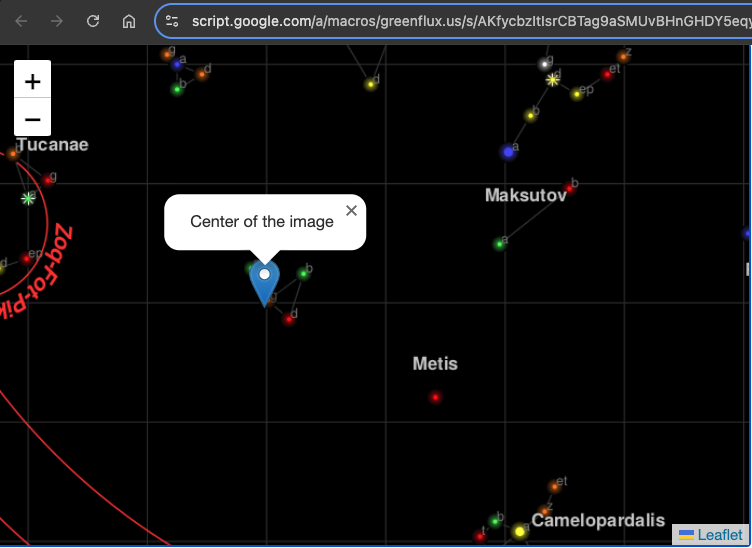
Initializing a Map with Data from Google Sheets
Next, we'll use data from the sheet to populate a set of markers on the map.
First, add a function to the Code.gs file to get the marker locations:
function getPinData(){
const ss = SpreadsheetApp.getActiveSpreadsheet();
const sh = ss.getSheetByName('map_pin');
const data = sh.getDataRange().getValues();
const json = arrayToJSON(data);
//Logger.log(json);
return json
}
function arrayToJSON(data=getPinData()){
const headers = data[0];
const rows = data.slice(1);
let jsonData = [];
for(row of rows){
const obj = {};
headers.forEach((h,i)=>obj[h] = row[i]);
jsonData.push(obj)
}
//Logger.log(jsonData)
return jsonData
}
Here I'm returning the pins as JSON so they're easier to work with in the HTML in the next section.
Now add a function to the HTML to loop over this JSON and create the map pins after the map has loaded.
// Add map pins from sheet data
google.script.run.withSuccessHandler(addMarkers).getPinData();
function addMarkers(mapPinData) {
mapPinData.forEach(pin => {
const marker = L.marker([pin.x, pin.y], {
draggable: true
}).addTo(map);
marker.bindPopup(`<b>${pin.title}`).openPopup();
marker.on('dragend', function(e) {
const latLng = e.target.getLatLng();
console.log(`Marker ${pin.title} moved to: ${latLng.lat}, ${latLng.lng}`);
});
});
}
Save, and then open the test deployment. You should now have markers generated from your sheet data!
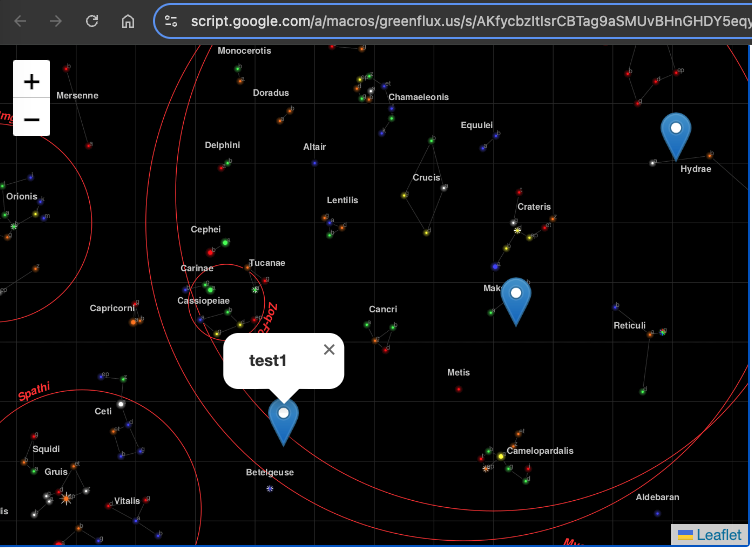
Each pin has a popup with the title from that row. The pins are draggable at this point, but we still need a function to save the new position.
Saving Marker Position When Dragged
To save the new position, we need two functions: one in the HTML to capture the event on the client side, and one to save the new position on the server side, in the Code.gs file.
Update the HTML with:
function addMarkers(mapPinData) {
mapPinData.forEach(pin => {
const { id, title, x, y } = pin;
const marker = L.marker([x, y], {
draggable: true
}).addTo(map);
marker.bindPopup(`<b>${title}</b>`).openPopup();
marker.on('dragend', function(e) {
const latLng = e.target.getLatLng();
console.log(`Marker ${title} moved to: ${latLng.lat}, ${latLng.lng}`);
saveMarkerPosition({ id, title, lat: latLng.lat, lng: latLng.lng });
});
});
}
function saveMarkerPosition({ id, title, lat, lng }) {
google.script.run.saveMarkerPosition({ id, title, lat, lng });
}
And then add a function to the Code.gs file to save the location:
function saveMarkerPosition({ id, lat, lng }) {
const ss = SpreadsheetApp.getActiveSpreadsheet();
const sh = ss.getSheetByName('map_pin');
const data = sh.getDataRange().getValues();
for (let i = 1; i < data.length; i++) {
if (data[i][0] === id) { // ID column (index 0)
sh.getRange(i + 1, 3).setValue(lat); // latitude column
sh.getRange(i + 1, 4).setValue(lng); // longitude column
break;
}
}
}
Save, and refresh the test deployment. You should now see the sheet update when a marker is dragged!
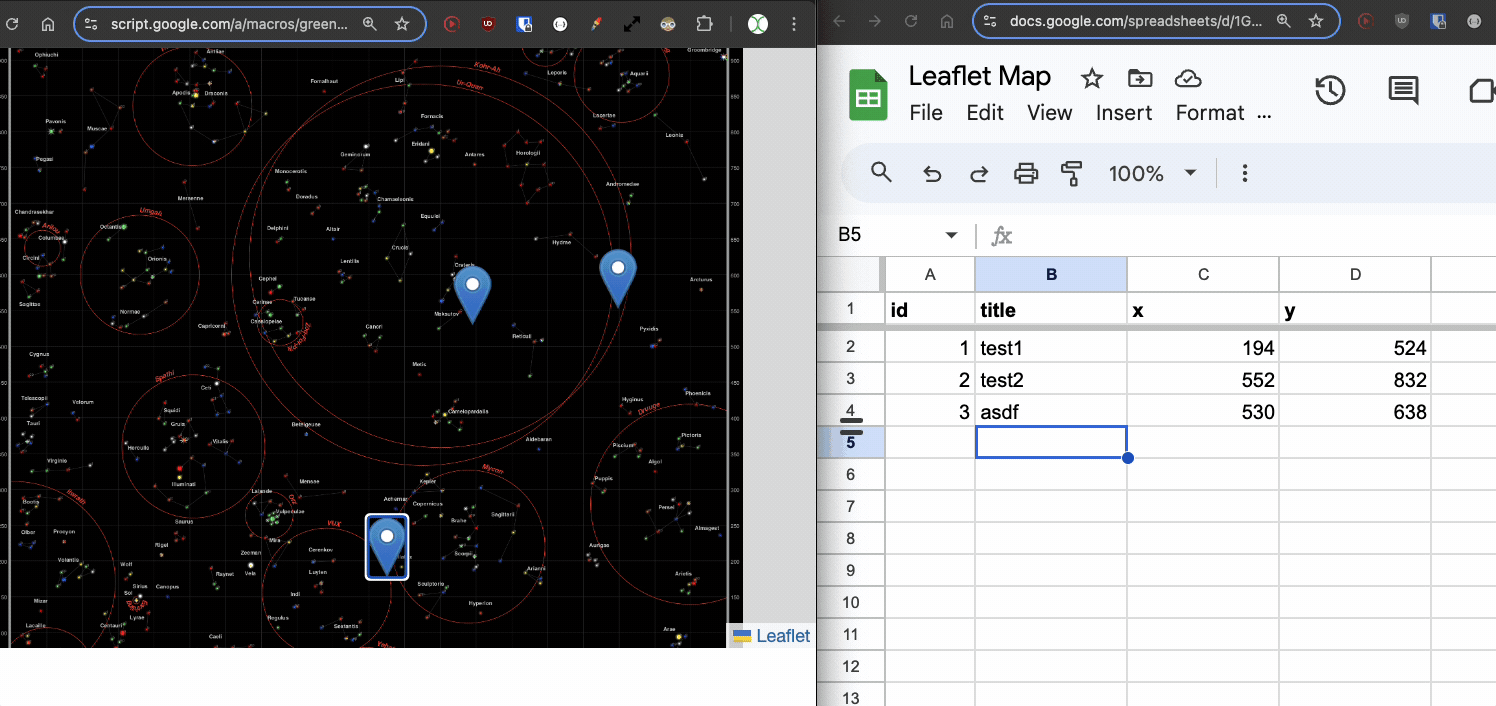
Adding New Points
We can now move the existing points, but what about adding new ones? Again, we'll need two functions, one in the HTML, and one in the Code.gs file.
First, add a function to the HTML to open a prompt when the user clicks an empty spot on the map, and pass the value to a server function.
// Function to add a new pin
map.on('click', function(e) {
const latLng = e.latlng;
const title = prompt('Enter a title for the new pin:');
if (title) {
google.script.run.withSuccessHandler(function(id) {
addNewMarker({ id, title, lat: latLng.lat, lng: latLng.lng });
}).addNewPin({ title, lat: latLng.lat, lng: latLng.lng });
}
});
function addNewMarker({ id, title, lat, lng }) {
const marker = L.marker([lat, lng], {
draggable: true
}).addTo(map);
marker.bindPopup(`<b>${title}</b>`).openPopup();
marker.on('dragend', function(e) {
const latLng = e.target.getLatLng();
saveMarkerPosition({ id, title, lat: latLng.lat, lng: latLng.lng });
});
}
Then add the function to the Code.gs to save the new row.
function addNewPin({ title, lat, lng }) {
const ss = SpreadsheetApp.getActiveSpreadsheet();
const sh = ss.getSheetByName('map_pin');
// Check if there are any rows present, if not initialize ID
const lastRow = sh.getLastRow();
let newId = 1;
if (lastRow > 0) {
const lastId = sh.getRange(lastRow, 1).getValue();
newId = lastId + 1;
}
sh.appendRow([newId, title, lat, lng]);
return newId;
}
Save once more and refresh the test deployment. Now when you click an empty spot, you can enter a title and save a new marker!
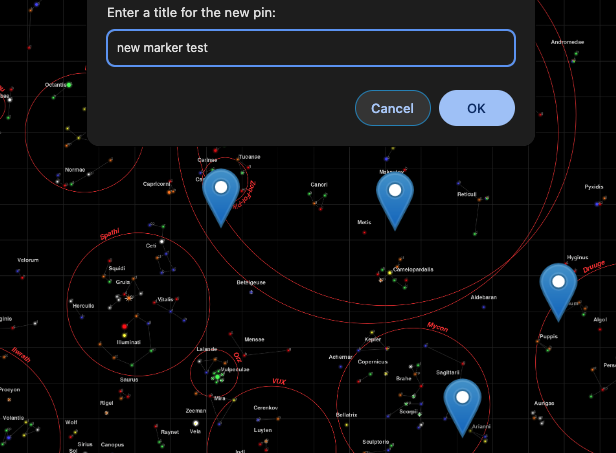
Deleting A Marker
Lastly, we should add a way to delete markers, giving us a full CRUD app in map view.
Update the add marker function to give the popup a delete button:
const popupContent = `<b>${title}</b><br><button onclick="deleteMarker(${id})">Delete Marker</button>`;
marker.bindPopup(popupContent).openPopup();
And then add a function for deleting from the client side:
// Function to delete a marker
function deleteMarker(id) {
const confirmed = confirm('Are you sure you want to delete this marker?');
if (confirmed) {
google.script.run.withSuccessHandler(() => {
// Refresh the markers after deletion
google.script.run.withSuccessHandler(addMarkers).getPinData();
}).deleteMarker(id);
}
}
Then add the matching function to the Code.gs file:
function deleteMarker(id) {
const ss = SpreadsheetApp.getActiveSpreadsheet();
const sh = ss.getSheetByName('map_pin');
const data = sh.getDataRange().getValues();
for (let i = 1; i < data.length; i++) {
if (data[i][0] === id) { // ID column (index 0)
sh.deleteRow(i + 1); // Delete the row
break;
}
}
}
What's Next?
There's a ton more you could do from here, like adding other data points to each marker, dynamic background images, or other click and drag interactions. You could even make a game! Got an idea for a use case? Drop a comment below!
以上是使用 Google Apps 腳本和 Leaflet.js 建立互動式 XY 圖像圖的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Stock Market GPT
人工智慧支援投資研究,做出更明智的決策

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 JavaScript實現點擊圖片切換效果:專業教程
Sep 18, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
JavaScript實現點擊圖片切換效果:專業教程
Sep 18, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
本文將介紹如何使用JavaScript實現點擊圖片切換的效果。核心思路是利用HTML5的data-*屬性存儲備用圖片路徑,並通過JavaScript監聽點擊事件,動態切換src屬性,從而實現圖片切換。本文將提供詳細的代碼示例和解釋,幫助你理解和掌握這種常用的交互效果。
 如何使用JavaScript中的GeOlocation API獲取用戶的位置?
Sep 21, 2025 am 06:19 AM
如何使用JavaScript中的GeOlocation API獲取用戶的位置?
Sep 21, 2025 am 06:19 AM
首先檢查瀏覽器是否支持GeolocationAPI,若支持則調用getCurrentPosition()獲取用戶當前位置坐標,並通過成功回調獲取緯度和經度值,同時提供錯誤回調處理權限被拒、位置不可用或超時等異常,還可傳入配置選項以啟用高精度、設置超時時間和緩存有效期,整個過程需用戶授權並做好相應錯誤處理。
 如何在JavaScript中創建多行字符串?
Sep 20, 2025 am 06:11 AM
如何在JavaScript中創建多行字符串?
Sep 20, 2025 am 06:11 AM
thebestatoreateamulti-linestlinginjavascriptsisisingsistisingtemplatalalswithbacktticks,whatpreserveticks,whatpreservereakeandeexactlyaswrite。
 NUXT 3組成API解釋了
Sep 20, 2025 am 03:00 AM
NUXT 3組成API解釋了
Sep 20, 2025 am 03:00 AM
Nuxt3的CompositionAPI核心用法包括:1.definePageMeta用於定義頁面元信息,如標題、佈局和中間件,需在中直接調用,不可置於條件語句中;2.useHead用於管理頁面頭部標籤,支持靜態和響應式更新,需與definePageMeta配合實現SEO優化;3.useAsyncData用於安全地獲取異步數據,自動處理loading和error狀態,支持服務端和客戶端數據獲取控制;4.useFetch是useAsyncData與$fetch的封裝,自動推斷請求key,避免重複請
 JavaScript中數字格式化:使用toFixed()方法保留固定小數位
Sep 16, 2025 am 11:57 AM
JavaScript中數字格式化:使用toFixed()方法保留固定小數位
Sep 16, 2025 am 11:57 AM
本教程詳細講解如何在JavaScript中將數字格式化為固定兩位小數的字符串,即使是整數也能顯示為"#.00"的形式。我們將重點介紹Number.prototype.toFixed()方法的使用,包括其語法、功能、示例代碼以及需要注意的關鍵點,如其返回類型始終為字符串。
 如何在JavaScript中使用setInterval創建重複間隔
Sep 21, 2025 am 05:31 AM
如何在JavaScript中使用setInterval創建重複間隔
Sep 21, 2025 am 05:31 AM
要創建JavaScript中的重複間隔,需使用setInterval()函數,它會以指定毫秒數為間隔重複執行函數或代碼塊,例如setInterval(()=>{console.log("每2秒執行一次");},2000)會每隔2秒輸出一次消息,直到通過clearInterval(intervalId)清除,實際應用中可用於更新時鐘、輪詢服務器等場景,但需注意最小延遲限制、函數執行時間影響,並在不再需要時及時清除間隔以避免內存洩漏,特別是在組件卸載或頁面關閉前應清理,確保
 JavaScript中DOM元素訪問的常見陷阱與解決方案
Sep 15, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
JavaScript中DOM元素訪問的常見陷阱與解決方案
Sep 15, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
本文旨在解決JavaScript中通過document.getElementById()獲取DOM元素時返回null的問題。核心在於理解腳本執行時機與DOM解析狀態。通過正確放置標籤或利用DOMContentLoaded事件,可以確保在元素可用時再嘗試訪問,從而有效避免此類錯誤。
 如何將文本複製到JavaScript中的剪貼板?
Sep 18, 2025 am 03:50 AM
如何將文本複製到JavaScript中的剪貼板?
Sep 18, 2025 am 03:50 AM
使用ClipboardAPI的writeText方法可複製文本到剪貼板,需在安全上下文和用戶交互中調用,支持現代瀏覽器,舊版可用execCommand降級處理。








