

This article introduces to you how to store and use sessions in the database in PHP (with code). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. , hope it helps you.
Example description:
It is safer to store SESSION data variables on the server side But imagine a large website like Xiaonei.com with over 100 million daily visits and tens of millions of users. If all user SESSION data is stored on the server, it will consume huge server resources. Therefore, when programmers create large websites, it is safe to store SESSION on the server side, but it is not the best choice. If the SESSION data is stored in the database, it can reduce thepressure on the server and the data is relatively safe.
Related topic recommendations
First create a table to store SESSION in the Mysql database:
table The table structure named t_session
is
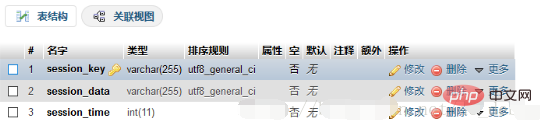
session_key: Yes
session_data used to store the session ID: is used to store the serialized $_SESSION[ ];
session_time: is used to store the timestamp. This timestamp refers to It is the validity period of time() session when the current session is created. It should be noted that the type of session_time here is int, so that size comparison can be performed when operating the database!
So what is serialization?
Serialization (Serialization) is the process of converting the state information of an object into a form that can be stored or transmitted. During serialization, an object writes its current state to temporary or persistent storage. Later, the object can be recreated by reading or deserializing the object's state from the store.
For example
$_SESSION[“user”]=”张三” $_SESSION[“pwd”]=”zhangsan”
The sequence becomes a string
user|s:6:"张三";pwd|s:8:"zhangsan";
where s represents the type as string, and the number represents the length of the string, so that you can operate on this string .
The next step is the text part
session.save_handlerDefine the name of the processor that stores and obtains data associated with the session . Default isfiles. If it is set to files (session.save_handler = files), the built-in mechanism of PHP is used. If you want to customize the storage method (such as storing in a database), use session_set_save_handler() to customize the settings,What we are talking about here is the second type.
So we have to modify the value ofsession_set_save_handlerin the php.ini file touser, such as picture:
boolsession_set_save_handler(callableopen,callable$close,callableread,callablewrite,callabledestroy,callablegc[,callable$create_sid[,callablevalidate_sid[,callableupdate_timestamp]]] )
If you don’t modify it, then you are using You can ignore him during the session, but when you make changes, you have to face him. This is a very special function, because the parameters of general functions are variables, but the parameters of this function are 6 functions (the last three parameters are optional parameters and can be ignored). Don’t be afraid, come one by one:
The first parameter:open(save_path,session_name), the two parameters here are automatically passed by php. save_path is session.save_path when session.save_handler = files, and session_name is the session ID used by the server to identify the client. However, if the user customizes it, these two parameters are not used, and only connect to the database. The open callback function is similar to the constructor of a class and will be called when the session is opened. This is the first callback function called after starting a session automatically or manually by calling session_start(). This callback function returns TRUE if the operation is successful, otherwise it returns FALSE.
The second parameter:close(), this function does not require parameters and is used to close the database. The close callback function is similar to the destructor of a class. Called after the write callback function is called. When the session_write_close() function is called, the close callback function will also be called. This callback function returns TRUE if the operation is successful, otherwise it returns FALSE.
The third parameter:read($key), the parameter here is the session ID, which is automatically passed by PHP. The premise of passing is that there is a session ID. If not, then this parameter Returns an empty string. Note that if there is no corresponding data in the database, an empty string must be returned, otherwise an error will be reported! If there is data in the session, the read callback function must return a string that encodes (serializes) the session data (in this case, the session_data taken from the table t_session). After starting the session automatically or manually by calling the session_start() function, PHP internally calls the read callback function to obtain the session data. Before calling read, PHP calls the open callback function. The format of the serialized string returned by the read callback must be exactly the same as the format when the write callback function saves the data. PHP will automatically deserialize the returned string and populate the $_SESSION super global variable.
The fourth parameter:write($key,$data), these two parameters are also automatically passed to this function by PHP, $key corresponds to the session ID, $data corresponds to the current ( Because the write function is usually called after the script execution is completed) the session variable processed by the script by the serialization processor (such as $_SESSION["user"]="Zhang San"$_SESSION["pwd"] mentioned above =”zhangsan”), the process of serializing session data is completed by PHP according to the session.serialize_handler setting value. The serialized data will be saved in association with the session ID. When calling the read callback function to obtain data, the returned data must be completely consistent with the data passed into the write callback function. PHP will call this callback function after the script completes execution or the session_write_close() function is called. Note that after calling this callback function, PHP will call the close callback function internally.
NOTE:PHP will not call the write callback function until the output stream is written and closed, so the debugging information in the write callback function will not be output to the browser. If you need to use debug output in the write callback function, it is recommended to write the debug output to a file.
第五个参数:destroy($key),当调用 session_destroy() 函数, 或者调用 session_regenerate_id() 函数并且设置 destroy 参数为 TRUE 时, 会调用此回调函数。用来注销session对应的SESSION键值,此回调函数操作成功返回 TRUE,反之返回 FALSE。它就是人们常常在点击注销登录的时候用到的函数。后面会有这个小细节。
第六个参数:gc(expire_time),这个函数的参数在默认机制下就是session.gc_maxlifetime设置的session有效时间。但是,user机制下session的过期时间在就是表里session_time,所以这里不需要传递参数的。为了清理会话中的旧数据,PHP 会不时的调用垃圾收集回调函数。 调用周期由 session.gc_probability 和 session.gc_pisor 参数控制。此回调函数操作成功返回 TRUE,反之返回 FALSE。
至此六个函数已经介绍完了,但是其中有许多需要说明的:
1、在open函数中本来是要传递save__path,目的是用来在这个路径下找到与session_name相对应的文件,然后通过read()函数来读取其中的数据,然后通过反序列化处理器将取到的字符串反序列化,在通过php自动填充各个$_session超全局变量。或者write函数来将序列化的数据存入这个路径下的文件。那么这里面的路径在非默认机制下难道就不需要吗,答案是肯定的*_*。当在非默认机制下,调试输出session_save_path,其结果为空值;而且如果未设置存储的路径,那被填充的$_session变量也只能在当前页面使用,而不能在别的页面使用,可以这样测试:在另一个页面利用session_start()函数打开会话,然后输出session_id和var_dump($_session),得到的是上一次浏览时服务器给客户端的session_id,但是$_session输出的是空数组(当然我这里只是大概的说一下我在验证时的过程)。其实我想说的就是我们在自定义会话存储机制的时候,是不需要自定义路径的,不然为什么还要存入数据库呢?
那么怎么在其他页面也能读取到$_session[]里面的值呢?
引入这个函数,即将六个 回调函数和session_set_save_handler放入一个文件里,然后在session_start()前用include()引入!
2、那他们的执行顺序是怎样呢?有点晕吧,来总结一下:首先session_start()函数打开session操作句柄,然后read函数读取数据,当脚本执行结束的时候执行write函数然后是close函数若有session_destroy()则执行完。
3、上面我提到过PHP 会在输出流写入完毕并且关闭之后才调用 write 回调函数,这个可把我玩坏啦,小编在上面可绕了不久呀,不然我也不会在write函数里调试那么久了!不过我也因此了解了register_shutdown_function这个函数,下面附上这个函数的特点吧:register_shutdown_function()是指在执行完所有PHP语句后再调用函数,不要理解成客户端关闭流浏览器页面时调用函数。
可以这样理解调用条件:
1、当页面被用户强制停止时
2、当程序代码运行超时时
3、当PHP代码执行完成时,代码执行存在异常和错误、警告
好了以上该说的都说完了,附上代码吧:
index.php用户登录界面
alert('您不久前刚来过');window.location.href='main.php';"; } } ?>
index_ok.php表单提交处理文件
alert('登录成功!');window.location.href='main.php';"; } } ?>
main.php主内容页
注销"; }else{ echo "您还没登录,请先登录!"; echo "登录"; } ?>
session_set_save_handler.php自定义session存储机制函数文件
$time"; $result=mysqli_query($con,$sql)or die("查询失败!"); if (!$result) {//用来检查出现再数据库部分的错误,很有用 printf("Error: %s\n", mysqli_error($con));//%s表示的是字符串,这是c里面的 exit(); } $row=mysqli_fetch_array($result);//or die()会终止后面的程序! if($row!=false){ return($row["session_data"]); }else{ return "";//再次强调如果空值 ,则一定 要返回”“而不是false } } //存储session function write($key,$data){ global $con; $over_time=time()+60;//注意time()为时间戳,在mysql中的数据类型不可用用date,datetime,timestamp来存储 $sql="select session_data from t_session where session_key='$key'"; $re=mysqli_query($con,$sql); $result=mysqli_fetch_array($re); //若$result为false,即结果 为空,说明数据库中未存有相应的session_id,那么就插入,如果不为空,那即使还有未过期的session_id,这是应更新 if($result==false){ $sql="insert into t_session(session_key,session_data,session_time ) values('$key','$data',$over_time)";//字符串的时候要加单引号,数字的时候是不用加的 $result=mysqli_query($con,$sql); if (!$result) {//用来检查出现再数据库部分的错误,很有用 printf("Error: %s\n", mysqli_error($con));//%s表示的是字符串,这是c里面的 exit(); } }else{ $sql="update t_session set session_key='$key',session_data='$data',session_time=$over_time where session_key='$key'"; $result=mysqli_query($con,$sql); } return($result); } 清楚相应的session数据 function destroy($key){ global $con; $sql="delete from t_session where session_key='$key'"; $result=mysqli_query($con,$sql); return($result); } //执行垃圾回收 function overdue($expire_time){//这个参数是自动传进去的,就是session.gc_maxlifetime最大有效时间,例如1440s; global $con; $time=time(); $sql="delete from t_session where session_time<$time"; $result=mysqli_query($sql); return($result); } session_set_save_handler('open','close','read','write','destroy','overdue'); ?>
相关文章推荐:
The above is the detailed content of How to store session in database and use it in PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!