Detailed explanation of operating MySQL database with PHP (2)
Read and delete news list
Implementation code
1. First write a separate PHP file (conn.php) to connect MySQL database
//*******************PHP连接MySQL数据库********************
<?php
//声明PHP输出数据的字符集
header("content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
//0.数据库配置信息
$db_host = "localhost:3306";
$db_user = "root";
$db_pwd = "yeoman";
$db_name = "yeoman92";
//1.PHP连接MySQL服务器
$link = @mysql_connect($db_host, $db_user, $db_pwd);
if(!$link){
echo "MySQL服务器连接失败!".mysql_error();
exit();
}
//2.选择数据库
if(!mysql_select_db($db_name, $link)){
echo "选择{$db_name}数据库失败!".mysql_error();
exit();
}
//3.设置MySQL返回的数据字符集
mysql_query("set names utf8");
?>Function Explanation:
header()
Description: Send a custom http message, in other words: the format of the data returned by PHP or character set.
Syntax: void header (string $string)
Example:
-
header(“content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8”) //Set the character set of data returned by PHP
header(“location:http:www .sina.com.cn”); //Web page jump
2. Write the main file (index.php)
<?php
//包含连接MySQL的文件,即文件引入
include "conn.php";
//执行查询的语句
$sql = "SELECT * FROM 007_news ORDER BY id DESC";
$result = mysql_query($sql); //返回的是结果集
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>新闻列表</title>
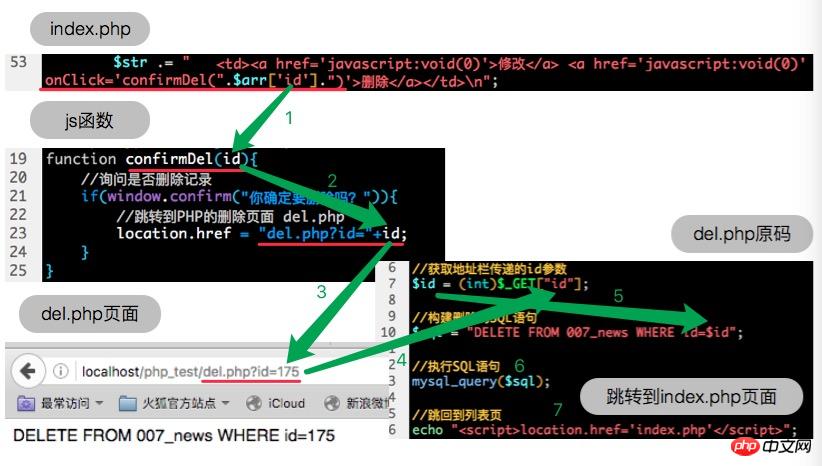
<script type="text/javascript">function confirmDel(id){
//询问是否删除记录
if(window.confirm("你确定要删除吗?")){
//跳转到PHP的删除页面 del.php
location.href = "del.php?id="+id;
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table width="70%" border="1" bordercolor="#CCC" rules="all" align="center" cellpadding="5">
<tr bgcolor="#efefef">
<th>编号</th>
<th>新闻标题</th>
<th>作者</th>
<th>来源</th>
<th>排序</th>
<th>点击率</th>
<th>发布日期</th>
<th>操作选项</th>
</tr>
<?php
$str = "";
while($arr = mysql_fetch_array($result,MYSQL_ASSOC)){ //输出表格内容
$str .= "<tr>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['id']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['title']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['author']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['source']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['orderby']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['hits']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".date("Y-m-d H:i", $arr['addate'])."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td><a href='javascript:void(0)'>修改</a>
<a href='javascript:void(0)' onClick='confirmDel(".$arr['id'].")'>删除</a></td>\n";
$str .= "</tr>\n";
}
echo $str;
?></table></body></html>Explanation of syntax structure
1. Include syntax structure, (not a function)
Description: Include and run the specified file.
Syntax: include $filename or include($filename)
Example: include “include/conn.php”
2. require syntax structure
If the included file does not exist, include will report a warning error and the script will continue to run below.
And require will report a fatal error and the script will terminate execution immediately.
Description: Include and run the specified file.
Syntax: require $filename or require($filename)
Example: require “include/conn.php”
Note: include and require both include and run files, but there is a difference.
For details on how to introduce files in PHP, please see: Four ways to introduce files in PHP and their differences
##3 . Write the file to delete the record (del.php)<?php
//包含连接MySQL的文件,即文件引入
include "conn.php";
//执行查询的语句
$sql = "SELECT * FROM 007_news ORDER BY id DESC";
$result = mysql_query($sql); //返回的是结果集
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>新闻列表</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function confirmDel(id){
//询问是否删除记录
if(window.confirm("你确定要删除吗?")){
//跳转到PHP的删除页面 del.php
location.href = "del.php?id="+id;
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table width="70%" border="1" bordercolor="#CCC" rules="all" align="center" cellpadding="5">
<tr bgcolor="#efefef">
<th>编号</th>
<th>新闻标题</th>
<th>作者</th>
<th>来源</th>
<th>排序</th>
<th>点击率</th>
<th>发布日期</th>
<th>操作选项</th>
</tr>
<?php
$str = "";
while($arr = mysql_fetch_array($result,MYSQL_ASSOC)){ //输出表格内容
$str .= "<tr>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['id']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['title']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['author']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['source']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['orderby']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".$arr['hits']."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td>".date("Y-m-d H:i", $arr['addate'])."</td>\n";
$str .= " <td><a href='javascript:void(0)'>修改</a>
<a href='javascript:void(0)' onClick='confirmDel(".$arr['id'].")'>删除</a></td>\n";
$str .= "</tr>\n";
}
echo $str;
?>
</table>
</body>
</html>The running effect is displayed
Business process for deleting news records
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of operating MySQL database with PHP (2). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to use the $_COOKIE variable in php
Aug 20, 2025 pm 07:00 PM
How to use the $_COOKIE variable in php
Aug 20, 2025 pm 07:00 PM
$_COOKIEisaPHPsuperglobalforaccessingcookiessentbythebrowser;cookiesaresetusingsetcookie()beforeoutput,readvia$_COOKIE['name'],updatedbyresendingwithnewvalues,anddeletedbysettinganexpiredtimestamp,withsecuritybestpracticesincludinghttponly,secureflag
 How to work with arrays in php
Aug 20, 2025 pm 07:01 PM
How to work with arrays in php
Aug 20, 2025 pm 07:01 PM
PHParrayshandledatacollectionsefficientlyusingindexedorassociativestructures;theyarecreatedwitharray()or[],accessedviakeys,modifiedbyassignment,iteratedwithforeach,andmanipulatedusingfunctionslikecount(),in_array(),array_key_exists(),array_push(),arr
 Describe the Observer design pattern and its implementation in PHP.
Aug 15, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
Describe the Observer design pattern and its implementation in PHP.
Aug 15, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
TheObserverdesignpatternenablesautomaticnotificationofdependentobjectswhenasubject'sstatechanges.1)Itdefinesaone-to-manydependencybetweenobjects;2)Thesubjectmaintainsalistofobserversandnotifiesthemviaacommoninterface;3)Observersimplementanupdatemetho
 phpMyAdmin security best practices
Aug 17, 2025 am 01:56 AM
phpMyAdmin security best practices
Aug 17, 2025 am 01:56 AM
To effectively protect phpMyAdmin, multiple layers of security measures must be taken. 1. Restrict access through IP, only trusted IP connections are allowed; 2. Modify the default URL path to a name that is not easy to guess; 3. Use strong passwords and create a dedicated MySQL user with minimized permissions, and it is recommended to enable two-factor authentication; 4. Keep the phpMyAdmin version up to fix known vulnerabilities; 5. Strengthen the web server and PHP configuration, disable dangerous functions and restrict file execution; 6. Force HTTPS to encrypt communication to prevent credential leakage; 7. Disable phpMyAdmin when not in use or increase HTTP basic authentication; 8. Regularly monitor logs and configure fail2ban to defend against brute force cracking; 9. Delete setup and
 How to lock tables in MySQL
Aug 15, 2025 am 04:04 AM
How to lock tables in MySQL
Aug 15, 2025 am 04:04 AM
The table can be locked manually using LOCKTABLES. The READ lock allows multiple sessions to read but cannot be written. The WRITE lock provides exclusive read and write permissions for the current session and other sessions cannot read and write. 2. The lock is only for the current connection. Execution of STARTTRANSACTION and other commands will implicitly release the lock. After locking, it can only access the locked table; 3. Only use it in specific scenarios such as MyISAM table maintenance and data backup. InnoDB should give priority to using transaction and row-level locks such as SELECT...FORUPDATE to avoid performance problems; 4. After the operation is completed, UNLOCKTABLES must be explicitly released, otherwise resource blockage may occur.
![You are not currently using a display attached to an NVIDIA GPU [Fixed]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/431/639/175553352135306.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) You are not currently using a display attached to an NVIDIA GPU [Fixed]
Aug 19, 2025 am 12:12 AM
You are not currently using a display attached to an NVIDIA GPU [Fixed]
Aug 19, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Ifyousee"YouarenotusingadisplayattachedtoanNVIDIAGPU,"ensureyourmonitorisconnectedtotheNVIDIAGPUport,configuredisplaysettingsinNVIDIAControlPanel,updatedriversusingDDUandcleaninstall,andsettheprimaryGPUtodiscreteinBIOS/UEFI.Restartaftereach
 How to select data from a table in MySQL?
Aug 19, 2025 pm 01:47 PM
How to select data from a table in MySQL?
Aug 19, 2025 pm 01:47 PM
To select data from MySQL table, you should use SELECT statement, 1. Use SELECTcolumn1, column2FROMtable_name to obtain the specified column, or use SELECT* to obtain all columns; 2. Use WHERE clause to filter rows, such as SELECTname, ageFROMusersWHEREage>25; 3. Use ORDERBY to sort the results, such as ORDERBYageDESC, representing descending order of age; 4. Use LIMIT to limit the number of rows, such as LIMIT5 to return the first 5 rows, or use LIMIT10OFFSET20 to implement paging; 5. Use AND, OR and parentheses to combine
 What are variadic functions and the splat operator (`...`) in PHP?
Aug 17, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
What are variadic functions and the splat operator (`...`) in PHP?
Aug 17, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
PHP's mutable functions are implemented through the splat operator (...). 1. Collect parameters in the function definition, such as functionsum(...$numbers) to aggregate the passed parameters into an array; 2. Use the...unpack array when calling the function, such as add(...[1,2,3]) to pass the array elements as independent parameters; this operator improves code readability, type safety and performance, replaces old methods such as func_get_args(), and is widely used in scenarios with uncertain parameters such as summing, logging, etc.







