
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the relevant knowledge points of MySQL statistical information through the introduction of the concept of statistical information and the advantages of MYSQL statistical information. I hope it can help friends in need.
MySQL will go through the process of SQL parsing and query optimization when executing SQL. The parser decomposes SQL into data structures and passes them to subsequent steps. The query optimizer finds the best solution for executing SQL queries and generates execution plan. The query optimizer determines how SQL is executed, relying on the statistics of the database. Below we introduce the relevant content of innodb statistics in MySQL 5.7.
The storage of MySQL statistical information is divided into two types, non-persistent and persistent statistical information.
Non-persistent statistical information is stored in memory. If the database is restarted, the statistical information will be lost. There are two ways to set non-persistent statistics:
1 Global variable, INNODB_STATS_PERSISTENT=OFF |
2 CREATE/ALTER table parameters, STATS_PERSISTENT=0 |
non-persistent Statistics will be automatically updated in the following situations:
1 Execute ANALYZE TABLE |
2 When innodb_stats_on_metadata=ON, execute SHOW TABLE STATUS, SHOW INDEX, query TABLES under INFORMATION_SCHEMA, STATISTICS |
| ##3 When the --auto-rehash function is enabled , use mysql client to log in |
| 4 The table is opened for the first time |
| 5 distance The last time statistics were updated, the data in table 1/16 was modified |
In this case, 10% of the data in the table is modified |
| Database name | |
| Table name | ##last_update |
| ##Last update time of statistical information | n_rows |
| The number of rows in the table | clustered_index_size |
| The number of pages in the clustered index | sum_of_other_index_sizes |
| The pages of other indexes Quantity | |
To better understand innodb_index_stats, create a test table for explanation:
CREATE TABLE t1 ( a INT, b INT, c INT, d INT, e INT, f INT, PRIMARY KEY (a, b), KEY i1 (c, d), UNIQUE KEY i2uniq (e, f) ) ENGINE=INNODB;
Write the data as follows:
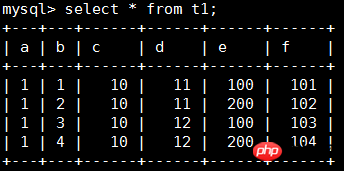
To view the statistical information of the t1 table, you need to focus on the stat_name and stat_value fields
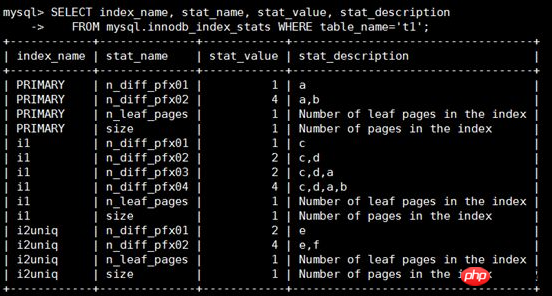
When tat_name=size: stat_value indicates the number of indexed pages
When stat_name=n_leaf_pages: stat_value represents the number of leaf nodes
When stat_name=n_diff_pfxNN: stat_value represents the number of unique values on the index field. Here is a detailed explanation:
1 , n_diff_pfx01 represents the number after the distinct of the first column of the index. For example, column a of PRIMARY has only one value 1, so when index_name='PRIMARY' and stat_name='n_diff_pfx01', stat_value=1.
2. n_diff_pfx02 represents the number after distinct in the first two columns of the index. For example, the e and f columns of i2uniq have 4 values, so when index_name='i2uniq' and stat_name='n_diff_pfx02', stat_value=4.
3. For non-unique indexes, the primary key index will be added after the original columns, such as index_name='i1' and stat_name='n_diff_pfx03', and the primary key column a will be added after the original index columns c and d, ( The distinct result of c, d, a) is 2.
Understanding the specific meaning of stat_name and stat_value can help us troubleshoot why a suitable index is not used when executing SQL. For example, the stat_value of a certain index n_diff_pfxNN is much smaller than the actual value. The query optimizer considers the index to be selective. If it is poor, it may lead to using the wrong index.
We checked the execution plan and found that the correct index was not used. If it is caused by a large difference in statistical information in innodb_index_stats, it can be handled in the following ways:
1. Manually update statistical information. Note that read locks will be added during execution:
ANALYZETABLE TABLE_NAME;
2. If the statistical information is still inaccurate after updating, consider adding The data page of table sampling can be modified in two ways:
a) Global variable INNODB_STATS_PERSISTENT_SAMPLE_PAGES, the default is 20;
b) A single table can specify the sampling of the table:
ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME STATS_SAMPLE_PAGES=40;
After testing, the maximum value of STATS_SAMPLE_PAGES here is 65535. If it exceeds, an error will be reported.
Currently MySQL does not provide a histogram function. In some cases (such as uneven data distribution), just updating statistical information may not necessarily result in an accurate execution plan. Indexes can only be specified through index hints. The new version 8.0 will add a histogram function, let us look forward to MySQL becoming more and more powerful!
Related recommendations:
Example analysis: statistical information management, Spring annotation development and EasyUI
Collecting SQL Server statistical information_PHP tutorial
database_name |
|
| ##table_name | |
| index_name | |
| ##last_update | Statistics last updated time |
| stat_name | Statistical information name |
| ##stat_value | ##Value of statistical information |
sample_size |
Sample size |
| ##stat_description | Type Description |
The above is the detailed content of Detailed overview of MySQL statistics. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




