
在node中还有很多内置对象,可以帮助我们进行很多操作,包括对路径、文件等操作。下面本篇文章给大家介绍一下node常用内置模块中的path模块和fs模块,希望对大家有所帮助!

path模块用于对路径和文件进行处理,提供了很多方法。
有一个需求是将路径和文件名进行拼接。
const basePath = '/user/why' const filename = 'abc.txt'
那么有人会使用字符串拼接的方式进行拼接。
const filePath = basePath + '/' + filename console.log(filePath);
这样的结果虽然没有问题,但是考虑到不同的系统,windows系统可以使用\或者\\或者/作为路径分隔符,而Mac OS、Linux的Unix操作系统使用/作为路径分隔符。
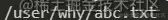
解决上述问题,我们可以使用path.resolve来进行路径的拼接。
const path = require('path') const basePath = '/user/why' const filename = 'abc.txt' const filePath = path.resolve(basePath, filename) console.log(filePath);

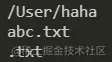
const path = require('path') const filePath = '/User/haha/abc.txt' console.log(path.dirname(filePath)); console.log(path.basename(filePath)); console.log(path.extname(filePath));
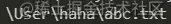
如果我们想要把多个路径进行拼接,但是不同的操作系统可能使用不同的分隔符,我们可以使用path.join函数。
const path = require('path') const basepath = '/User/haha' const filename = 'abc.txt' const filePath = path.join(basepath, filename) console.log(filePath);
如果我们想要将某个文件和文件夹拼接,可以使用path.resolve。
const basepath = 'User/haha' const filename = 'abc.txt'

path.resolve和path.join一样也可以进行路径的拼接,那么它们的区别是什么呢?
const basepath = '../User/haha' const filename = './abc.txt' const othername = './haha.js' const filePath1 = path.join(basepath, filename, othername) console.log(filePath1); const filePath2 = path.resolve(basepath, filename, othername) console.log(filePath2);
我们可以看到它们的差别。

nodejs文件系统的API大都提供三种操作方式:
同步操作文件:代码会被阻塞,不会继续执行
异步回调函数操作文件:代码不会被阻塞,需要传入回调函数,当获取到结果时,回调函数执行
异步Promise操作文件:代码不会被阻塞,通过fs.promises调用方法操作,会返回一个Promise,可以通过then、catch进行处理。
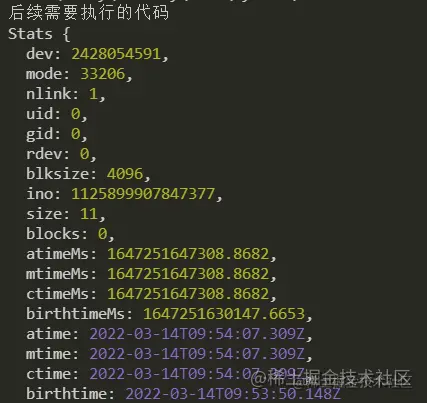
方式一 同步操作:fs.statSync
const fs = require('fs') const filepath = './abc.txt' const info = fs.statSync(filepath) console.log('后续需要执行的代码'); console.log(info);
方式二 异步操作
fs.stat(filepath, (err, info) => { if(err) { console.log(err); return } console.log(info); console.log(info.isFile()); // 判断是否是一个文件 console.log(info.isDirectory()); // 判断是否是一个文件夹 }) console.log('后续需要执行的代码');
方式三: Promise
fs.promises.stat(filepath).then(info => { console.log(info); }).catch(err => { console.log(err); }) console.log('后续需要执行的代码');
node为所有打开的文件分配了一个数字型的文件描述符。所有文件系统操作都使用这些文件描述符来标识和跟踪每个特定的文件。
fs.open()方法用于分配新的文件描述符fd。一旦被分配,则文件描述符可用于从文件读取数据、向文件写入数据、或请求关于文件的信息。
const fs = require('fs') fs.open('./abc.txt', (err, fd) => { if(err) { console.log(err); return } // 通过文件描述符去获取文件信息 fs.fstat(fd, (err, info) => { console.log(info); }) })
fs.readFile(path[, options], callback):读取文件内容
fs.writeFile(path[, options], callback):往文件中写入内容
option参数:
flag: 写入的方式
encoding:字符的编码
文件的写入
fs.writeFile('./abc.txt', content, {flag: "a"}, err => { console.log(err); })
文件的读取
fs.readFile('./abc.txt', (err, data) => { console.log(data); })
如果不填写encoding,返回的结果Buffer(二进制)。
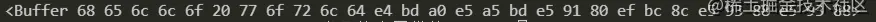
fs.readFile('./abc.txt', {encoding: 'utf-8'}, (err, data) => { console.log(data); })
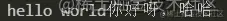
使用fs.mkdir()或者fs.mkdirSync创建一个新的文件夹。
const fs = require('fs') // 创建文件夹 const dirname = './haha' if(!fs.existsSync(dirname)) { fs.mkdir(dirname, (err) => { console.log(err); }) }
fs.readdir
fs.readdir(dirname, (err, files) => { console.log(files); })
获取文件夹中的所有文件,此时目录如下图所示,可以使用递归。
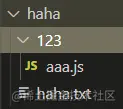
const fs = require('fs') const path = require('path') const dirname = './haha' function getFiles(dirname) { fs.readdir(dirname, {withFileTypes: true}, (err, files) => { // console.log(files); for(let file of files) { // 判断是否是文件夹 if(file.isDirectory()) { const filepath = path.resolve(dirname, file.name) getFiles(filepath) } else { console.log(file.name); } } }) } getFiles(dirname)
可以使用fs.rename对文件夹进行重命名。
fs.rename('./haha', './xixi', err => { console.log(err); })
更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci 浅析node中的常用模块:path模块和fs模块. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
 connectionresetSolution
connectionresetSolution Mengapa Windows tidak boleh mengakses laluan peranti atau fail yang ditentukan
Mengapa Windows tidak boleh mengakses laluan peranti atau fail yang ditentukan Pengumpulan kekunci pintasan komputer
Pengumpulan kekunci pintasan komputer Pengenalan kepada maksud javascript
Pengenalan kepada maksud javascript Apakah nama aplikasi telekomunikasi?
Apakah nama aplikasi telekomunikasi? Hubungan antara lebar jalur dan kelajuan rangkaian
Hubungan antara lebar jalur dan kelajuan rangkaian minidump.dmp
minidump.dmp Foto Windows tidak boleh dipaparkan
Foto Windows tidak boleh dipaparkan