
1) 把jar包复制到项目目录下
2) 把jar包加入项目的buildpath环境变量中, 使得classpath也和buildpath一致, 让类加载器便于加载具体子类
3) 反射加载驱动程序类, 会自动注册驱动程序4) 通过驱动程序管理器获取连接.
在当前工程下创建jdbc.properties文件,其中内容如下(是连接Oracle、MySql数据库所需要的四大参数分别是:加载驱动、获取连接数据库的IP及端口、用户名,密码),目的是方便调用和修改!
#driverClass = oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver #url = jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:orcl #user = scott#password = tigerdriverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driverurl = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/companyuser = root password = 123456
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Driver;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* 获取连接
* 1) 把jar包复制到项目目录下
* 2) 把jar包加入项目的buildpath环境变量中, 使得classpath也和buildpath一致, 让类加载器便于加载具体子类
* 3) 反射加载驱动程序类, 会自动注册驱动程序
* 4) 通过驱动程序管理器获取连接.
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class DriverTest {
// 使用Properties类对象的getPropety方法与FileInputStream方法获取文件中的内容,从而创建Connection对象
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}
}鉴于每一次jdbc的操作都需要建立连接,我们将建立连接的方法、关闭资源的方法作为固定方法放在JdbcUtil类中,方便使用:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtil {
// 获取建立连接对象
public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException,
SQLException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return connection;
}
// 关闭资源
public static void close(Connection connection) {
close(connection, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement) {
close(connection, statement, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}建立连接成功,现在进行与数据库的交流,与数据库交流需要使用到Statement类,首先我们需要建立一个User类以与Statement类中创建的在company数据库中的的user表相对应:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class User {
private String user;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String user, String password) {
super();
this.user = user;
this.password = password;
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [user=" + user + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}使用Statement执行创建user表,并插入三行数据:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.junit.Test;
// 使用Statement执行创建user表,并插入三行数据
public class StatementTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();// 获取执行体对象
// 执行SQL
// 创建user表
String sql = "create table if not exists user(user varchar(50), password varchar(100))";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql); // 执行的DDL语句, 还可以执行DML
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('admin','admin')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user1','user1')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user2','123456')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, statement);
}
}
}然而Statement存在弊端:不仅需要拼写sql语句,并且存在SQL注入的问题,具体问题在下面的小例子中体现
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestStatement {
// 弊端:需要拼写sql语句,并且存在SQL注入的问题
@Test
public void testLogin() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户名:");
String userName = scan.nextLine();
System.out.print("密 码:");
String password = scan.nextLine();
String sql = "select user, password from user where user = '"
+ userName + "' and password = '" + password + "'";
System.out.println(sql);
User user = get(sql, User.class);
if(user != null){
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}else{
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
public <T> T get(String sql, Class<T> clazz) {// (sql, Customer.class)
T t = null;
Connection conn = null;
Statement stam = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
stam = conn.createStatement();
rs = stam.executeQuery(sql);
// 获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// 获取结果集的列数
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
t = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// //1. 获取列的名称
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
// 1. 获取列的别名
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 注意:
// 获取结果集中(相当于数据表)列的名称(别名)
// 2. 根据列名获取对应数据表中的数据
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(columnName);
// 3. 将数据表中得到的数据,封装进对象
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); // 注意:反射根据Java中类的属性获取Field对象
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//JDBCUtils.close(rs, stam, conn);
}
return t;
}
}
此程序我们需要使用正确的用户名,和对应的密码才能进入登陆成功,通过上面的程序我们可知用户名和密码分别是:
+-------+----------+
| user | password |
+-------+----------+
| admin | admin |
| user1 | user1 |
| user2 | 123456 |
+-------+----------+
正常情况下我们登陆情况如下图:
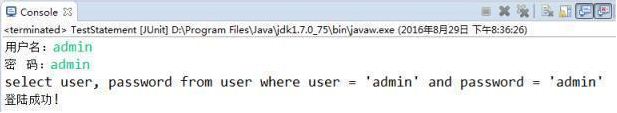
但是SQL高手通过如下操作就能登陆成功,这就是SQL注入的问题
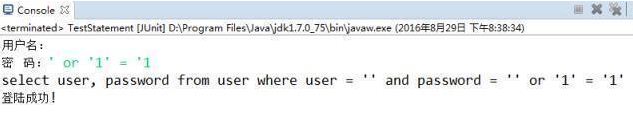
为了防止SQL注入问题,于是我们需要使用他的子类PreparedStatement预编译执行体,下面我们进行PreparedStatement的练习:
首先先创建Customer类
// 写一个类Customer, 包含属性name, gender, phone
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class Customer {
private String name;
private String gender;
private String phone;
public Customer(String name, int age, String gender, String phone,) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.phone = phone;
}
public Customer() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [name=" + name + ", gender=" + gender + ", phone=" + phone + "]";
}
}在测试类中使用PreparedStatment执行体对象创建相应的表, 并插入2条数据。
public class PreparedStatementTest {
@Test
public void exer1() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "create table if not exists customer(name varchar(30), gender enum('男','女') default '男', phone varchar(20))";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement); // 在获取新的预编译对象前,一定要先关闭原来的.
String sql2 = "insert into customer(name, gender, phone) values(?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2); // 要想重新执行新的SQL,必须再次预编译
preparedStatement.setString(1, "张三");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "13343493434");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
preparedStatement.setString(1, "李四");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "1322243434");
rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
// 并通过客户端验证.
}
}在Customer类中添加属性int age,double weight,给Customer表中添加对应的列,并添加记录
public class PreparedStatementTest {
// 在Customer类中添加属性int age,double weight,给Customer表中添加对应的列,并添加记录
@Test
public void test3() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add age int after name";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "alter table customer add weight double";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 50);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "134234234234");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 98.5);
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 添加记录
@Test
public void test4() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add birthdate date";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "赵六");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 60);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "13882342323");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 40);
preparedStatement.setString(6, "1960-2-3");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 再添加记录
@Test
public void test5() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "张七");
preparedStatement.setObject(2, 20);
preparedStatement.setObject(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setObject(4, "1343434343");
preparedStatement.setObject(5, 58.8);
preparedStatement.setObject(6, "1980-3-8");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (rows == 1) {
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
}像上面那样添加每次重复同样的代码,我们这里设置通用的更新操作,并存入CommonUtil类中,作为工具类通用更新操作。具体实现如下:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class CommonUtil {
/**
* 通用更新操作
* @param sql 一个可以包含?的SQL语句
* @param values SQL中有多少个?,可变参数就有多少个具体值
* @return 更新以后影响的记录数
*/
public static int commonUpdate(String sql, Object... values) throws FileNotFoundException,
ClassNotFoundException, IOException,
SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection(); // 获取连接
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 把带有?的SQL编译
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) { // 可变参数的长度就是?的个数
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, values[i]); // 统一给所有的?替换成具体的值
}
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 替换完?或没有?, 执行更新操作
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement); // 关闭资源
}
}
}至此我们实现了数据库数据的建表,插入,更新,删除,下面进行数据库操作中比较难的查询,需要使用到查询结果集ResultSet类,循序渐进的练习实现如下:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.util.List;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.junit.Test;
public class ResultSetTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
// select * from customer; 结果如下
/*
+------+------+--------+------------+--------+------------+
| name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
+------+------+--------+------------+--------+------------+
| 张七 20 | 女 | 1343434343 | 58.8 | 1980-03-08 |
| 张九 | 40 | 男 | 1349932423 | 78.2 | 1977-08-08 |
| 张三 | 3 | 女 | 1332324234 | 70 | 1979-08-08 |
+------+------+--------+------------+--------+------------+
*/
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from customer";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 调用PreparedStatement对象的executeQuery方法产生ResultSet对象
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
System.out.println(resultSet);
while (resultSet.next()) { // 根据列的<span style="color:#ff0000;">序号</span>,
先检测当前游标的下一行是否有数据, 如果有数据则移动游标,并返回true, 如果没有数据,直接返回false
String name = resultSet.getString(1); // 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第1列的值
int age = resultSet.getInt(2);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第2列的值
String gender = resultSet.getString(3);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第3列的值
String phone = resultSet.getString(4);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第4列的值
double weight = resultSet.getDouble(5);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第5列的值
Date birthDate = resultSet.getDate(6);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第6列的值
System.out.println(name + "\t" + age + "\t" + gender + "\t" + phone + "\t" + weight + "\t" + birthDate);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
// 我们改变查询列名的顺序进行查询操作,使用下标不能实现了,我们需要根据虚表中的<span style="color:#ff0000;">列名</span>
进行查询,并将查询结果封装成对象,添加到list集合中
@Test
public void test2() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
// name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
String sql = "select name custName, gender, age, weight, phone, birthdate birth from customer";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
List<Customer> list = new ArrayList<Customer>();
// 基于虚表的结果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
String name = resultSet.getString("custName");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为name列的值
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为age列的值
String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为gender列的值
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
double weight = resultSet.getDouble("weight");
Date birthDate = resultSet.getDate("birth");
Customer customer = new Customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthDate); // 封装成对象 O/R mapping
list.add(customer);
}
// 遍历集合
for (Customer cust : list) {
System.out.println(cust);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
// 我们改变查询列名的顺序进行查询年龄大于任意数的操作,使用下标不能实现了,我们需要根据<span style="color:#ff0000;">虚表中的列名</span>
进行查询,并将查询结果封装成对象,添加到list集合中
@Test
public void test3() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
// name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
String sql = "select name custName, gender, age, weight, phone, birthdate birth from customer where age > ?";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
prepareStatment.setObject(1, 20);
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
List<Customer> list = new ArrayList<Customer>();
// <span style="color:#ff0000;">基于虚表的结果集</span>
while (resultSet.next()) {
String name = resultSet.getString("custName");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的
<span style="color:#ff0000;">虚表</span>中名字为name列的值
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为age列的值
String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为gender列的值
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
double weight = resultSet.getDouble("weight");
Date birthDate = resultSet.getDate("birth");
Customer customer = new Customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthDate); // 封装成对象 O/R mapping
list.add(customer);
}
// 遍历集合
for (Customer cust : list) {
System.out.println(cust);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
// 获取查询结果,若查询结果并没有类与其对应,就需要获取虚表的表结构进行查询操作的打印输出
@Test
public void test4() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
// name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
String sql = "select name custName, gender, age, weight, phone, birthdate birth from customer";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
/*
+----------+--------+------+--------+------------+------------+
| custName | gender | age | weight | phone | birth |
+----------+--------+------+--------+------------+------------+
| 张七 | 女 | 20 | 58.8 | 1343434343 | 1980-03-08 |
| 张九 | 男 | 40 | 78.2 | 1349932423 | 1977-08-08 |
| 张三 | 女 | 30 | 70 | 1332324234 | 1979-08-08 |
+----------+--------+------+--------+------------+------------+
*/
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); // 获取虚表的表结构对象
int cols = metaData.getColumnCount(); // 获取虚表共有多少列
//System.out.println(cols);
String colName = metaData.getColumnName(3);// 获取基表的列名, 参数中的是第几列
//System.out.println(colName);
colName = metaData.getColumnName(6);// 获取基表列名, 参数中的是第几列
//System.out.println(colName);
String colLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(6); // 获取虚表列名, 参数是第6列
//System.out.println(colLabel);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++) {
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 列的索引总是从1开始
System.out.print(columnLabel + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
while (resultSet.next()) {
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++) {
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 先获取列的别名
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnLabel); // 根据列的别名再获取对应的值
System.out.print(value + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
}
以上就是Jdbc--具体代码实现的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(m.sbmmt.com)!
 Perkara yang perlu dilakukan jika anda tidak dapat memadamkan fail pada komputer anda
Perkara yang perlu dilakukan jika anda tidak dapat memadamkan fail pada komputer anda
 vcruntime140.dll tidak dapat ditemui dan pelaksanaan kod tidak dapat diteruskan
vcruntime140.dll tidak dapat ditemui dan pelaksanaan kod tidak dapat diteruskan
 Cara menggunakan storan awan
Cara menggunakan storan awan
 Bagaimana untuk mengunci skrin pada oppo11
Bagaimana untuk mengunci skrin pada oppo11
 Kabel rangkaian dicabut
Kabel rangkaian dicabut
 Tutorial melaraskan jarak baris dalam dokumen perkataan
Tutorial melaraskan jarak baris dalam dokumen perkataan
 penggunaan fungsi sampel semula
penggunaan fungsi sampel semula
 Platform dagangan kuantitatif mata wang digital
Platform dagangan kuantitatif mata wang digital




