
Pengaturcara menggunakan fail teks dalam Java semasa bekerja dengan aplikasi Java yang memerlukan membaca dan menulis pada fail. Fail teks ialah cara universal untuk menyimpan maklumat, kod atau sebarang data lain. Fail teks dianggap sebagai urutan aksara yang disusun secara mendatar. Fail teks dalam Java mempunyai sambungan seperti .java yang mengandungi kod Java. Java menyediakan utiliti yang berbeza yang membolehkan anda berurusan dengan fail teks biasa dengan sama ada membaca daripadanya atau menulis kepadanya. Anda boleh memilih mana-mana utiliti baca/tulis mengikut pemahaman anda.

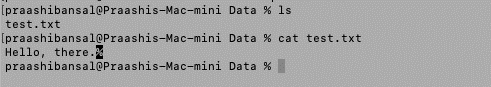
Sebelum bermula dengan kaedah, kami sedang mempertimbangkan fail teks "test.txt" di laluan "/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt" dengan kandungan "Hello, there".
IKLAN Kursus Popular dalam kategori ini JAVA MASTERY - Pengkhususan | 78 Siri Kursus | 15 Ujian Olok-olok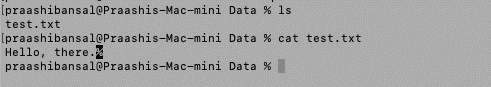
Kod:
import java.io.*;
public class BReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
File f = new File(
"https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
// Creating an object
BufferedReader b
= new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
// Declaring a string variable
String s;
// Condition holds till
// there is a character in a string
while ((s = b.readLine()) != null)
// Print the string
System.out.println(s);
}
}Output:
Kod:
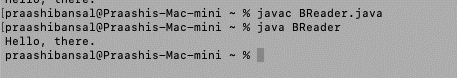
import java.io.*;
public class RFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Passing the file’s path
FileReader f = new FileReader(
"https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
// declaring loop variable
int i;
while ((i = f.read()) != -1)
// Print the content of a file
System.out.print((char)i);
}
}Output:
Kod:
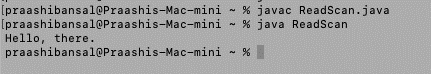
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadScan
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// passing the file’s path
File file = new File("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
Scanner s = new Scanner(file);
while (s.hasNextLine())
System.out.println(s.nextLine());
}
}Output:
Kod:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
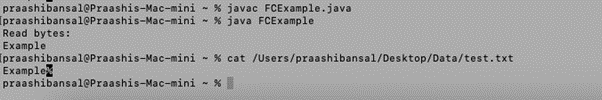
public class FCExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path path = Paths.get("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
try {
byte[] b = Files.readAllBytes(path);
System.out.println("Read bytes: \n"+new String(b));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}Output:
Code:
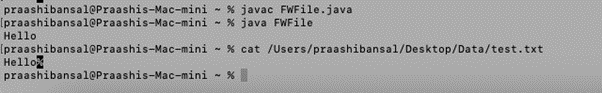
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class FWFile {
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
FileWriter f=new FileWriter("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
f.write("Hello");
f.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}Output:
Code:
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BRExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String data = "data for output file";
try {
// Creates a FileWriter
FileWriter file = new FileWriter("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
try ( // Creates a BufferedWriter
var o = new BufferedWriter(file)) {
// Writes the string to the file
o.write(data);
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}Output:

Code:
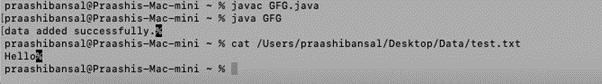
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String f = "Hello";
FileOutputStream o = null;
// starting Try block
try {
// creating an object of FileOutputStream
o = new FileOutputStream("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
// storing byte content from string
byte[] str = f.getBytes();
// writing into the file
o.write(str);
// printing success message
System.out.print(
"data added successfully.");
}
// Catch block for exception handling
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
finally {
// closing the object
if (o != null) {
// checking if the file is closed
try {
o.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
// showing exception message
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
}Output:
Code:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
/**
* Java Files write file example
*
* @author pankaj
*
*/
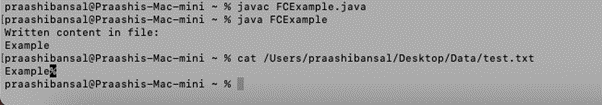
public class FCExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path path = Paths.get("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
try {
String str = "Example";
byte[] bs = str.getBytes();
Path w = Files.write(path, bs);
System.out.println("Written content in file:\n"+ new String(Files.readAllBytes(w)));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}Output:
Reading and writing a file in Java is a straightforward process. With the availability of different methods and utilities in Java, you can choose a specific way to read from and write to a file. Each utility has its functionality that makes it different from others.
Answer: To read, you can use Reader Class or utility class. Some utility classes are- File Class, FileReader, BufferedReader, and Scanner class.
Answer: To write a file in Java, you can use FileWriter, BufferedWriter, java 7 Files, FileOutputStream, and many other methods.
Answer: You can easily import the File class from the java.io package to work with files.
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Fail Teks dalam Java. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!




