Home > Article > Backend Development > How to use Python's Try and Except
try blocks allow you to test blocks of code to find errors.
except block allows you to handle errors.
finally blocks allow you to execute code regardless of the results of try and except blocks.
When we call Python and an error or exception occurs, it usually stops and generates an error message.
These exceptions can be handled using a try statement:
Example
The try block will generate an exception because x is undefined:
try:
print(x)
except:
print("An exception occurred")Run Example
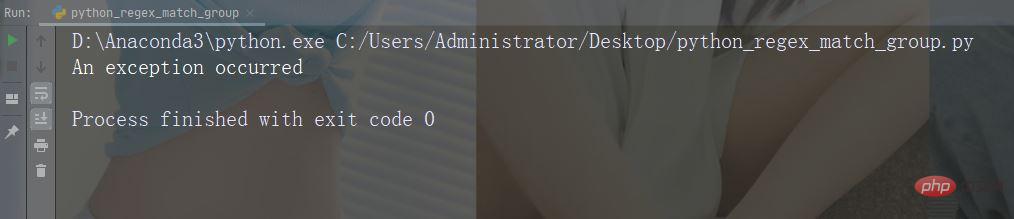
#Since the try block throws an error, the except block will be executed.
Without the try block, the program will crash and throw an error:
Example
This statement will throw an error because x is not defined:
print(x)
You can define as many exception blocks as you need, for example, if you want to execute a special code block for a special type of error:
Example
Print a message if the try block raises NameError, and another message if it is another error:
try:
print(x)
except NameError:
print("Variable x is not defined")
except:
print("Something else went wrong")Run the instance
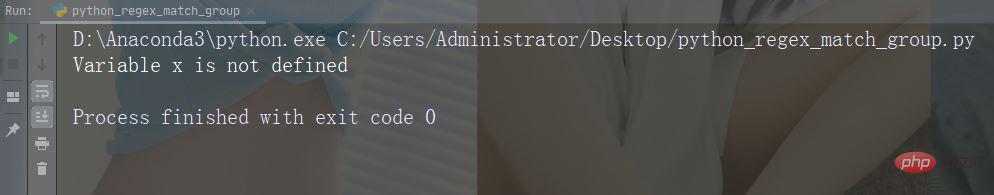
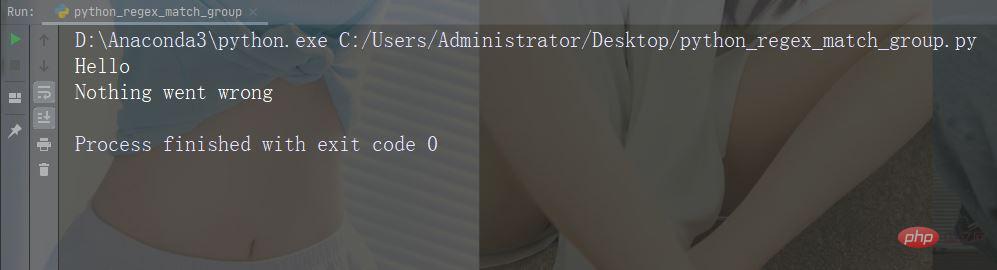
If no error is raised, then you can use the else keyword to define a block of code to be executed:
Example
In this case, the try block will not generate any errors:
try:
print("Hello")
except:
print("Something went wrong")
else:
print("Nothing went wrong")Run the instance
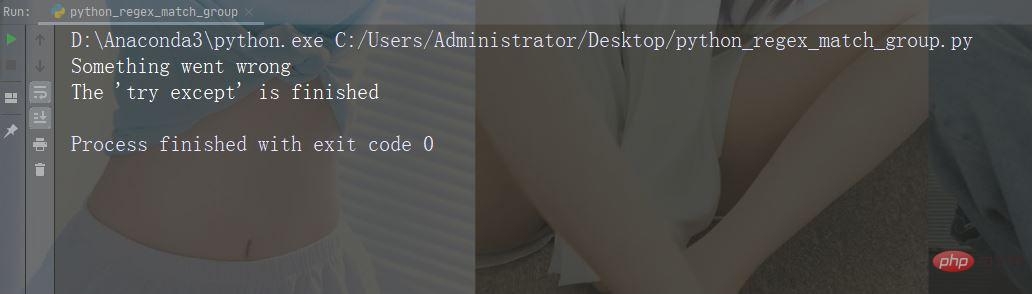
If the finally block is specified, Then the finally block will be executed regardless of whether the try block raises an error.
Instance
try:
print(x)
except:
print("Something went wrong")
finally:
print("The 'try except' is finished")Running Instance
Example
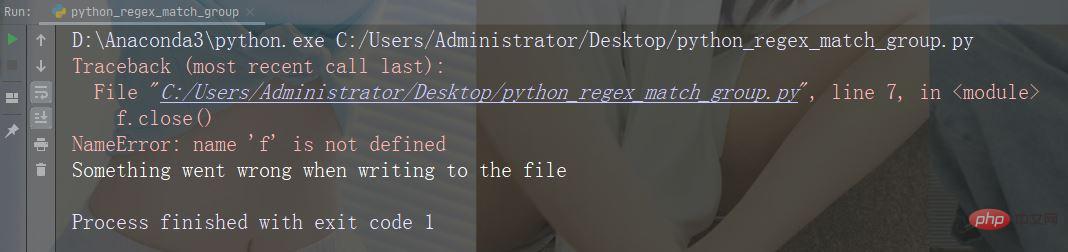
Attempt to open and write to a non-writable file:try:
f = open("demofile.txt")
f.write("Lorum Ipsum")
except:
print("Something went wrong when writing to the file")
finally:
f.close()Run Example
Example
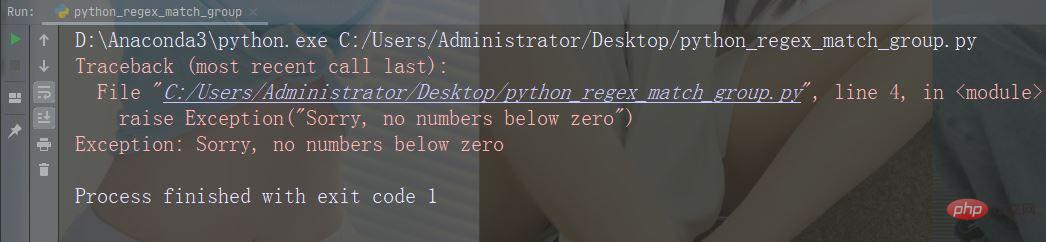
If x is less than 0, an exception is thrown and the program is terminated:x = -1
if x < 0:
raise Exception("Sorry, no numbers below zero")Running example
Example
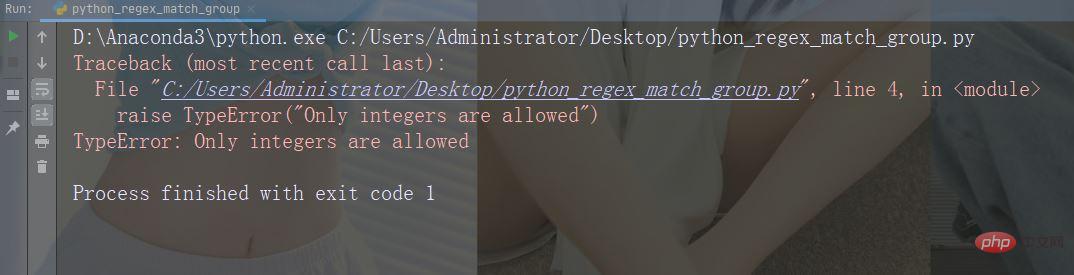
If x is not an integer, TypeError is raised:x = "hello"
if not type(x) is int:
raise TypeError("Only integers are allowed")Running Example
The above is the detailed content of How to use Python's Try and Except. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!