Home > Article > Backend Development > Python code example to implement port scanner
This article mainly introduces the relevant code for implementing a simple port scanner in Python. It has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it.
Based on some information on the Internet, I have added some new content, which can be regarded as a practice in Python socket programming.
#coding=utf-8
import socket
import time
import sys
import struct
import threading
from threading import Thread,activeCount
results=[]
def portScanner(ip,port):
server = (ip,port)
sockfd = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sockfd.settimeout(0.1) #设置阻塞模式下socket的超时时间
ret = sockfd.connect_ex(server) #成功返回0,失败返回error的值。
if not ret:
sockfd.close()
results.append([ip,port])
#print '%s:%s is opened...' % (ip,port)
else:
sockfd.close()
pass
return ''
def ip2num(ip): #将ip地址转换成数字
lp = [int(x) for x in ip.split('.')]
return lp[0] << 24 | lp[1] << 16 | lp[2] << 8 |lp[3]
def num2ip(num):
ip = ['','','','']
ip[3] = (num & 0xff)
ip[2] = (num & 0xff00) >> 8
ip[1] = (num & 0xff0000) >> 16
ip[0] = (num & 0xff000000) >> 24
return '%s.%s.%s.%s' % (ip[0],ip[1],ip[2],ip[3])
def iprange(ip1,ip2):
num1 =socket.ntohl(struct.unpack("I",socket.inet_aton(str(ip1)))[0])
num2 =socket.ntohl(struct.unpack("I",socket.inet_aton(str(ip2)))[0])
tmp = num2 - num1
if tmp < 0:
return None
else:
return num1,num2,tmp
if name == 'main':
if((len(sys.argv)!= 4)&(len(sys.argv)!= 2)): #用法说明
print 'Usage:\n\tscanner.py startip endip port'
print '\tscanner.py ip'
sys.exit()
if len(sys.argv)==4: #对某一IP段的扫描
time_start=time.time() #起始时间
startip = sys.argv[1] #起始IP
endip = sys.argv[2] #结束IP
port = int(sys.argv[3]) #端口号
res = iprange(startip,endip)
if not res:
print 'endip must be bigger than startone'
sys.exit()
elif res[2] == 0:
portScanner(startip,port)
else:
for x in xrange(int(res[2])+1): #IP地址依次递增
startipnum = ip2num(startip)
startipnum = startipnum + x
if activeCount() <=1000:
Thread(target=portScanner,args=(num2ip(startipnum),port)).start()
print "There are %d hosts." %len(results)
results.sort()
for ip,port in results:
print "%s:%d is opened..." %(ip,port)
times=time.time()-time_start #用时
print 'use time : %s' % times
if len(sys.argv)==2:
time_start=time.time()
port=0
ip=sys.argv[1]
while(port<2000):
if activeCount() <= 40: #设置40线程扫描
Thread(target = portScanner, args = (ip, port)).start()
port=port+1
results.sort()
for ip,port in results:
print "%s:%d is opened..." %(ip,port)
times=time.time()-time_start
print 'use time : %s' % timesThe usage effect is as follows:
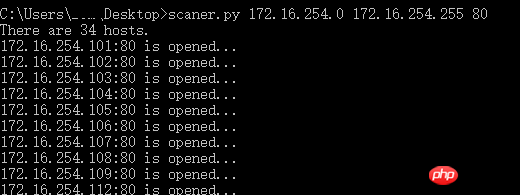
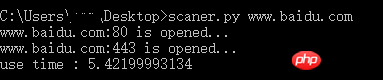
Python object-oriented video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Python code example to implement port scanner. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!