Home > Article > Operation and Maintenance > What is total in linux
Total in Linux refers to the total disk space usage of all files in the list, that is, the total resource usage. The statistical unit is kb; total is the first line of results displayed when using the "ls -l" command. , where the size of the directory obtained is not the total size of the files contained in the directory, but only the size of the directory itself.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
When we use the ls -l command, we will see information similar to the following
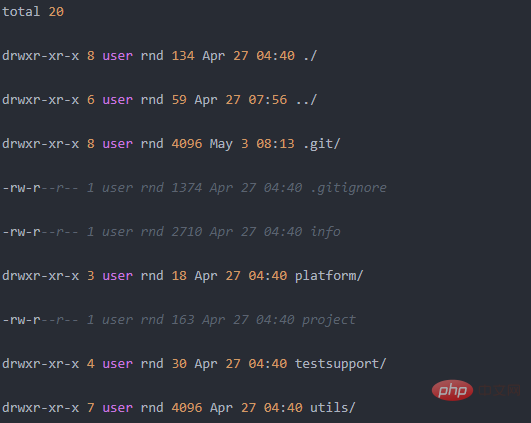
Total means: the total disk space occupied by all files in the list, that is, the total resource occupied, and its statistical unit is kb.
We know that the value in column 5 listed by ls -l is the size of the file or directory. The size of the directory here is not the total size of the files contained in the directory. It's just the size of the directory itself.
If you can't understand this concept, please think about the meaning of the sentence "Everything in Linux is a file".
So, that is to say, the total 12k in the picture should be equal to the value of 767 4096 4096. Let’s do the math and see if that’s the case.
767 4096 4096=8959 Then the unit here is of course bytes, so if we convert it to k, the value is 8959/1024=8.74902k
So obviously 12 ≠8.74902
But why is total "the total disk space occupied by the listed content."? Please pay attention to the word "occupied". What is occupied?
We know that there is a concept of block in the file system. Blocks are like rooms. If your file system stores some larger files, then use larger ones. block will get better performance, and vice versa.
Then the size of the block occupied by the data during storage is the "occupied" space.
Recommended learning: Linux video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of What is total in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!