 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Issues related to text avoidance in front-end algorithms (detailed tutorial)
Issues related to text avoidance in front-end algorithms (detailed tutorial)Issues related to text avoidance in front-end algorithms (detailed tutorial)
This article mainly introduces you to the relevant information about text avoidance in the front-end algorithm. I believe many friends do not know this knowledge, but they will be amazed when they see the effect. The main use of inMap text to achieve this effect is The avoidance function is introduced in detail through sample code in this article. Friends who need it can refer to it. Let’s learn it together.
Preface
inMap is a big data visualization library based on canvas, focusing on the visual display of big data direction points, lines and surfaces. Currently supports scatter, fence, thermal, grid, aggregation and other methods; committed to making big data visualization simple and easy to use.
GitHub address: https://github.com/TalkingData/inmap (local download)
Document address: http://inmap.talkingdata.com/
at In geographic information visualization, we often encounter the need to mark text on the map. The following shows the effect of a popular chart chart frame:

The text space to be displayed When it is not enough, it will cause overlapping text and confusing display, making the user experience very unfriendly.
How to solve this problem? We use text avoidance algorithm to solve this cheating problem.
The following shows the inMap text avoidance effect:
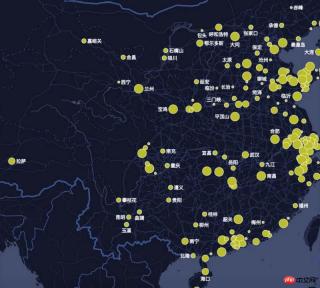
Text labeling algorithm is one of the most complex problems in GIS (belongs to NP complexity problem, so the optimal solution cannot usually be found, only the better solution).
inMap The avoidance algorithm uses the quartile model algorithm. Next, I will teach you step by step how to write the avoidance algorithm. An experienced driver will help you show off and help you fly.
Prepare data
inMap receives latitude and longitude data and needs to map it to the pixel coordinates of the canvas, which uses Mercator Conversion, Mercator's algorithm is very complicated. We will have a separate article to explain its principles in the future. After conversion, the data you get should look like this:
[
{
"name": "海门",//要显示的文字
"lng": 121.15,
"lat": 31.89,
"count": 7,
"pixel": { //像素坐标
"x": 968,
"y": 736
}
},
{
"name": "鄂尔多斯",
"lng": 109.781327,
"lat": 39.608266,
"count": 5,
"pixel": {
"x": 659,
"y": 478
}
},
...
]Okay, now that we have the converted pixel coordinate data (x, y), we can do the following.
Find the actual size of each text rectangle
measureText() is a built-in method of canvas, which returns the pixel unit of the font width:
let ctx = this.container.getContext('2d'); // canvas 上下文 let width= ctx.measureText(name).width;
We get the width of each text through measureText. Canvas does not have a direct method to obtain the text. So how do we get the height of the text?
We found through repeated testing that when the font of canvas is equal to the "13px Arial" font (other fonts cannot be guaranteed), the height of the text is about 1.1 times the fontSize.
So the code is as follows:
let fontSize = parseInt(ctx.font); let height = fontSize * 1.1;
After the width and height of the text are obtained, we can create the coordinate system of the text rectangle.
Create a quartile model

The so-called quartile model, each marker point has There are four places for text on the top, bottom, left and right. If you can't put it on the left side, try putting it on the right side. If it still doesn't work, try putting it on the bottom. And so on. The principle is that simple, haha.
Create a description of the coordinates of the virtual rectangle on the right:

The description of the coordinates of the virtual rectangle on the right also includes dots to prevent text and Dots overlap.
There are some pitfalls when calculating the height of the virtual rectangle. The size of the dots is not fixed, but is dynamically configured according to the user. The diameter of the dots may be greater than the height of the text, so we set the height of the virtual rectangle to always be It's the largest one and requires some special handling.
The code is as follows:
_getLeftAnchor() {
let x = this.center.x - this.radius - this.textReact.width,
y = this.center.y - this.textReact.height / 2,
diam = this.radius * 2,
maxH = diam > this.textReact.height ? diam : this.textReact.height; //矩形的高度
return {
x,
y,
minX: x,
maxX: this.center.x + this.radius,
minY: this.center.y - maxH / 2,
maxY: this.center.y + maxH / 2
};
}And so on, describing the coordinates of the virtual rectangle below, left, and above.
Determine collision
Determine whether two rectangles cover and intersect. The intersection is determined based on the minX, maxX, minY, maxY of the rectangle. The principle is relatively simple. , the code is as follows:
/**
* 判断分位是否相交
* @param {*} target
*/
isAnchorMeet(target) {
let react = this.getCurrentRect(),
targetReact = target.getCurrentRect();
if ((react.minX < targetReact.maxX) && (targetReact.minX < react.maxX) &&
(react.minY < targetReact.maxY) && (targetReact.minY < react.maxY)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}Create a virtual text collection object
let labels = pixels.map((val) => {
let radius = val.pixel.radius + this.style.normal.borderWidth; //圆点半径
return new Label(val.pixel.x, val.pixel.y, radius, fontSize, byteWidth, val.name);
});Recursively traverse the virtual text collection and determine whether it intersects with others. If there is an intersection Just move the current text position until they no longer intersect. When you can't find a suitable location, choose to hide the current text.
The code is as follows:
do {
var meet = false; //本轮是否有相交
for (let i = 0; i < labels.length; i++) {
let temp = labels[i];
for (let j = 0; j < labels.length; j++) {
if (i != j && temp.show && temp.isAnchorMeet(labels[j])) {
temp.next();
meet = true;
break;
}
}
}
} while (meet);Painting text
labels.forEach(function (item) {
if (item.show) { //是否显示
let pixel = item.getCurrentRect();
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.fillText(item.text, pixel.x, pixel.y);
ctx.fill();
}
});The text avoidance algorithm has been introduced so far, the corresponding inMap file address It is https://github.com/TalkingData/inmap/blob/master/src/worker/helper/Label.js. I will continue to share useful information with you in the future.
The above is what I compiled for everyone. I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future.
related articles:
How to fix the header and first column in Vue
How express multer implements the image upload function
Native JS How to implement a music player
How to set user permissions in VueJS
How to use YDUI’s ScrollTab component in WeChat applet
The above is the detailed content of Issues related to text avoidance in front-end algorithms (detailed tutorial). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and ProjectsApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and ProjectsApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AMJavaScript's application in the real world includes front-end and back-end development. 1) Display front-end applications by building a TODO list application, involving DOM operations and event processing. 2) Build RESTfulAPI through Node.js and Express to demonstrate back-end applications.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMThe main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnderstanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools





