Home > Article > Web Front-end > How to solve the cross-domain problem of Angular client requesting Rest service
This article mainly introduces to you the solution to the cross-domain problem of Angular client requesting Rest service. It has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it. I hope it can help everyone.
1. Problem description: The origin is http://localhost:4200 and the service of http://localhost:8081 is requested. The console reports the following error, but the response is 200. The client and server IPs are the same, but the ports are different, so there is a cross-domain problem.
Copy code The code is as follows:
XMLHttpRequest cannot load No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource. Origin ' http://localhost:4200' is therefore not allowed access.
2. Solution: Add @CrossOrigin annotation to the Restful method of server/api/v1/staffs, for example:
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*", maxAge = 3600)
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/v1/staffs", produces = { "application/json" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
RestResponseList queryStaffs(@RequestParam(value = "limit", required = false, defaultValue = "20") int limit,
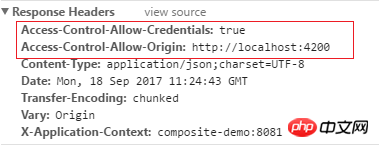
@RequestParam(value = "offset", required = false, defaultValue = "0") int offset);3. Resend the request to http://localhost:8081/api/v1/..., the request is successful. And the response header adds Access-Control-Allow-Credentials and Access-Control-Allow-Origin parameters. The @CrossOrigin annotation adds these two parameters to the response header to solve cross-domain problems.
#4. Also use the annotation @CrossOrigin in the server-side POST method to solve cross-domain problems.
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*", maxAge = 3600)
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/v1/staffs", produces = { "application/json" }, method = RequestMethod.POST)
RestResponse createStaff(@RequestBody RestRequest request); The error is reported as follows:
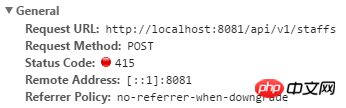
5. Check the response code 415, the error reason:
"status": 415,
"error": "Unsupported Media Type",
"exception": "org.springframework.web.HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException",
"message": "Content type 'text/plain ;charset=UTF-8' not supported"
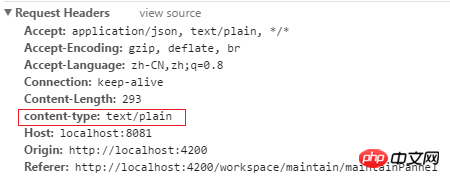
6. Further check the request header information, the content-type is text/plain. It does not match the Content-Type:application/json;charset=UTF-8 type of Response Headers, so an error is reported.
#7. Specify the request header content-type as application/json, such as adding Headers in Angular. Send a Post request and the request is successful.
let headers = new Headers({ 'Content-Type': 'application/json' });
let options = new RequestOptions({ headers });
return this.http.post(this.staffCreateURL, body, options).map((response: Response) => {
//return this.http.get(this.userLoginURL).map((response:Response)=> {
let responseInfo = response.json();
console.log("====请求staffCreateURL成功并返回数据start===");
console.log(responseInfo);
console.log("====请求staffCreateURL成功并返回数据end===");
let staffName = responseInfo.responseInfo.staffName;
console.log(staffName);
return responseInfo;
})Another: You can also add response header parameters to the HttpServletResponse object through the setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*") method to solve cross-domain problems. , which is the @CrossOrigin annotation method. It is recommended to use annotations for convenience.
Related recommendations:
Understand JavaScript, Rest parameters in functions
The above is the detailed content of How to solve the cross-domain problem of Angular client requesting Rest service. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!