Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Laravel framework performance tuning methods
This is a summary afterwards. After going through many pitfalls in the tuning process, we finally perfected and implemented a preliminary performance testing plan, and summarized some practical skills in the Laravel development process through real test data.
Recently, a colleague reported that the response of the application written in Laravel is a bit slow, and more than 20 concurrency runs the CPU full... In order to solve the slow problem, even some interfaces use nodejs Come and write.
And my first reaction was how could a popular framework be so bad? There must be something wrong with the use. In order to find out, I started this Laravel application performance tuning journey.
The optimization techniques used in this performance test plan are mainly based on the Laravel framework itself and the tools it provides.
Turn off application debug app.debug=false
Cache configuration informationphp artisan config:cache
Cache routing informationphp artisan router:cache
php artisan optimize
composer dumpautoload
APP_DEBUG=false2. Cache configuration information
php artisan config:cache
bootstrap/cache/config.php file. Reduce the number of files loaded at runtime.
php artisan config:clearRun the above command to clear the cache of configuration information, that is, delete the
bootstrap/cache/config.php file
php artisan route:cache
bootstrap/cache/routes.php. Route caching can effectively improve the router's registration efficiency, and the effect is more obvious in large applications.
php artisan route:clearRunning the above command will clear the routing cache, which means deleting the
bootstrap/cache/routes.php file.
php artisan optimize --force
bootstrap/cache/compiled.php and bootstrap/cache/services.json.
config/compile.php file.
--force The parameter file can also be automatically generated.
php artisan clear-compiledRunning the above command will clear the class mapping loading optimization, that is, delete the two files
bootstrap/cache/compiled.php and bootstrap/cache/services.json .
composer dumpautoload -o
Note: This operation has already been done in the6. Load only necessary middleware as neededThe Laravel application has a lot of middleware built in and enabled. Every Laravel request loads related middleware and generates various data. Commenting out unnecessary middleware (such as session support) inphp artisan optimize --force
command.
app/Http/Kernel.php can greatly improve performance.
Well, limited to your real enterprise environment, this may not change for a long time, so I didn’t mention it.0x02 Test PlanWe use a simple Apache ab command to test only the application entry file, and record and analyze the data.
ab -t 10 -c 10 {url}. This command means to initiate 10 requests to the url at the same time and last for 10 seconds. The specific parameter settings in the command need to be selected based on the server performance to be tested.
Every time the test conditions are adjusted, you need to access the welcome page on the browser to ensure that there are no access errors due to the modification of the test conditions. If page access errors occur, the test results will be incorrect.
Server environment description
All test data divorced from the specific environment is meaningless, and comparisons can only be made under similar conditions.
This environment runs on a Mac with 8G memory, 2.8GHz processor, and SSD hard drive.
The test server is built using Homestead. The virtual machine is configured with a single-core CPU and 2G memory.
The server PHP version is 7.1. If not specified, OPcache is turned on.
The Laravel application tested was written in version 5.2. There are 85 routes defined in app\Http\routes.php.
During the test process, except for the virtual machine, terminal and fixed browser window, there are no programs that will affect the operation of the machine.
The above data can be referred to when you conduct your own testing.
Perform the corresponding check items according to the following operate.
Runab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php
Basic check items
APP_DEBUG=true
does not exist in the .env file bootstrap/cache/config.php
does not existbootstrap/cache/routes.php
No There are bootstrap/cache/compiled.php and bootstrap/cache/services.json
##app/Http/Kernel.php Most of the middleware is enabled in
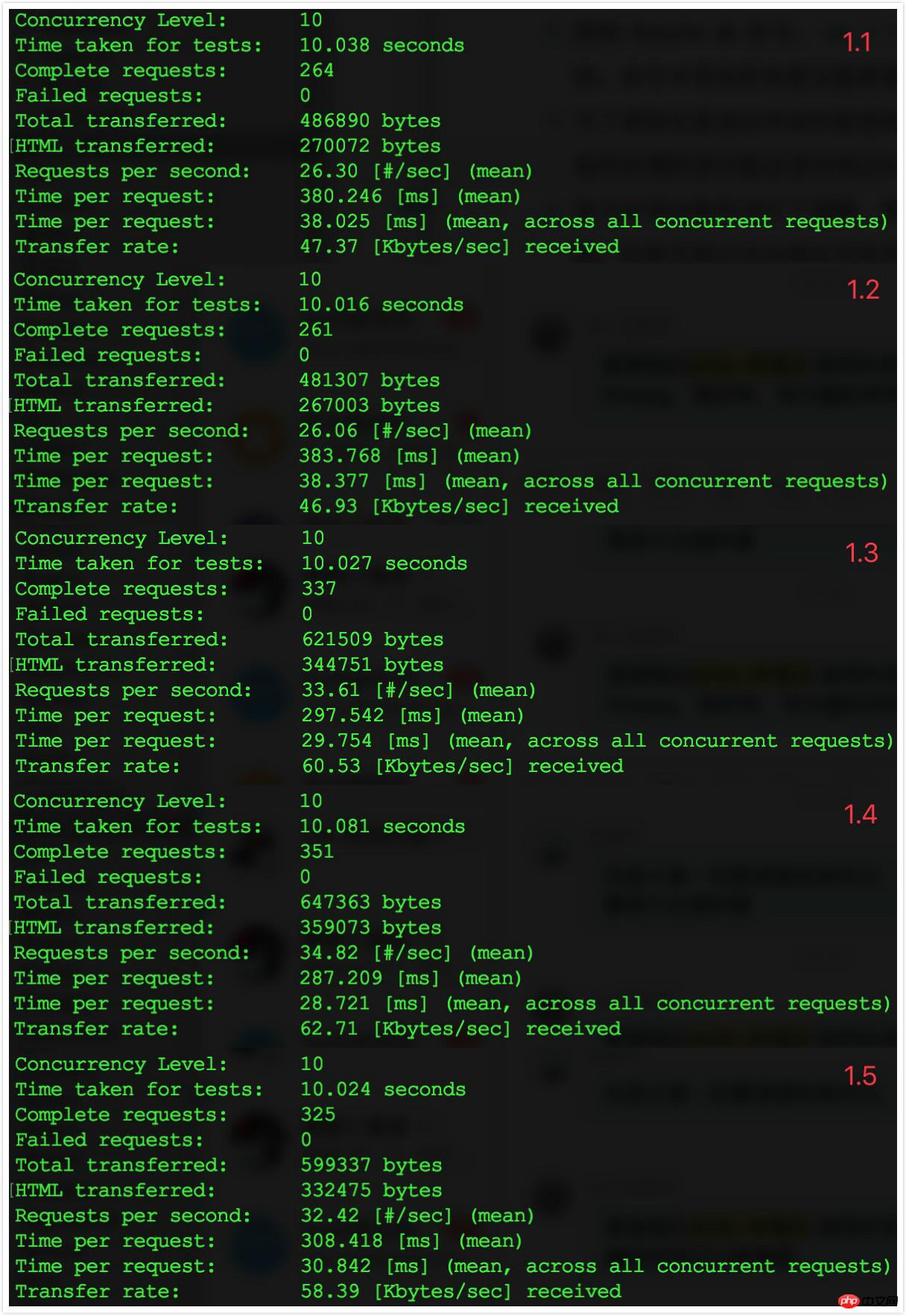
APP_DEBUG=false in the .env file.
ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php.
 ##2.3 Comparison results
##2.3 Comparison results
Note: This part is closely related to the usage of logs in the application.
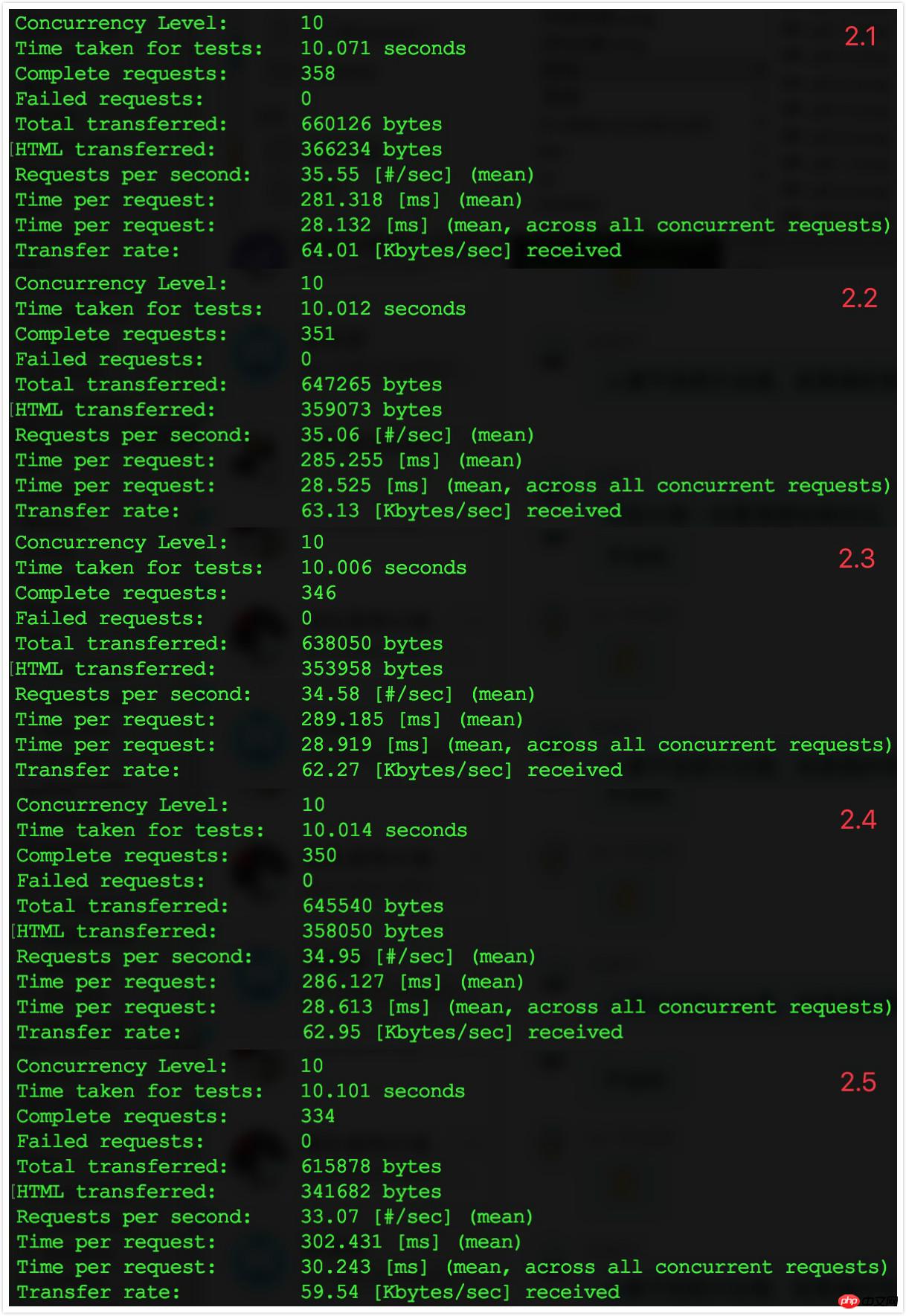
3. Enable cache configuration information
, confirm the generation of bootstrap/cache/config.php.
.
 ##3.3 Comparison results
##3.3 Comparison results
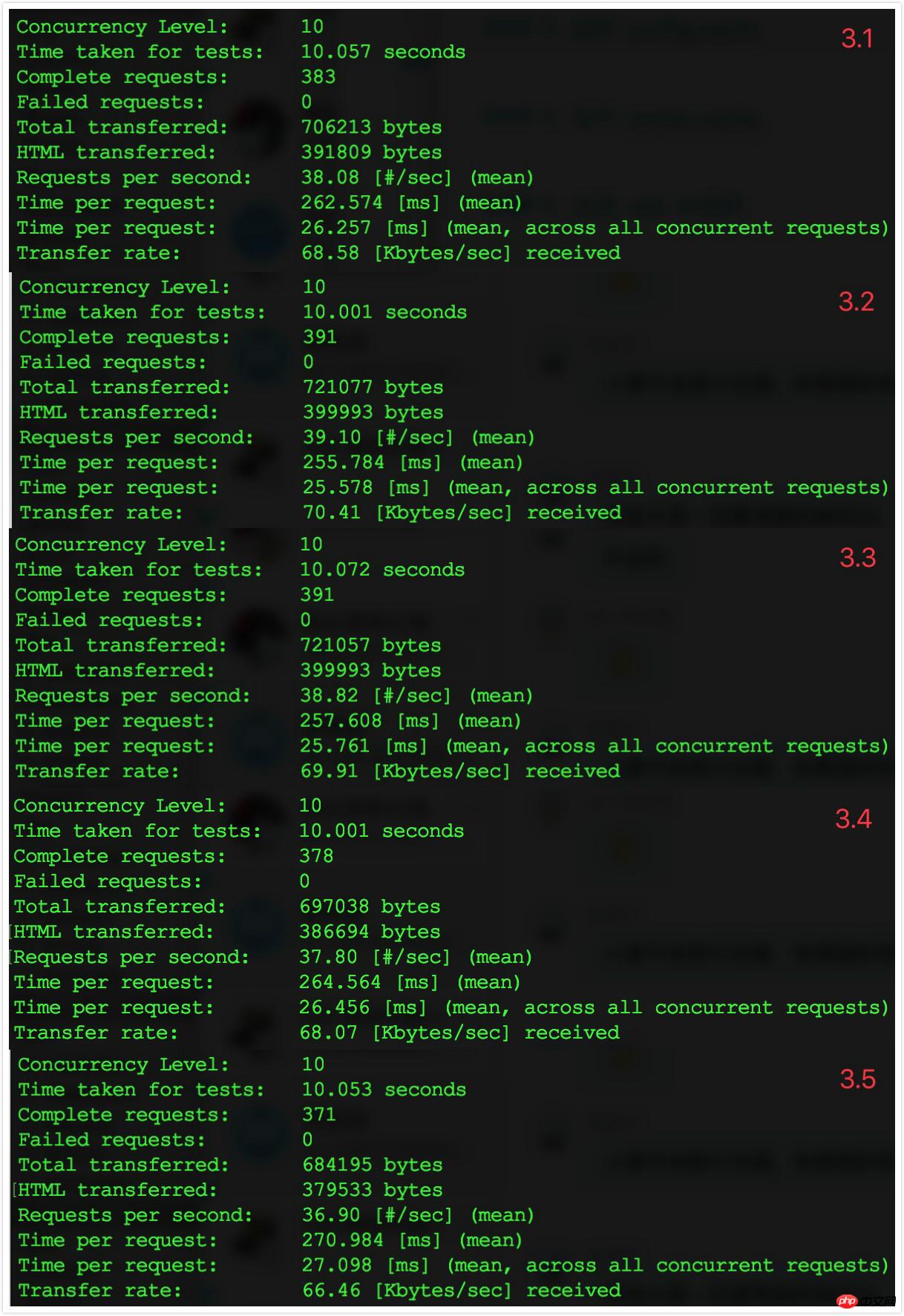
4. Enable cache routing information
4.1 Operation. Visit the Laravel application welcome page with your browser to ensure normal access.
Run
ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php4.2 Data record
##4.3 Comparison results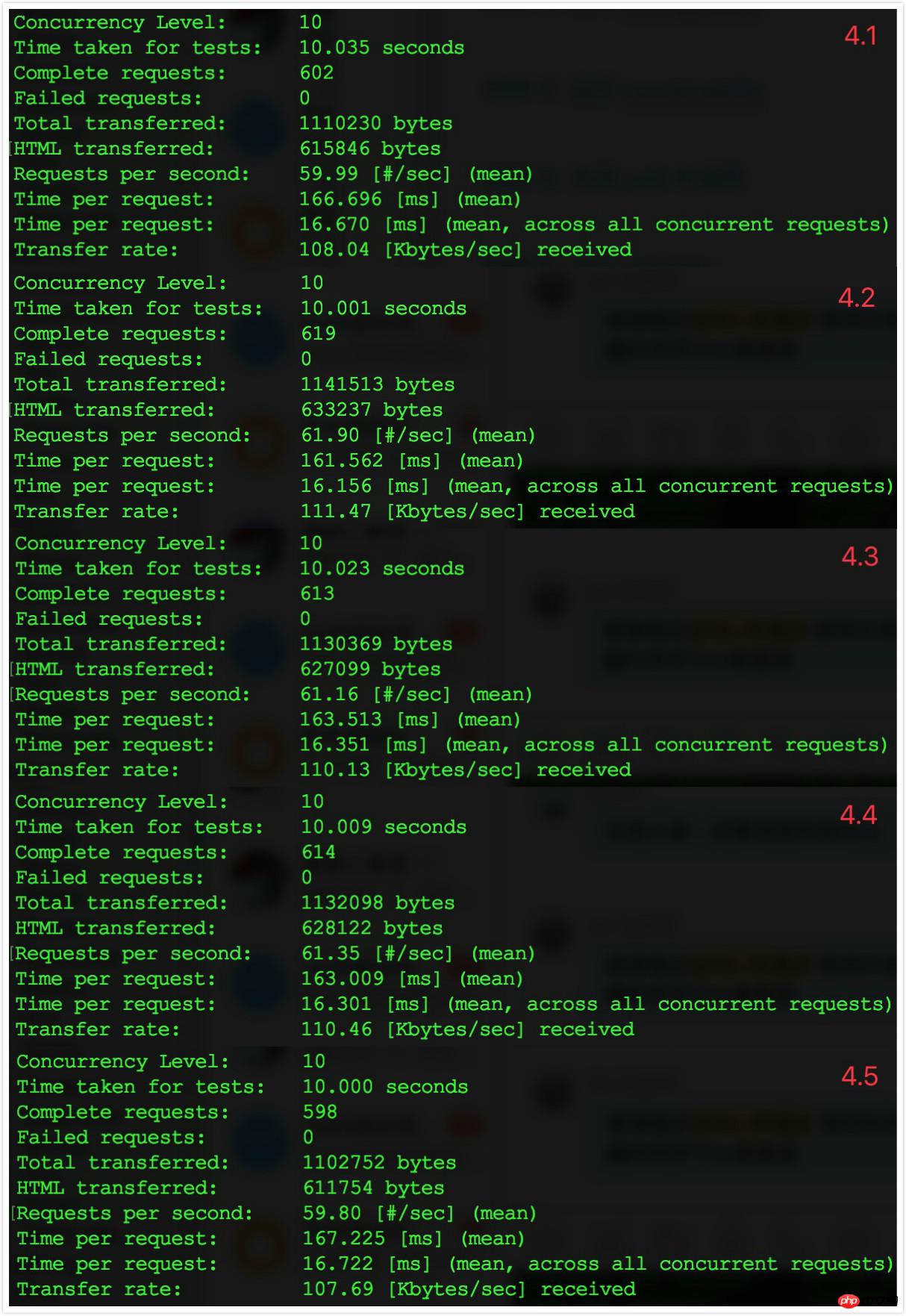 Compare with the results of step 3 Discovery: After turning on the routing information cache, the number of requests processed per second increased from 36-38 to about 60, and the request response time dropped from 260ms to about 160ms. The effect was significant. From the perspective of TPS, it increased by 70%.
Compare with the results of step 3 Discovery: After turning on the routing information cache, the number of requests processed per second increased from 36-38 to about 60, and the request response time dropped from 260ms to about 160ms. The effect was significant. From the perspective of TPS, it increased by 70%.
5.1 Operation
Based on step 4, comment out unnecessary middleware code.ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php
.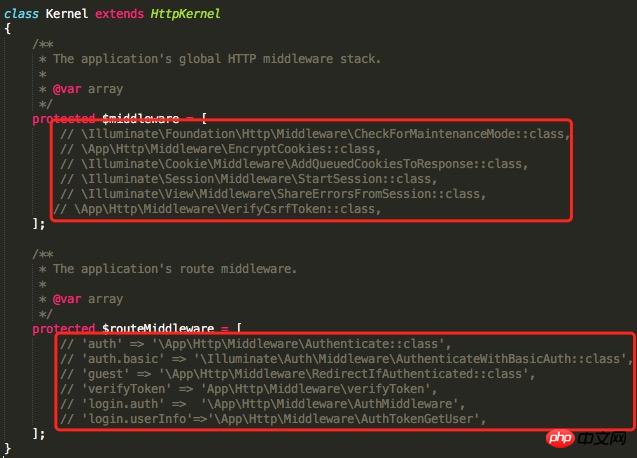
Note: I commented out all the middleware in this test. In actual situations, you should try to keep only necessary middleware.
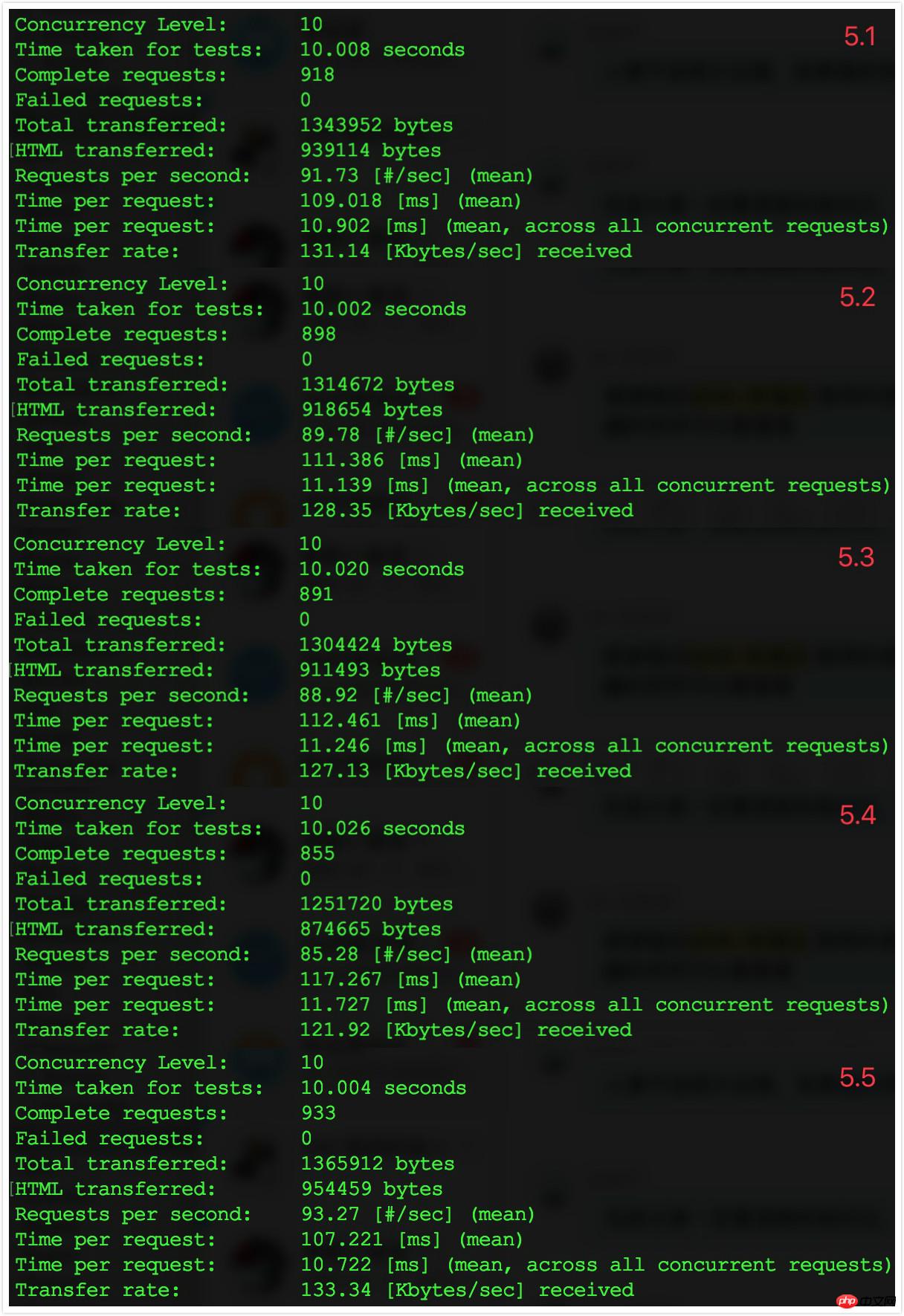
The effect is very obvious. From the perspective of TPS, it has increased by 50%.
6. Turn on class map loading optimization6.1 Operationphp artisan optimize - -force, confirm the generation of bootstrap/cache/compiled.php and bootstrap/cache/services.json.
ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php.
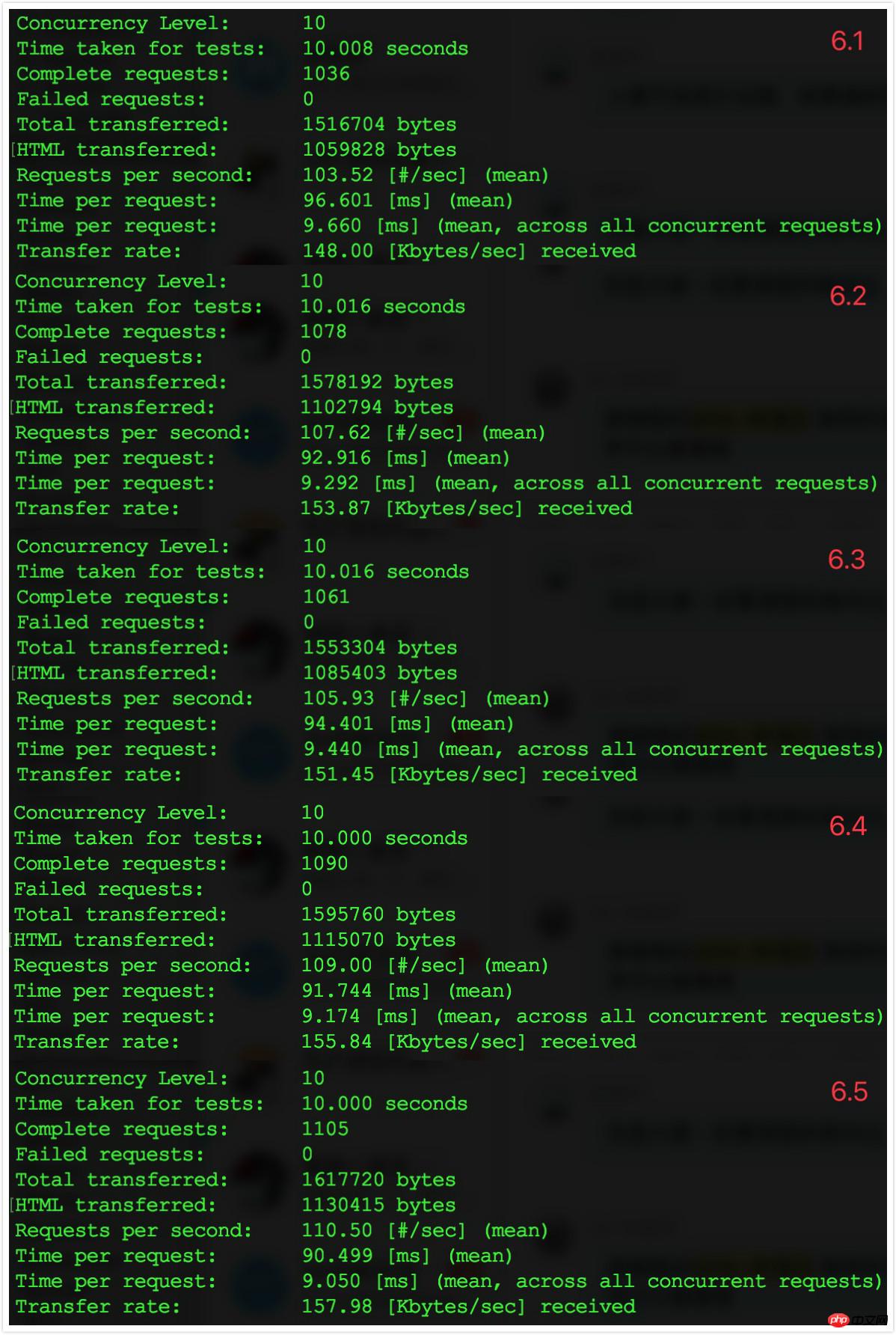 ##6.3 Comparison results
##6.3 Comparison results
7. Close OPcache
.
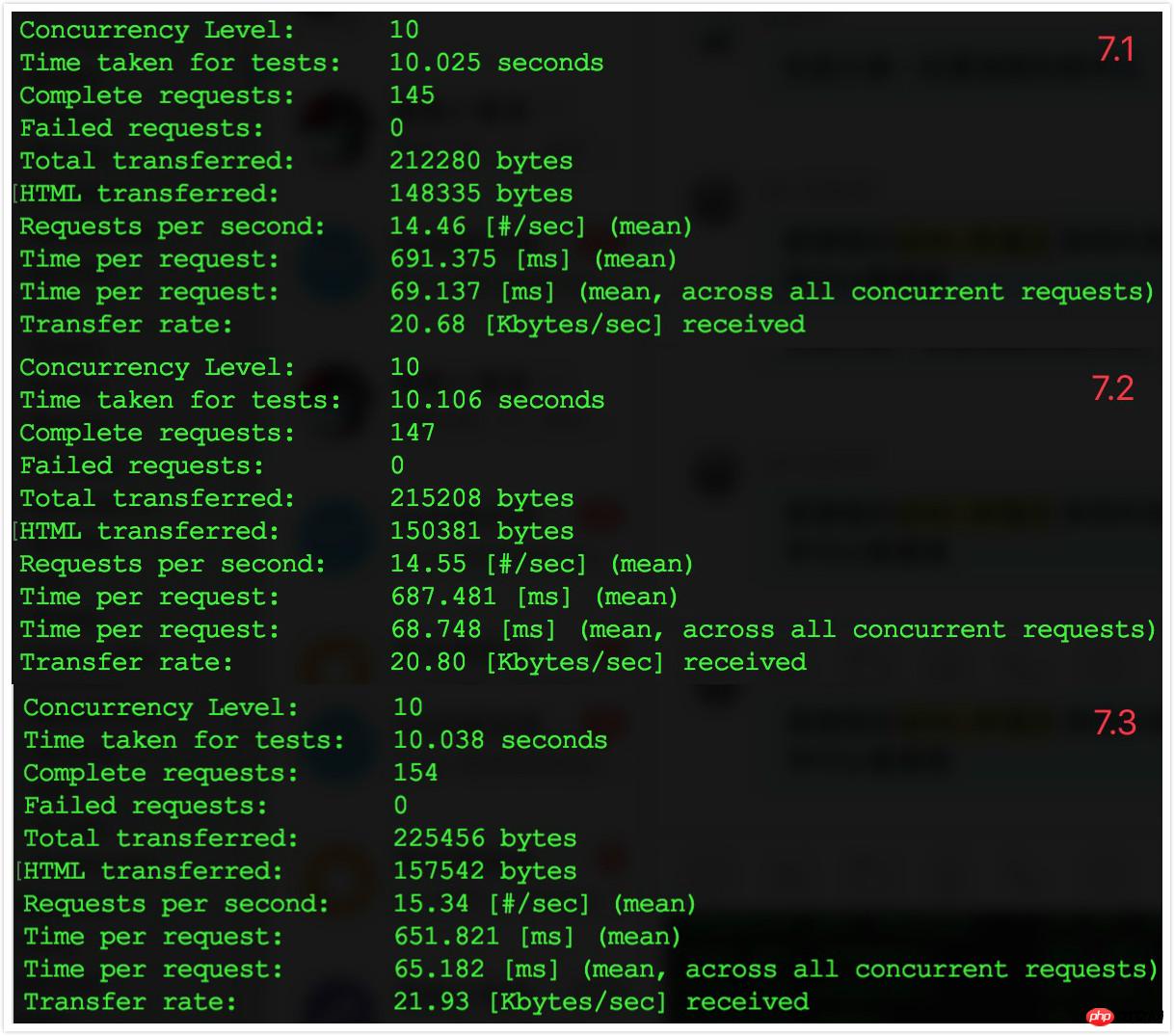 ##7.3 Comparison results
##7.3 Comparison results
After that, I reopened PHP’s OPcache and the data was restored to the level of step 6.
1. [LogicException] Unable to prepare route [/] for serialization. Uses Closure.Running0x04 Pitfalls
Cause: Closure is used when processing "/" in the routing file. To run this command, the routing implementation must not use closures.
Cause: Duplicate routes are defined in the routing file.
resource
method which is likely to result in duplication of its methods.3. [RuntimeException] Invalid filename provided.
Cause: The corresponding file was not found when loading the class that needs to be compiled. The file path to be compiled is defined in the 5.2 version of vendor/laravel/framework/src/Illuminate/Foundation/Console/Optimize/config.php
/vendor/laravel/framework /src/Illuminate/Database/Eloquent/ActiveRecords.php was not found, so this error was reported. Modification plan: Temporarily comment out the ../ActiveRecords.php
4. InvalidArgumentException in FileViewFinder.php line 137: View [welcome] not found.
Reason: The Laravel application server is built on a virtual machine using Homestead. I ran this command outside the virtual machine, which caused the path in the generated config.php to be the local path, not the path on the virtual machine. So the view file cannot be found.
Class map loading optimizationphp artisan optimize(including automatic loading optimizationcomposer dumpautoload)
As needed Only load necessary middleware
Use a just-in-time compiler (JIT), such as: HHVM, OPcache
The specific implementation of routing is placed in the controller.
Do not define duplicate routes, pay special attention to the resouce method.
Clear the role of each middleware and delete unnecessary middleware references.
The above tuning skills and coding considerations are mainly for the framework itself. There are many specific optimization skills in real business logic coding. This is not discussed.
Following optimization will focus on specific coding practices:
Use Memcached to store session config/session.php
Use a professional cache driver
Database request optimization
Write caching logic for the data set
Front-end resource merge Elixir
![]()
The above is the detailed content of Laravel framework performance tuning methods. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!