We have introduced ASM in detail before. Friends who need it can click here: In-depth study of java bytecode framework ASM
JVM type signature comparison table
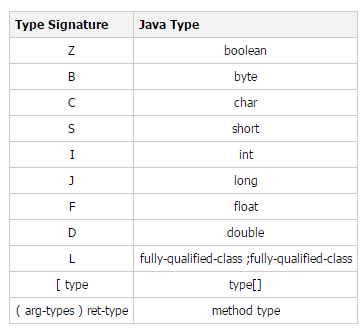
For example, the java method is
long f (int n, String s, int[] arr);
and the corresponding type signature is
f (ILjava/lang/String;[I)J
Another example, The java method is
private void hi(double a, Listb);
, and the corresponding type signature is
hi (DLjava/util/List;)V
. Next, you can use ASM to verify whether the above two type signatures are correct:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPrinter printer = new ClassPrinter();
//读取静态内部类Bazhang
ClassReader cr = new ClassReader("Test$Bazhang");
cr.accept(printer, 0);
}
//静态内部类
static class Bazhang {
public Bazhang(int a) {
}
private long f (int n, String s, int[] arr){
return 0;
}
private void hi(double a, List b){
}
}
static class ClassPrinter extends ClassVisitor {
public ClassPrinter() {
super(Opcodes.ASM5);
}
@Override
public void visit(int version, int access, String name, String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) {
super.visit(version, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces);
//打印出父类name和本类name
System.out.println(superName + " " + name);
}
@Override
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String desc, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
//打印出方法名和类型签名
System.out.println(name + " " + desc);
return super.visitMethod(access, name, desc, signature, exceptions);
}
}
}
The last printed content:
java/lang/Object Test$Bazhang()V f (ILjava/lang/String;[I)J hi (DLjava/util/List;)V
Verified the previous correctness, where you can see the default The constructor is also printed.
Then let’s do something interesting next. Let’s add a new method to the Bazhang class and set it as:
public void newFunc(String str){
}
At this time, you need to use ClassWriter , used to splice bytecode. For specific articles about ClassReader, ClassVisitor, and ClassWriter, you can view this article: Detailed explanation of ClassReader, ClassVisitor, and ClassWriter for ASM source code learning
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassReader cr = new ClassReader(Bazhang.class.getName());
ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(cr, ClassWriter.COMPUTE_MAXS);
cr.accept(cw, Opcodes.ASM5);
MethodVisitor mv = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "newFunc", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", null, null);
mv.visitInsn(Opcodes.RETURN);
mv.visitEnd();
// 获取生成的class文件对应的二进制流
byte[] code = cw.toByteArray();
//将二进制流写到out/下
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("out/Bazhang222.class");
fos.write(code);
fos.close();
}
This will generate Bazhang222.class in the out/folder:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
import java.util.List;
class Test$Bazhang {
Test$Bazhang() {
}
private long f(int n, String s, int[] arr) {
return 0L;
}
private void hi(double a, List b) {
}
public void newFunc(String var1) {
}
}
Combined with the previously organized JVM instruction set, use ASM to directly operate the bytecode It’s no problem. At the end, the ASM source code download address is attached: http://forge.ow2.org/projects/asm/
Summary
The above is the entire content of this article. I hope the content of this article can be of some help to everyone's study or work. If you have any questions, you can leave a message to communicate.
For more related articles on the methods of java bytecode framework ASM operating bytecode, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!