 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial How does JavaScript realize that basic types have properties and methods like objects?
How does JavaScript realize that basic types have properties and methods like objects?How does JavaScript realize that basic types have properties and methods like objects?
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, which mainly introduces related issues about basic types having properties and methods like objects, including using basic types as objects and basic Type constructors, etc. Let’s take a look at them together. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end]
"Attribute method of basic type ”
This article will explore an extremely interesting concept, namely the property methods of basic types. How about it, are you a little confused? Let me tell you slowly~
Preface
In other object-oriented programming languages, such as Java, C , attributes are objects The unique concept of , the basic type is the basic type, and there is no concept of attribute method.
Yes, this is another bad idea of JavaScript. Its engine allows us to use property methods to manipulate basic types of data like objects.
Before explaining this strange feature, we must first clarify what is the difference between basic types and object types?
- What is a basic type
-
JavaScriptA value in a basic type; -
Exists in JavaScript7basic types, namely:String,Number,Boolean,BigInt,Symbol,nullandundefined;
-
- What is the object type
- A data packet, use
{ }Created, can store multiple values; -
JavaScriptThere are also other types of objects, such as functions;
- A data packet, use
Object-oriented will be covered. A key feature of introducing objects is encapsulation, which can store all kinds of messy data and methods in one object, thereby reducing the complexity of use.
For example:
let user = {
name : "xiaoming",
hello() {
console.log(`你好,我是${this.name}`);
}}user.hello();
We encapsulate the properties and methods of the object user into an object, so that it is very simple to use, we only need to use obj.attr method can call methods or properties.
However, doing so involves additional overhead (object-oriented has additional overhead), which is also where the object-oriented language C is slower than C .
Using basic types as objects
Problems faced
There are two problems that are difficult to reconcile when using basic types as objects:
- We hope that the operation of basic types can be like using objects, such as
"abc".toUpperCase(); - Objects have additional overhead, and we hope to maintain the basic types Simple and efficient features;
Solution method
JavaScriptThe way to solve the above problems is quite "harmony":
- The basic type is the basic type, providing an independent, single value;
- allows access to
String,Number,Boolean Methods and properties ofandSymboltypes; - In order to ensure the completeness of the theory, when using methods and properties of basic types, they are first packaged into objects and then destroyed;
The above rules mean that the basic type is still a basic type, but if we want to access the methods and properties of the basic type, we will wrap the basic type into an object (object wrapper), Destroy it after the visit is complete. To be honest, it sounds a bit ridiculous.
The events behind
For example:
let name = "Trump";console.log(name.toUpperCase());//访问基础类型的方法
The execution results of the above code are as follows:

It seems that there is no big problem, but a lot of things happened. We need to know the following points:
-
nameis a string basic type. There is nothing special about it; - When accessing the
nameattribute method, a special object containing a string value is created. This object has thetoUpperCasemethod; - Calling the method of a special object
toUpperCaseReturns a new string; - The special object is destroyed when used up;
The value of the variable itself has not changed, as follows:

The result of compromise
Although the solution is full of compromises (bad ideas), however, The result is still good, and the achievements achieved are as follows:
- 基础类型保持了本身的简单、高效;
- 基础类型通过特殊对象拥有了属性和方法;
- 保持了理论的完整,即只有对象才有属性和方法;
理论上虽然如此,但实际上JavaScript引擎高度优化了这个过程,我怀疑它根本就没有创建额外的对象。只是在口头上表示自己遵循了规范,好像真的搞了个临时对象一样。
常用方法举例
本文只是简单的介绍基础类型方法的概念,并不对各种方法进行讲解,伴随着教程不断深入,会逐步涉及大量的方法。这里只简单的列举基础类型常用的一些方法和属性。
不同的基础类型,拥有不同的属性方法,以下分类列举:
String
-
length属性,返回字符串长度console.log("abc".length);以上代码结果如下:

-
indexOf(ch)方法,返回字符串中第一个字符ch的下标console.log("abc".indexOf('b'));console.log("abc".indexOf('d'));代码执行结果如下:

当字符存在于字符串返回下标(从
0开始计),如果找不到就返回-1。 -
concat(str)方法,拼接两个字符串let str1 = "hello ";let str2 = "world!";console.log(str1.concat(str2));console.log(str1);console.log(str2);
代码执行结果如下:

-
replace(str1,str2)方法,使用str2替换str1let str = "javascript";console.log(str.replace('java','996'));console.log(str);代码执行结果如下:

Number
-
toFixed(num)方法,四舍五入小数到指定精度console.log(9.3333333.toFixed(3));console.log(9.3333333.toFixed(0));
代码执行结果如下:

-
toString()方法,转数字为字符串3.14.toString();//转为'3.14'console.log((8).toString(2));//转为二进制'1000'console.log((9).toString(2));//转为二进制'1001'console.log((996).toString(16));//转为16进制字符串'3e4'
代码执行结果如下:

-
toExponential()方法,转为指数计数法console.log(3.1415926.toExponential());console.log(3.1415926.toExponential(2));console.log(3.1415926.toExponential(3));
代码执行结果如下:

后继章节会展示更多的方法,这里就不过的赘述。
基础类型构造函数(不推荐使用的特性)
和Java一样,JavaScript可以通过new操作符,显式的为基础类型创建“对象包装器”,这种做法是极其不推荐的,这里提出,仅为了知识的完整性。
这种做法存在问题,举例如下:
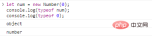
let num = new Number(0);console.log(typeof num);console.log(typeof 0);
代码执行结果如下:
亦或者,在判断中会出现混淆:
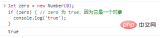
let zero = new Number(0);if (zero) { // zero 为 true,因为它是一个对象
console.log('true');}
代码执行结果如下:
同时,大家不要忘了,不带 new(关键字)的 String/Number/Boolean 函数可以将一个值转换为相应的类型:转成字符串、数字或布尔值(原始类型)。
例如:
console.log(typeof Number('123'));
注意:
null和undefined两种类型没有任何方法
本文小节
除
null和undefined以外的基础类型都提供了许多有用的方法;虽然
JavaScript使用了妥协的实现方式,但取得了较为满意的结果,以较低的成本实现了基础类型的属性和方法调用;
【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、web前端】
The above is the detailed content of How does JavaScript realize that basic types have properties and methods like objects?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMThis article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.













