 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial A brief analysis of Angular's change detection mechanism and how to optimize performance?
A brief analysis of Angular's change detection mechanism and how to optimize performance?A brief analysis of Angular's change detection mechanism and how to optimize performance?
What is change detection? The following article will take you to understand the change detection mechanism in Angular, talk about how change detection works, and introduce the performance optimization method of Angular change detection. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

#What is change detection (Change Detection)?
The concept of change detection
After the data status in the component changes, the view needs to be updated accordingly. This mechanism for synchronizing views and data is called change detection. [Related tutorial recommendations: "angular tutorial"]
Trigger timing of change detection
As long as an asynchronous operation occurs (Events, Timer, XHR ), Angular will think that the state may have changed, and then it will perform change detection.
- Events::click, mouseover, mouseout, keyup, keydown and other browser events;
- Timer: setTimeout/setInterval;
- XHR: Various requests, etc.
Since change detection is performed on asynchronous operations, how does Angular subscribe to asynchronous requests and perform change detection?
Here is an introduction to NgZone and its fork object Zone.js.
Zone.js is used to encapsulate and intercept asynchronous activities in the browser. It also provides Asynchronous life cycle hooks and unified asynchronous error handling mechanism.
Zone.js uses Monkey Patching to intercept common methods and elements in the browser, such as setTimeout and HTMLElement.prototype.onclick. Angular leverages Zone.js on startup to patch several low-level browser APIs to capture asynchronous events and call change detection after the capture time.
Angular forksZone.js and expands its own zoneNgZone, so that all asynchronous operations in the application will run in this zone.
How does Angular's change detection work?
Angualr will generate a change detector changeDetector for each component to record the change status of the component.
After we create an Angular application, Angular will also create an instance of ApplicationRef. This instance represents the instance of the Angular application we are currently creating. ApplicationRef When created, it will subscribe to the onMicrotaskEmpty event in ngZone, and after all microtasks are completed, detectChanges() of all views will be called to perform change detection. .
Execution order of change detection
Update the properties bound to all sub-subcomponents
Call all sub-component life cycle hooks OnChanges, OnInit, DoCheck, AfterContentInit
Update the DOM of the current component
Call the change detection of sub-components
Call the life cycle hook ngAfterViewInit of all sub-components
For example, we may encounter this kind of error when we are in development mode :

This is because change detection follows the change detection starting from the root component, from top to bottom, performing change detection for each component until the last component reaches a stable state. Before the next change detection, descendant components are not allowed to modify the properties in the parent component.
Case 1 In development mode, Angular will perform secondary detection (call enableProdMode()## in production environment #, the number of detections will be reduced to 1). Once we modify the properties of the parent component in the descendant component after Step 4 is completed, then when Angular performs the second detection and finds that the two values are inconsistent, the above error will occur.
Case 2 As long as the parent component binds properties to the child component, no matter it is any life in OnChanges, OnInit, DoCheck, AfterContentInit and AfterViewInit Executing the following code in the cycle hook will also report an error.
// #parent
{{data}}
<child [data]="data"></child>
// in child component ts, execute:
this.parent.data = 'new Value';
Execution strategy for change detection
##Default strategy
This default strategy checks every component in the component tree from top to bottom every time an event triggers change detection (such as user events, timers, XHR, promises, etc.). This conservative checking method that does not make any assumptions about component dependencies is called Dirty Check. This strategy will have a performance impact on our application when we apply too many components.
-
Modify the component decorator
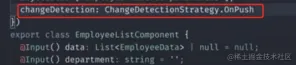
changeDetection, after setting it to OnPush strategy, Angular will skip the change detection of this component and all sub-components of this component every time it triggers change detection.Under the
OnPushstrategy, only the following situations will trigger component change detection:- Input value (@Input) change (The value entered into the input must be a new reference)
-
One of the current components or subcomponents triggered the event (but in the onPush strategy, the following operations will not trigger changes Detection)
- setTimeout()
- setInterval()
- Promise.resolve().then()
- this.http.get('...').subscribe()
-
Manually trigger change detection (Each component will be associated with a component view ChangeDetectorRef)
- detectChanges(): It will trigger change detection of the current component and sub-components
- markForCheck(): It will not trigger change detection, but it will mark the current OnPush component and all the components whose parent component is OnPush as requiring detection status , Detect in the current or next change detection cycle
- ApplicationRef.tick(): It will trigger change detection of the entire application according to the component's change detection strategy

- async pipe
How about change detection in Angular optimization?
Since the component executes Default strategy by default, any asynchronous operation will trigger a top-to-bottom check of the entire component number. Even if the Angular team continues to improve performance and can complete hundreds of detections within milliseconds, when the application expands to hundreds or thousands of components, the change detection corresponding to the huge component tree will reach a performance bottleneck.
At this point, we need to start analyzing and reducing the number of unnecessary tests.
How to reduce the number of tests
-
Zone Pollution
Generally we are in life When using third-party libraries in cycle hooks, such as chart class library initialization, it will come with requestAnimationRequest/setTimeout/addEventListener. We can write the initialization method into the
runOutsideAngularmethod ofNgZone.
-
OnPush strategy
Views that do not involve update operations can be stripped Exit the component and use the onPush strategy to refresh the view by notifying the update (see the Execution Strategy for Change Detection section above).

-
##Use pure pipe instead of {{function(data)}}
In the html file, the writing method of{{function(data)}}
At this time, we can use the pipe method, Only changed values will trigger operations and update part of the view.will cause all values to be recalculated every time change detection occurs. (?: When you have a list of 1,000 items, you only modify one piece of data, but the other 999 pieces of data that do not need to be updated will also be recalculated.)
-
Faced with rendering a large amount of data, choose virtual scrolling/paging to request data
The above 4-point solution comes from the video introduction of the
插件:Angular devtool使用介绍
- Angular 9+, 支持Ivy。
- Guide和下载地址
- 保证运行环境为开发环境
// environment.dev.ts ... production: false ... - angular.json > dev配置项 >
"optimization": falseprojects > your-project-name > architect > build > configurations > dev > "optimization": false
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程教学!!
The above is the detailed content of A brief analysis of Angular's change detection mechanism and how to optimize performance?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnderstanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMThis article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment







