Home >Backend Development >PHP7 >Summary of how to upgrade PHP5.6 to PHP7

This article is a summary of the lecture + follow-up research.
Speaking of following the fashion back then, I immediately installed php7 on my computer as soon as it came out. php5 and php7 coexisted. I immediately wrote a super time-consuming loop script and tested it. It is true that php7 is much more powerful, and I paid some attention to it. New features and some discarded usage.
Since php upgrade is a top priority, the company only plans to upgrade in the near future, so before I could only appreciate the pleasure brought by php7 in private. The friend in charge of the upgrade made a sharing, which is quite comprehensive. Mark it here. Take notes.
Recommended (free): PHP7
Main research questions:
1. Benefits of PHP7
2.PHP7 New things brought
3. Abandonment brought by PHP7
4. Changes brought by PHP7
5. How to give full play to the performance of PHP7
6. How to write better code to welcome PHP7?
7. How to upgrade the current project code to be compatible with PHP7?
Yes, the performance has been greatly improved , can save machines and save money. 
You can use string (string), integer (int), floating point number (float), and Boolean value (bool) to declare the parameter type and function return value of the function.
declare(strict_types=1);
function add(int $a, int $b): int {
return $a+$b;
}
echo add(1, 2);
echo add(1.5, 2.6);
php5 cannot execute the above code. When php7 is executed, it will first output a 3 and an error (Argument 1 passed to add() must be of the type integer, float given);
There are two modes for scalar type declarations: mandatory (default) and strict mode.
declare(strict_types=1), must be placed in the first line of the file to execute the code, the current file is valid!
In PHP 7, there are many fatal errors and recoverable fatal errors , are converted into exceptions for processing. These exceptions inherit from the Error class, which implements the Throwable interface (all exceptions implement this base interface).
PHP7 further facilitates developers' processing and allows developers to have greater control over the program. Because by default, Error will directly cause the program to interrupt, while PHP7 provides the ability to capture and process it, allowing the program to continue. The implementation continues to provide programmers with more flexible options.
Syntax: $c = $a <=> $b
If $a > $ b, the value of $c is 1
If $a == $b, the value of $c is 0
If $a < $b, the value of $c is -1
If the variable exists and the value is not NULL, it will return its own value, otherwise it will return its second operand .
//原写法 $username = isset($_GET['user]) ? $_GET['user] : 'nobody'; //现在 $username = $_GET['user'] ?? 'nobody';
define('ARR',['a','b']); echo ARR[1];// a
AST serves as an intermediate in the PHP compilation process It replaces the original method of spitting out opcode directly from the interpreter and decouples the interpreter (parser) and compiler (compliler), which can reduce some Hack codes and at the same time make the implementation easier to understand and maintain.
PHP5: PHP code-> Parser syntax analysis-> OPCODE -> Execution
PHP7: PHP code-> Parser syntax analysis-> AST -> OPCODE -> Execution
Reference: https://wiki.php.net/rfc/abstract_syntax_tree
$anonymous_func = function(){return 'function';};
echo $anonymous_func(); // 输出function
Prevents code injection of illegal data and provides safer deserialized data.
// PHP7以前语法的写法
use FooLibrary\Bar\Baz\ClassA;
use FooLibrary\Bar\Baz\ClassB;
// PHP7新语法写法
use FooLibrary\Bar\Baz\{ ClassA, ClassB};
Ereg regular expression
mssql
mysql
sybase_ct
Cannot use constructors with the same name
Instance methods cannot be called as static methods
method call
call_user_method() call_user_method_array()
should use call_user_func() and call_user_func_array()
Encryption related functions
mcrypt_generic_end() mcrypt_ecb() mcrypt_cbc() mcrypt_cfb() mcrypt_ofb()
Note: PHP7.1 and later mcrypt_* Sequence functions will be removed. Recommended use: openssl sequence function
Miscellaneous
set_magic_quotes_runtime set_socket_blocking Split imagepsbbox() imagepsencodefont() imagepsextendfont() imagepsfreefont() imagepsloadfont() imagepsslantfont() imagepstext()
$HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA variable has been removed, use php://input instead
Ini files no longer support comments starting with #, use ";"
Removed ASP format support and script syntax support: <% and < script language=php >
Strings containing hexadecimal characters are no longer regarded as numbers and are no longer treated differently.
var_dump("0x123" == "291"); // false
var_dump(is_numeric("0x123")); // false
var_dump("0xe" + "0x1"); // 0
var_dump(substr("f00", "0x1")) // foo
Int64 support, unify the integer length under different platforms, string and file upload support greater than 2GB. 64-bit PHP7 string length Can exceed 2^31 bytes.
// 无效的八进制数字(包含大于7的数字)会报编译错误 $i = 0681; // 老版本php会把无效数字忽略。 // 位移负的位置会产生异常 var_dump(1 >> -1); // 左位移超出位数则返回0 var_dump(1 << 64);// 0 // 右位移超出会返回0或者-1 var_dump(100 >> 32);// 0 var_dump(-100 >> 32);// -1
Does not support repeated parameter naming
function func(a,a,b, c,c,c) {} ;会报错
func_get_arg() and func_get_args( ) These two methods return the current value of the parameter, not the value passed in. The current value may be modified
所以需要注意,在函数第一行最好就给记录下来,否则后续有修改的话,再读取就不是传进来的初始值了。
function foo($x) {
$x++;
echo func_get_arg(0);
}
foo(1); //返回2
foreach()循环对数组内部指针不再起作用
$arr = [1,2,3];
foreach ($arr as &$val) {
echo current($arr);// php7 全返回0
}
按照值进行循环的时候, foreach是对该数组的拷贝操作
$arr = [1,2,3];
foreach ($arr as $val) {
unset($arr[1]);
}
var_dump($arr);
最新的php7依旧会打印出[1,2,3]。(ps:7.0.0不行)
老的会打印出[1,3]
按照引用进行循环的时候, 对数组的修改会影响循环
$arr = [1];
foreach ($arr as $val) {
var_dump($val);
$arr[1]=2;
}
最新的php7依旧会追加新增元素的循环。(ps:7.0.0不行)
不再按照相反的顺序赋值
//$arr将会是[1,2,3]而不是之前的[3,2,1] list($arr[], $arr[], $arr[]) = [1,2,3];
不再支持字符串拆分功能
// $x = null 并且 $y = null $str = 'xy'; list($x, $y) = $str;
空的list()赋值不再允许
list() = [123];
list()现在也适用于数组对象
list($a, $b) = (object)new ArrayObject([0, 1]);
对变量、属性和方法的间接调用现在将严格遵循从左到右的顺序来解析,而不是之前的混杂着几个特殊案例的情况。 下面这张表说明了这个解析顺序的变化。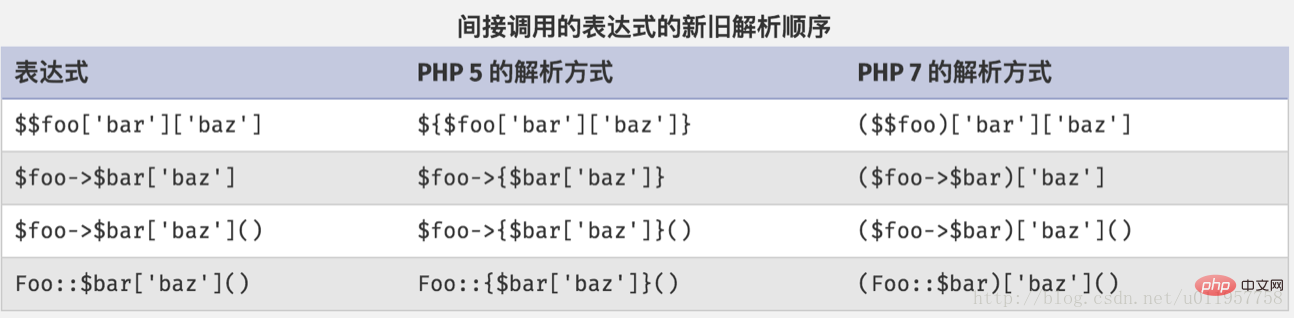
引用赋值时自动创建的数组元素或者对象属性顺序和以前不同了
$arr = []; $arr['a'] = &$arr['b']; $arr['b'] = 1; // php7: ['a' => 1, 'b' => 1] // php5: ['b' => 1, 'a' => 1]
1.debug_zval_dump() 现在打印 “int” 替代 “long”, 打印 “float” 替代 “double”
2.dirname() 增加了可选的第二个参数, depth, 获取当前目录向上 depth 级父目录的名称。
3.getrusage() 现在支持 Windows.mktime() and gmmktime() 函数不再接受 is_dst 参数。
4.preg_replace() 函数不再支持 “\e” (PREG_REPLACE_EVAL). 应当使用 preg_replace_callback() 替代。
5.setlocale() 函数不再接受 category 传入字符串。 应当使用 LC_* 常量。
6.exec(), system() and passthru() 函数对 NULL 增加了保护.
7.shmop_open() 现在返回一个资源而非一个int, 这个资源可以传给shmop_size(), shmop_write(), shmop_read(), shmop_close() 和 shmop_delete().
8.为了避免内存泄露,xml_set_object() 现在在执行结束时需要手动清除 $parse。
9.curl_setopt 设置项CURLOPT_SAFE_UPLOAD变更
TRUE 禁用 @ 前缀在 CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS 中发送文件。 意味着 @ 可以在字段中安全得使用了。 可使用 CURLFile作为上传的代替。
PHP 5.5.0 中添加,默认值 FALSE。 PHP 5.6.0 改默认值为 TRUE。. PHP 7 删除了此选项, 必须使用 CURLFile interface 来上传文件。
zend_extension=opcache.so opcache.enable=1 opcache.enable_cli=1
只有GCC 4.8以上PHP才会开启Global Register for opline and execute_data支持, 这个会带来5%左右的性能提升(Wordpres的QPS角度衡量)

第一次编译成功后,用项目代码去训练PHP,会产生一些profile信息,最后根据这些信息第二次gcc编译PHP就可以得到量身定做的PHP7
需要选择在你要优化的场景中: 访问量最大的, 耗时最多的, 资源消耗最重的一个页面.
参考: http://www.laruence.com/2015/06/19/3063.html
参考: http://www.laruence.com/2015/12/04/3086.html
不使用php7废弃的方法,扩展
使用2个版本都兼容的语法特性【 list ,foreach, func_get_arg 等】
检测工具:https://github.com/sstalle/php7cc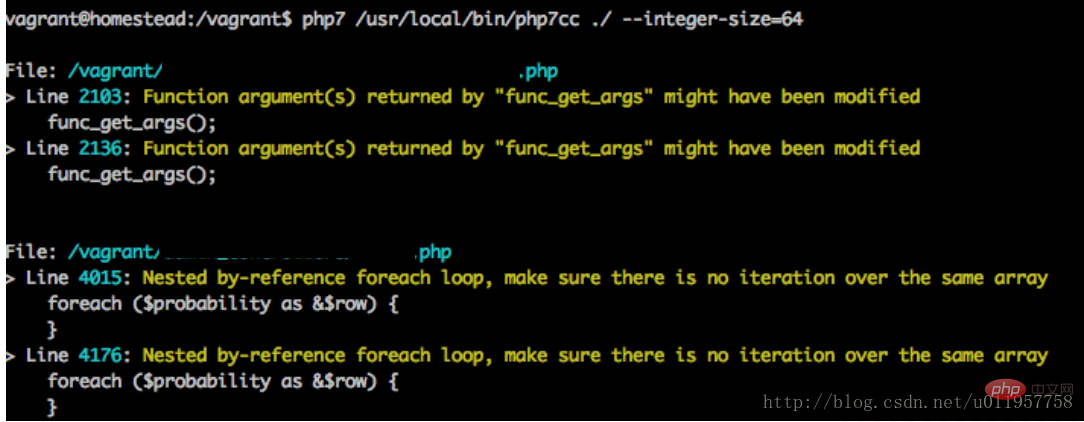
官方5.6.x移植7.0.x 文档
Laruence 让PHP7达到最高性能的tips
博客-PHP7特征
Zval的变更
The above is the detailed content of Summary of how to upgrade PHP5.6 to PHP7. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!