Home>Article>Backend Development> Python explains the os module and shutil module in detail

Article directory
(Related free learning recommendations:python video tutorial)
osmodule andshutilmodule are Python processing files / directory's primary mode. The os module provides a convenient way to use operating system-related functions, and the shutil module is an advanced file/directory operation tool.
File processing
osThe module provides some convenient functions to use operating system resources, such as reading files in the resource directory files, view all contents of files under a certain path on the command line, etc.
Get the system type
When developing code compatibility to adapt to different operating systems, it can be easily solved by judging the operating system type.
import osimport sysprint(os.name) # 返回nt代表Windows,posix代表Linuxprint(sys.platform) # 更详细信息

Get the system environment
When setting environment variables, the moduleenviron is often calledModule.os.environreturns system environment variables in the form of a dictionary. To obtain specific attribute values, you can use the index or the methodgetenv():
import osprint(os.environ)print(os.environ['PATH'])print(os.getenv('PATH'))

Execute system commands
Use the os modulesystem()method to execute shell commands, normal execution will return 0. The usage format isos.system("bash command").
When writing in non-console mode,system()will only call the system command but not execute it. The execution result can be returned through thepopen()functionThe fileobject is read and obtained.
import os os.system('ping www.baidu.com')os.popen('ping www.baidu.com').read()

Operation directories and files
One of the most common functions of Python development when using the os module to operate directories and files one.
(插播反爬信息)博主CSDN地址:https://wzlodq.blog.csdn.net/
文件和目录高级处理
相比
os模块,shutil模块用于文件和目录的高级处理,提供了支持文件赋值、移动、删除、压缩和解压等功能。
复制文件
shutil模块的主要作用是赋值文件,大概有以下七种实现:
shutil.copyfileobj(file1,file2)覆盖复制
将file1的内容覆盖file2,file1、file2表示打开的文件对象。
shutil.copyfile(file1,file2)覆盖复制
也是覆盖,但是无须打开文件,直接用文件名进行覆盖(其源码还是调用的copyfileobj)。
shutil.copymode(file1,file2)权限复制
仅复制文件权限,不更改文件内容、组和用户,无返回对象。
shutil.copystart(file1,file2)状态复制
复制文件的所有状态信息,包括权限、组、用户和时间等,无返回对象。
shutil.copy(file1,file2)内容和权限复制
复制文件的内容和权限,相当于先执行了copyfile再执行了copysmode。
shutil.copy2(file1,file2)内容和权限复制
复制文件的内容及所有状态信息,相当于先执行了copyfile再执行了copystart。
shutil.copytree()递归复制
递归地复制文件内容及状态信息
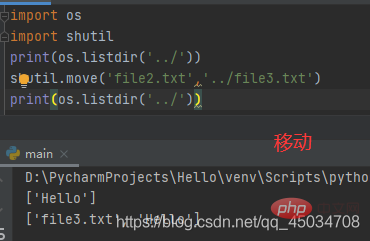
移动文件
使用函数shutil.move()函数可以递归地移动文件或重命名,并返回目标,若目标是现有目录则src再当前目录移动;若目标已经存在且不是目录,则可能会被覆盖。
读取压缩及归档压缩文件
使用函数shutil.make_archive()创建归档文件,并返回归档后的名称。
语法如下:shutil.make_archive(base_name,format[,root_dir[,base_dir[,verbose[,dry_run[,owner[,group[,logger]]]]]]])
import shutil path_1 = r'D:\PycharmProjects\Hello'path_2 = r'D:\PycharmProjects\Hello\shutil-test'new_path = shutil.make_archive(path_2,'zip',path_1)print(new_path)

解压文件
使用函数shutil.unpack_archive(filename[,extract_dir[,format]])分析拆档。
import shutilimport os shutil.unpack_archive('D:\PycharmProjects\Hello\shutil-test.zip','D:\\testdir')print(os.listdir('D:\\testdir'))

小结
需要注意的是不同的操作系统中,路径分隔符不一样,在文件处理时需要考虑。也可以使用os.sep()来替代文件分隔符,因为操作系统而造成的程序异常。此外处理文件时往往需要注意文件权限,还有注意文件和文件夹的区别,使用递归等。
Python系列博客持续更新中
大量免费学习推荐,敬请访问python教程(视频)
| Method | Description | Example |
| os.getcwd() | Get the current directory path |  |
| Change the current script directory |  |
|
| List all files in the directory |  |
|
| Create a single directory |  |
|
| Create a multi-level directory | ||
| Delete a single-level empty directory | ||
| Delete multi-level directories | ##os.rename("File or directory name", "Target name") | |
 ##os.path.abspath() ##os.path.abspath() |
||
 os.path.split(path) os.path.split(path) |
||
| If there is no \ in the path string, only the file name part has a value; | If the path string contains \ and is no longer the last, then the folder and file names all have values.##os.path.join(path1,path2) | Combining paths
|
| os.path.dirname(path) | Get the folder part in path | |
os.path.basename( path) | Get the file name in path
||
| os.path.exists(path) | Judge whether the file or folder exists | |
os.path.isfile(path) | Determine whether the path is a file
||
os.path.isdir(path) | Determine whether the path is a directory
||
os.path.getsize(path) | Get file or folder size
||
| ##os.path.getctime(path) |  Get the file or folder creation time Get the file or folder creation time |
|
| os.path.getatime(path) |  Get the file or Folder last access time Get the file or Folder last access time |
|
| ##os.path.getmtime(path) | Get the last modification time of a file or folder |
|
| os.sep() | Path separator |
|
| os.extsep() | Separator between file name and suffix |
|
| Path separator | ||
| Newline symbol | ||
The above is the detailed content of Python explains the os module and shutil module in detail. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!