Home>Article>Web Front-end> CSS3 selector attribute selector
The previous section mainly introduced the first part of CSS3 selector in "CSS3 Selector - Basic Selector". This section mainly introduces the second part of CSS3 selector - attribute selector with everyone. Attribute selectors were introduced as early as CSS2, and their main function is to set styles for HTML elements with specified attributes. Using CSS3 attribute selectors, you can specify only an attribute of an element, or you can specify both an attribute of an element and its corresponding attribute value.From the CSS3 selector chart shown in the previous section, we can know that CSS3 attribute selectors mainly include the following types:
<div class="demo clearfix"> <a href="http://www.w3cplus.com" target="_blank" class="links item first" id="first" title="w3cplus">1a> <a href="" class="links active item" title="test website" target="_blank" lang="zh">2a> <a href="sites/file/test.html" class="links item" title="this is a link" lang="zh-cn">3a> <a href="sites/file/test.png" class="links item" target="_balnk" lang="zh-tw">4a> <a href="sites/file/image.jpg" class="links item" title="zh-cn">5a> <a href="mailto:w3cplus@hotmail" class="links item" title="website link" lang="zh">6a> <a href="" class="links item" title="open the website" lang="cn">7a> <a href="" class="links item" title="close the website" lang="en-zh">8a> <a href="" class="links item" title="http://www.sina.com">9a> <a href="" class="links item last" id="last">10a> div>Preliminary beautification of the above code:
.demo { width: 300px; border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 10px; } .demo a { float: left; display: block; height: 20px; line-height: 20px; width: 20px; -moz-border-radius: 10px; -webkit-border-radius: 10px; border-radius: 10px; text-align: center; background: #f36; color: green; margin-right: 5px; text-decoration: none; }The initial effect is as follows:
Let’s start with a detailed analysis of how to use each of the attribute selectors listed above.
1. E[attr]
.demo a[id] {background: blue; color:yellow;font-weight:bold;}The above code represents that all a elements with id attributes under div.demo are selected, and the background color is blue, the foreground color is yellow, and the font is bold on this element. Compare the above html , it is not difficult for us to find that only the first and last links use the id attribute, so these two a elements are selected, and the effect is as follows:
 The above is the use of a single attribute. You can also use multiple attributes to select elements, such as E[attr1][attr2], so that all elements with both attributes will be selected:
The above is the use of a single attribute. You can also use multiple attributes to select elements, such as E[attr1][attr2], so that all elements with both attributes will be selected:
.demo a[href][title] {background: yellow; color:green;}
不用我说,上面的代码大家都知道是什么意思了,他表示的是选择div.demo下的同时具有href,title两个属性的a元素,并且应用相对应的样式,如下所示:

IE6不支持这个选择器。
E[attr="value"]选择器和E[attr]选择器,从字面上就能很清楚的理解出来,E[attr="value"]是指定了属性值“value”,而E[attr]只是选择了有对应的属性,并没有明确指其对应的属性值"value",这也是这两种选择器的最大区是之处。从而缩小了选择 围,更能精确选择自己需要的元素,在前面实例基础上我们进行一下简单的修改:
.demo a[id="first"] {background: blue; color:yellow;font-weight:bold;}
和前面代码相比较,此处在id的属性基础上指定了相应的value值为“first”,这样一来我们选中的是div.demo中的a元素,并且这个元素有一个"id="first""属性值,请看下在的效果图:

E[attr="value"]属性选择器也可以多个属性并写,进一步缩小选择范围:
.demo a[href="http://www.w3cplus.com"][title] {background: yellow; color:green;}
效果如下:

对于E[attr="value"]这种属性值选择器有一点需要注意:属性和属性值必须完全匹配,特别是对于属性值是词列表的形式时,如:
例如上面的代码,如果你写成:
.demo a[class="links"]{color:red};/*这是一种写法不能和上面的html所匹配*/
上面的属性选择器并不会和上在的html匹配,因为他们的属性和属性值没有完全匹配,需要改成如下所示的代码,才能正确匹配:
.demo a[class="links item"]{color:red};/*这样才是匹配的,记得中间的空格不能少的哟*/
IE6浏览器不支持这种选择器。
如果你想根据属性值中的词列表的某个词来进行选择元素,那么就需要使用这种属性选择器:E[attr~="value"],这种属性选择器是属性值是一个或多个词列表,如果是列表时,他们需要用空格隔开,只要属性值中有一个value相匹配就可以选中该元素,而我们前面所讲的E[attr="value"]是属性值需要完全匹配才会被选中,他们两者区别就是一个有“〜”号,一个没有“〜”号。我们来看一个这方面的实例:
.demo a[title~="website"]{background:orange;color:green;}
上面代码表示的是,div.demo下的a元素的title属性中,只要其属性值中含有"website"这个词就会被选择,回头看看我们的html,不难发现所有a元素中“2,6,7,8”这四个a元素的title中都含有,所以被选中,请看效果:

如果我们在上面的代码中,把那个“〜”号省去,大家看看他们不同之处:
.demo a[title="website"]{background:orange;color:green;}
这样将不会选择中任何元素,因为在所有a元素中无法找到完全匹配的"title='website'",换句话说就没有选中任何元素,效果如下:

这个实例再次证明了E[attr="value"]和E[attr~="value"]之间的区别,和其中“〜”所取的作用,我总结了一句话:属性选择器中有波浪(〜)时属性值有value时就相匹配,没有波浪(〜)时属性值要完全是value时才匹配。
IE6不支持E[attr~="value"]属性选择器。
E[attr^="value"]属性选择器,指的是选择attr属性值以“value”开头的所有元素,换句话说,选择的属性其以对应的属性值是以“value”开始的,一起来看个实例:
.demo a[href^="http://"]{background:orange;color:green;} .demo a[href^="mailto:"]{background:green;color:orange;}
上面代码表示的是选择了以href属性,并且以"http://"和"mailto:"开头的属性值的所有a元素,换过更简单一点的呢?只要a元素中的href属性值是以"http://"或"mailto:"开头的a元素都会以选中,那么下面大家请对照上面的html和下面的效果图,看看是不是那么一回事:

IE6不支持E[attr^="value"]选择器。
E[attr$="value"]属性选择器刚好与E[attr^="value"]选择器相反,E[attr$="value"]表示的是选择attr属性值以"value"结尾的所有元素,换句话说就是选择元素attr属性,并且他的属性值是以value结尾的,这个运用在给你一些特殊的链接加背景图片很方便的,比如说给pdf,png,doc等不同文件加上不同icon,我们就可以使用这个属性来实现,如:
.demo a[href$="png"]{background:orange;color:green;}
上面代码表示的是,选择div.demo中元素有href属性,并以png值结尾的a元素。(正如上面所说,只不过这里使用的是改变元素的背景色),效果如下:

IE6不支持E[attr$="value"]属性选择器。
E[attr*="value"]属性选择器表示的是选择attr属性值中包含子串"value"的所有元素。也就是说,只要你所选择的属性,其属性值中有这个"value"值都将被选中,如:
.demo a[title*="site"]{background:black;color:white;}
上面代码表示的是:选择了div.demo中a元素,而a元素的title属性中只要有"site"就符合选择条件。效果如下:

IE6不支持E[attr*="value"]选择器。
E[attr|="value"]是属性选择器中的最后一种,在说这个选择器使用之前先提醒大家attr后面的是一个竖线“|”而不是l,小心搞错了。E[attr|="value"]被称作为特定属性选择器。这个选择器会选择attr属性值等于value或以value-开头的所有元素,我们来看个实例:
.demo a[lang|="zh"]{background:gray;color:yellow;}
上面的代码会选中了div.demo中lang属性等于zh或以zh-开头的所有a元素,大家可以对照前面的html代友,其中"2,3,4,6"被选中,因为他们都有一个lang属性,并且他们的属性值都符合以"zh"或"zh-"开始的元素。具体效果如下:
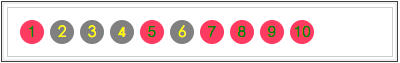
所以这种属性选择器用来匹配以“女value-1”,"value-2"的属性是很方便的,比如说你页面中有很多图片,图片文件名都是以"figure-1","figure-2"这样的方式来命名的,那么使用这种选择器选中图片就很方便了,大家可以在本地尝试一下,这种属性选择器最常常用的地方是如上面的示例用来匹配语言。
IE6不支持E[attr|="value"]选择器。
有关于属性选择器就上面这些内容了,属性选择器除了IE6不支持外,其他的浏览器都能支持,这样一来,如果你在你的页面上使用了属性选择器,而且你需要处理ie6兼容问题,那你就需要确保IE6用别的方法来实现或者你应该确保IE6用户将能获得一个可用的页面。七种属性选择器中E[attr="value"]和E[attr*="value"]是最实用的,其中E[attr="value"]能帮我们定位不同类型的元素,特别是表单form元素的操作,比如说input[type="text"],input[type="checkbox"]等,而E[attr*="value"]能在网站中帮助我们匹配不同类型的文件,比如说你的网站上不同的文件类型的链接需要使用不同的icon图标,用来帮助你的网站提高用户体验,就像前面的实例,可以通过这个属性给".doc",".pdf",".png",".ppt"配置不同的icon图标。
到这里,CSS3的属性选择器就介绍完了,下一节将主要介绍CSS3的伪类选择器,特别是其中的nth-child选择器,将是CSS3选择器中最有吸引力的一部分,大家如果感兴趣的话,请观注本站的有关更新吧。让我们一起期待CSS3的无穷力量。
来源:W3CPLUS