typeof를 사용하여 데이터 유형 감지
Javascript에는 기본 데이터 유형(정의되지 않음, 문자열, null, 부울, 함수, 객체)과 객체 유형이라는 두 가지 유형 세트가 있습니다.
그러나 typeof를 사용하여 객체 유형을 감지하려고 하면 항상 "객체"를 반환하고 구별할 수 없습니다.
typeof null // "object" typeof [] // "object" typeof document.childNodes //"object" typeof /\d/ //"object" typeof new Number() //"object"
생성자 속성을 사용하여 유형의 생성자를 감지하세요.
[].constructor === Array //true
document.childNodes === NodeList //true
/\d/.constructor === RegExp //true
function isRegExp(obj) {
return obj && typeof obj === "object" && obj.constructor === RegExp;
} //检测正则表达式对象
function isNull(obj){
return obj === null;
}구조 감지를 사용하면 대부분의 유형 감지가 완료될 수 있으며 특히 null은 직접 비교됩니다. 그러나 iframe에서 올바른 유형의 배열 유형을 감지할 수 없습니다. 이는 동시에 구조에 의해 감지되는 결함이며, 이전 버전의 IE에서는 DOM 및 BOM 구조에 액세스할 수 없습니다.
Object.prototype.toString을 사용하여 결정
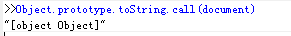
Object.prototype.toString.call([]) //"[object Array]" Object.prototype.toString.call(/\d/) // "[object RegExp]" Object.prototype.toString.call(1)//"[object Number]"
jQuery 소스코드에서 toString 메소드를 사용하는 방법
/*
* jQuery JavaScript Library v1.11.2
*/
var class2type = {}; //用来保存js数据类型
jQuery.each("Boolean Number String Function Array Date RegExp Object Error".split(" "), function(i, name) {//构造class2type存储常用类型的映射关系,遍历基本类型并赋值,键值为 [object 类型]
class2type[ "[object " + name + "]" ] = name.toLowerCase();
});
type: function( obj ) {
if ( obj == null ) {//首先如果是null则返回null字符串
return obj + "";
}
//接着判断给定参数类型是否为object或者function,是的话在映射表中寻找 toString后的键值名称并返回,不是的话利用typeof就可以得到正确类型。
return typeof obj === "object" || typeof obj === "function" ?
class2type[ toString.call(obj) ] || "object" :
typeof obj;
},
/****************************/
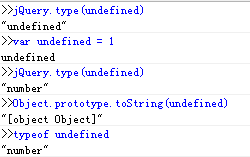
jQuery.type(/\d/) //"regexp"
jQuery.type(new Number()) //"number"
특수한 감지 유형에 대해 이야기해 보겠습니다

jQuery 감지 특수 유형에 대해 알아보기
isWindow: function( obj ) {//ECMA规定window为全局对象global,且global.window === global
return obj != null && obj == obj.window;
},
isPlainObject: function( obj ) {
var key;
if ( !obj || jQuery.type(obj) !== "object" || obj.nodeType || jQuery.isWindow( obj ) ) {
return false;
}
try {//判断它最近的原形对象是否含有isPrototypeOf属性
if ( obj.constructor &&
!hasOwn.call(obj, "constructor") &&
!hasOwn.call(obj.constructor.prototype, "isPrototypeOf") ) {
return false;
}
} catch ( e ) {
return false;
}
if ( support.ownLast ) {
for ( key in obj ) {
return hasOwn.call( obj, key );
}
}
jQuery 대비 대용량 프레임워크의 개선
var class2type = {//将可能出现的类型都映射在了class2type对象中,从而减少isXXX函数
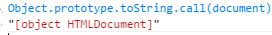
"[object HTMLDocument]": "Document",
"[object HTMLCollection]": "NodeList",
"[object StaticNodeList]": "NodeList",
"[object DOMWindow]": "Window",
"[object global]": "Window",
"null": "Null",
"NaN": "NaN",
"undefined": "Undefined"
};
type: function(obj, str) {
var result = class2type[(obj == null || obj !== obj) ? obj : serialize.call(obj)] || obj.nodeName || "#"; //serialize == class2type.toString
if (result.charAt(0) === "#") { //兼容旧式浏览器与处理个别情况,如window.opera
//利用IE678 window == document为true,document == window竟然为false的神奇特性
if (obj == obj.document && obj.document != obj) {//对DOM,BOM对象采用nodeType(单一)和item(节点集合)进行判断
result = "Window"; //返回构造器名字
} else if (obj.nodeType === 9) {
result = "Document"; //返回构造器名字
} else if (obj.callee) {
result = "Arguments"; //返回构造器名字
} else if (isFinite(obj.length) && obj.item) {
result = "NodeList"; //处理节点集合
} else {
result = serialize.call(obj).slice(8, -1);
}
}
if (str) {
return str === result;
}
return result;
}배열형
공통 클래스 배열: 아래와 같이 인수, document.forms, document.getElementsByClassName(예: 일련의 노드 컬렉션 NodeList, HTMLCollection) 또는 일부 특수 객체:
var arrayLike={
0:"a",
1:"b",
2:"c",
length:3
}
jQuery가 유사 배열을 처리하는 방법
makeArray: function( arr, results ) {
var ret = results || [];
if ( arr != null ) {
if ( isArraylike( Object(arr) ) ) {
jQuery.merge( ret,
typeof arr === "string" ?
[ arr ] : arr
); //jQuery.merge 合并数组 ,若是字符串则封装成数组河滨,不是则世界合并
} else {
push.call( ret, arr );
}
}
return ret;
}Ext.js가 배열을 처리하는 방법
toArray: function(iterable, start, end) {
if (!iterable || !iterable.length) {
return []; //非类数组类型直接返回[]
}
if (typeof iterable === 'string') {
iterable = iterable.split(''); //分解字符串
}
if (supportsSliceOnNodeList) {
return slice.call(iterable, start || 0, end || iterable.length); //对于NodeList支持
}
var array = [],
i;
start = start || 0;
end = end ? ((end < 0) ? iterable.length + end : end) : iterable.length;
for (i = start; i < end; i++) {
array.push(iterable[i]);
}
return array;
}대량 Framework.js가 클래스 배열을 처리하는 방법
slice: W3C ? function(nodes, start, end) { //var W3C = DOC.dispatchEvent; IE9开始支持W3C的事件模型
return factorys.slice.call(nodes, start, end);
} : function(nodes, start, end) {
var ret = [],
n = nodes.length;
if (end === void 0 || typeof end === "number" && isFinite(end)) {
start = parseInt(start, 10) || 0;
end = end == void 0 ? n : parseInt(end, 10);
if (start < 0) {
start += n;
}
if (end > n) {
end = n;
}
if (end < 0) {
end += n;
}
for (var i = start; i < end; ++i) {
ret[i - start] = nodes[i];
}
}
return ret;