Java 예외 포착 및 처리 방법: 1. throws 키워드, 시스템은 캡처된 예외 정보를 상위 호출 메서드에 자동으로 전달합니다. 2. throw 기능은 예외 클래스의 인스턴스화 개체를 수동으로 발생시키는 것입니다. Exception의 서브클래스이며 이를 처리할지 여부는 사용자가 선택합니다.

【관련 학습 권장사항: java 기본 튜토리얼】
Java 예외 캡처 및 처리 방법:
1 finally 블록을 생략할 수 있으므로 예외는 예외입니다. 처리 형식은 try{ }——catch{ }, try{ }——catch{ }——finally{ }, try{ }——finally{ }의 세 가지 범주로 나눌 수 있습니다.
1 public class DealException
2 {
3 public static void main(String args[])
4 {
5 try
6 //要检查的程序语句
7 {
8 int a[] = new int[5];
9 a[10] = 7;//出现异常
10 }
11 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex)
12 //异常发生时的处理语句
13 {
14 System.out.println("超出数组范围!");
15 }
16 finally
17 //这个代码块一定会被执行
18 {
19 System.out.println("*****");
20 }
21 System.out.println("异常处理结束!");
22 }
23 } 1 public class DealException
2 {
3 public static void main(String args[])
4 {
5 try
6 //要检查的程序语句
7 {
8 int a[] = new int[5];
9 a[0] = 3;
10 a[1] = 1;
11 //a[1] = 0;//除数为0异常
12 //a[10] = 7;//数组下标越界异常
13 int result = a[0]/a[1];
14 System.out.println(result);
15 }
16 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex)
17 //异常发生时的处理语句
18 {
19 System.out.println("数组越界异常");
20 ex.printStackTrace();//显示异常的堆栈跟踪信息
21 }
22 catch(ArithmeticException ex)
23 {
24 System.out.println("算术运算异常");
25 ex.printStackTrace();
26 }
27 finally
28 //这个代码块一定会被执行
29 {
30 System.out.println("finally语句不论是否有异常都会被执行。");
31 }
32 System.out.println("异常处理结束!");
33 }
34 }2. throws 키워드
throws로 선언된 메서드는 해당 메서드가 예외를 처리하지 않지만 시스템이 캡처된 예외 정보를 상위 호출 메서드에 자동으로 throw한다는 의미입니다.
1 public class throwsDemo
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 int[] a = new int[5];
6 try
7 {
8 setZero(a,10);
9 }
10 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex)
11 {
12 System.out.println("数组越界错误!");
13 System.out.println("异常:"+ex);
14 }
15 System.out.println("main()方法结束。");
16 }
17 private static void setZero(int[] a,int index) throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
18 {
19 a[index] = 0;
20 }
21 }3. throw 키워드
throw는 예외 클래스의 인스턴스화된 개체를 수동으로 던지는 데 사용됩니다.
1 public class throwDemo
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 try
6 {
7 //抛出异常的实例化对象
8 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("\n个性化异常信息:\n数组下标越界");
9 }
10 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex)
11 {
12 System.out.println(ex);
13 }
14 }
15 }4. RuntimeException 클래스
Exception과 RuntimeException의 차이점:
Exception: 사용자가 반드시 처리해야 합니다. RunException: Exception의 하위 클래스로, 처리 여부를 사용자가 선택합니다.义 determin 5. 맞춤형 이상 클래스맞춤형 클래스 상속은 Exception 클래스에서 상속되며, 특정 이벤트를 처리하는 메서드를 작성할 수도 있습니다. Java는 사용자가 작성한 예외 클래스를 실행하기 위한 상속 방법을 제공합니다.
1 class MyException extends Exception
2 {
3 public MyException(String message)
4 {
5 super(message);
6 }
7 }
8 public class DefinedException
9 {
10 public static void main(String[] args)
11 {
12 try
13 {
14 throw new MyException("\n自定义异常类!");
15 }
16 catch(MyException e)
17 {
18 System.out.println(e);
19 }
20 }
21 }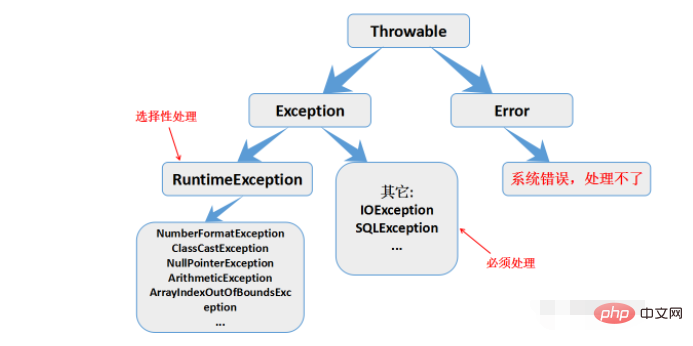 관련 학습 권장 사항:
관련 학습 권장 사항:
위 내용은 Java 예외를 포착하고 처리하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!