
1단계: 클래스 로드 초기화 전에 Java 객체가 로드되고 JVM에 Class 객체가 생성됩니다. 클래스를 로드하면 다음 작업이 수행되며 재귀적 설명은 아래와 같습니다.
클래스에 상위 클래스가 있는 경우 해당 상위 클래스를 먼저 로드하세요.
i 이 클래스의 정적 멤버 초기화
ii 이 클래스의 정적 코드 블록 실행
2단계: 객체 생성 클래스에 상위 클래스가 있는 경우 해당 상위 클래스의 객체는 객체를 생성할 때 먼저 생성되면 외부 레이어는 하위 클래스의 속성과 메서드를 래핑한 다음 하위 클래스의 참조를 반환합니다. 재귀적 설명은 다음과 같습니다.
클래스에 상위 클래스가 있는 경우 먼저 상위 클래스의 개체를 만듭니다.普I는 이러한 유형의 일반 멤버를 초기화합니다.
II 일반 코드 블록의 실행
III는 이러한 유형의 구조적 메소드를 호출합니다. 예:
멤버 변수로서의 객체 public class Info{ public Info(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
public class Parent {
public static Info info = new Info("Parent static member"); //静态成员
public Info info2 = new Info("Parent common member"); //普通成员
static { //静态代码块
System.out.println("parent static block");
}
{ //普通代码块
System.out.println("parent common block");
}
public Parent() { //父类构造方法
System.out.println("Parent.Parent()");
}
}public class Child extends Parent{
public static Info info = new Info("Child static member"); //静态成员
public Info info2 = new Info("Child common member"); //普通成员
static { //静态代码块
System.out.println("Child static block");
}
{ //普通代码块
System.out.println("Child common block");
}
public Child() { //子类构造方法
System.out.println("Child.Child()");
}
}public class InitObjectTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
//Class.forName("Parent");
Class.forName("Child");
}catch(Exception e){
}
//System.out.println("=============== now , we create an Object below ===========");
//new Parent();
}
}: 클래스 로딩은 한 번만 수행되며, 객체를 생성한 후에는 더 이상 클래스가 로드되지 않습니다. 이것이 바로 정적 코드 블록이 한 번만 실행되는 이유입니다. 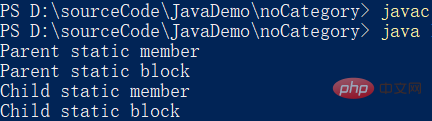
Java 입문 튜토리얼
위 내용은 Java에서 객체를 초기화하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!


