서버 측 렌더링(SSR)은 한동안 사용되어 왔지만 더 자세히 살펴볼 가치가 있습니다. 이 기술을 사용하면 웹 앱을 더 빠르고 SEO 친화적으로 만들 수 있습니다.
이 가이드에서는 SSR을 사용하고 싶은 이유, 그리고 손을 떼지 않고 구현하는 방법에 대해 설명합니다. 기본 사항을 다루고 이를 클라이언트 측 렌더링과 비교하고 몇 가지 실제 사례에 대해 논의하겠습니다.
기본적으로 SSR은 브라우저가 아닌 서버에서 웹페이지를 렌더링하는 것입니다. 사용자가 페이지를 요청하면 서버는 모든 무거운 작업을 수행하고 완전히 렌더링된 페이지를 클라이언트에 보냅니다. 그런 다음 클라이언트 측 JavaScript가 대신하여 대화형으로 만듭니다.
서버는 주방에서 준비작업을 하고, 브라우저는 접시를 담아 서빙만 하면 됩니다.
다음은 최소한의 Express.js 예입니다.
const express = require('express');
const React = require('react');
const ReactDOMServer = require('react-dom/server');
const App = require('./App');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
const html = ReactDOMServer.renderToString(<App />);
res.send(`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div>
<h2>
From server to browser with fully rendered pages
</h2>
<p>When we talk about SSR delivering "fully rendered pages," it's important to understand what that actually means. Let's break it down:</p>
<h3>
What is a fully rendered page?
</h3>
<p>A fully rendered page is an HTML document containing all the content users would get when they first load the page. This includes:</p>
<ol>
<li>The complete DOM structure</li>
<li>All text content</li>
<li>Image placeholders and other media elements</li>
<li>Initial styles</li>
</ol>
<p>Here's a basic example:<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My SSR Page</title>
<style>
/* Initial styles */
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>Welcome to My Site</h1>
<nav><!-- Fully populated navigation --></nav>
</header>
<main>
<article>
<h2>Article Title</h2>
<p>This is the full content of the article...</p>
</article>
</main>
<footer><!-- Fully populated footer --></footer>
<script src="hydration.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
반대로 클라이언트측 렌더링(CSR) 초기 HTML은 다음과 같을 수 있습니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My CSR Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>The CSR page relies entirely on JavaScript to populate the content.</p>
<h3>
Benefits of fully rendered HTML
</h3>
<ol>
<li>
<strong>Faster Initial Paint</strong>: The browser can start rendering content immediately.</li>
<li>
<strong>Better SEO</strong>: Search engines read all your content without executing JavaScript.</li>
<li>
<strong>Improved Accessibility</strong>: Screen readers and other assistive technologies can access content immediately.</li>
<li>
<strong>Resilience</strong>: Basic content is available even if JavaScript fails to load.</li>
</ol>
<h3>
The hydration process
</h3>
<p>After sending the fully rendered HTML, SSR applications typically go through a process called hydration:</p>
<ol>
<li>The server sends the fully rendered HTML.</li>
<li>The browser displays this HTML immediately.</li>
<li>JavaScript loads and <em>hydrates</em> the page, adding interactivity.</li>
</ol>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">// Simplified React hydration example
import { hydrateRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
const domNode = document.getElementById('root');
hydrateRoot(domNode, <App />);
이 프로세스를 사용하면 최신 웹 앱의 풍부한 상호 작용 기능을 계속 제공하면서 빠른 초기 로드가 가능합니다.
SSR은 완전히 렌더링된 페이지를 제공하지만 단점이 없는 것은 아닙니다. 서버는 더 많은 작업을 수행하므로 서버와 클라이언트 간의 상태를 주의 깊게 처리해야 합니다. 그러나 많은 애플리케이션의 경우 완전히 렌더링된 페이지의 이점으로 인해 SSR이 매력적인 선택이 됩니다.
CSR(클라이언트 측 렌더링)과 SSR(서버 측 렌더링)은 웹 페이지를 렌더링하는 두 가지 서로 다른 접근 방식입니다. 주요 차이점은 다음과 같습니다.
장점:
단점:
장점:
단점:
간단한 시각적 비교는 다음과 같습니다.
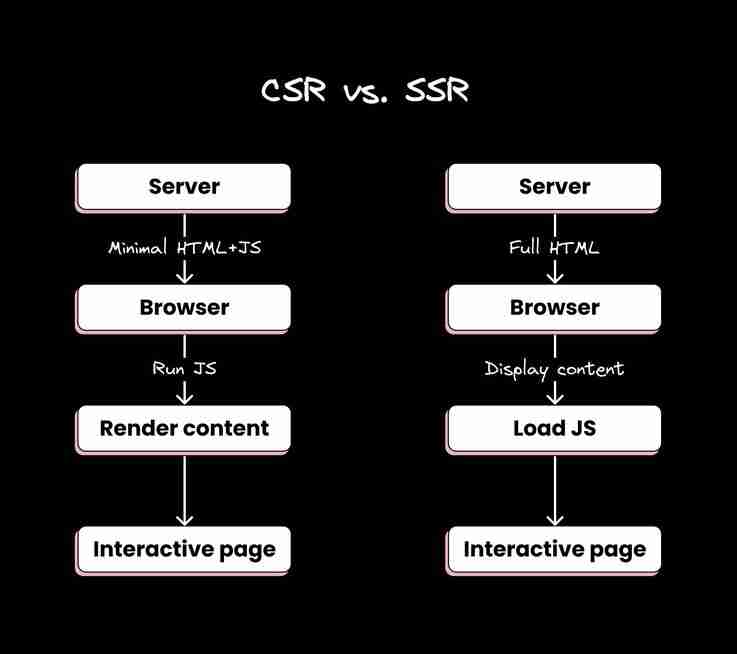
본질적으로 CSR은 브라우저에서 더 많은 작업을 수행하는 반면 SSR은 서버에서 더 많은 작업을 수행합니다. 이들 중 선택은 프로젝트의 특정 요구 사항, 초기 로드 시간, SEO 요구 사항 및 서버 리소스와 같은 균형 요소에 따라 달라집니다.
서버측 렌더링은 검색 엔진이 사이트를 보는 방식에 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 분석해 보겠습니다.
검색 엔진 봇은 참을성이 없습니다. 그들은 지금 귀하의 콘텐츠를 보고 싶어합니다. SSR을 사용하면 봇이 공격할 때 페이지를 바로 사용할 수 있습니다. JavaScript가 로드되고 렌더링될 때까지 기다리지 않아도 됩니다.

SSR은 검색 엔진이 사용자와 동일한 콘텐츠를 볼 수 있도록 보장합니다. 클라이언트측 렌더링을 사용하면 봇이 동적으로 로드된 일부 콘텐츠를 놓칠 위험이 항상 존재합니다.
검색 엔진은 빠른 사이트를 좋아합니다. SSR은 초기 로드 시간을 크게 줄여 순위에서 약간의 우위를 점할 수 있습니다.
const express = require('express');
const React = require('react');
const ReactDOMServer = require('react-dom/server');
const App = require('./App');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
const html = ReactDOMServer.renderToString(<App />);
res.send(`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div>
<h2>
From server to browser with fully rendered pages
</h2>
<p>When we talk about SSR delivering "fully rendered pages," it's important to understand what that actually means. Let's break it down:</p>
<h3>
What is a fully rendered page?
</h3>
<p>A fully rendered page is an HTML document containing all the content users would get when they first load the page. This includes:</p>
<ol>
<li>The complete DOM structure</li>
<li>All text content</li>
<li>Image placeholders and other media elements</li>
<li>Initial styles</li>
</ol>
<p>Here's a basic example:<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My SSR Page</title>
<style>
/* Initial styles */
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>Welcome to My Site</h1>
<nav><!-- Fully populated navigation --></nav>
</header>
<main>
<article>
<h2>Article Title</h2>
<p>This is the full content of the article...</p>
</article>
</main>
<footer><!-- Fully populated footer --></footer>
<script src="hydration.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Google의 모바일 우선 색인 생성을 통해 느린 모바일 연결에서 SSR의 성능 이점이 더욱 중요해졌습니다.
엄밀히 말하면 검색 엔진 기능은 아니지만 SSR을 사용하면 콘텐츠가 소셜 플랫폼에서 공유될 때 정확한 미리보기를 더 쉽게 생성할 수 있습니다. 이는 참여도와 백링크를 높여 SEO를 간접적으로 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My CSR Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>The CSR page relies entirely on JavaScript to populate the content.</p>
<h3>
Benefits of fully rendered HTML
</h3>
<ol>
<li>
<strong>Faster Initial Paint</strong>: The browser can start rendering content immediately.</li>
<li>
<strong>Better SEO</strong>: Search engines read all your content without executing JavaScript.</li>
<li>
<strong>Improved Accessibility</strong>: Screen readers and other assistive technologies can access content immediately.</li>
<li>
<strong>Resilience</strong>: Basic content is available even if JavaScript fails to load.</li>
</ol>
<h3>
The hydration process
</h3>
<p>After sending the fully rendered HTML, SSR applications typically go through a process called hydration:</p>
<ol>
<li>The server sends the fully rendered HTML.</li>
<li>The browser displays this HTML immediately.</li>
<li>JavaScript loads and <em>hydrates</em> the page, adding interactivity.</li>
</ol>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">// Simplified React hydration example
import { hydrateRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
const domNode = document.getElementById('root');
hydrateRoot(domNode, <App />);
SSR은 SEO를 위한 강력한 도구이지만 이것이 유일한 요소는 아닙니다. 콘텐츠 품질, 관련성 및 전반적인 사용자 경험은 검색 엔진 순위에 매우 중요합니다. SSR은 단순히 검색 엔진이 콘텐츠를 효율적으로 크롤링하고 색인화할 수 있도록 보장하여 잠재적으로 가시성 및 성능 지표 측면에서 우위를 점할 수 있도록 해줍니다.
SSR 구현이 복잡할 필요는 없습니다. SSR을 간단하게 만드는 인기 있는 React 프레임워크인 Next.js를 사용하여 이를 수행하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
다음은 앱 라우터를 사용하는 간단한 Next.js 예입니다.
// Pseudo-code for search engine ranking
function calculateRanking(site) {
let score = site.relevance;
if (site.loadTime < FAST_THRESHOLD) {
score += SPEED_BONUS;
}
return score;
}
이 예에서는:
Next.js는 SSR 프로세스를 자동으로 처리합니다.
이 접근 방식은 수동으로 서버를 설정하거나 렌더링 프로세스를 직접 관리할 필요 없이 SSR의 이점을 제공합니다.
바퀴를 다시 만들고 싶지 않다면 SSR 복잡성을 처리하는 여러 프레임워크가 있습니다. 다음은 다양한 생태계에서 인기 있는 옵션을 요약한 것입니다.

이러한 각 프레임워크는 정적 사이트 생성, API 경로 등과 같은 추가 기능과 함께 SSR에 대한 고유한 접근 방식을 제공합니다. 선택은 선호하는 언어, 생태계, 특정 프로젝트 요구 사항에 따라 달라집니다.
SSR 앱 배포 시:
기본 배포 흐름은 다음과 같습니다.

캐싱을 잊지 마세요! 서버에서 렌더링된 페이지를 캐싱하면 서버 부하를 크게 줄일 수 있습니다.
Builder.io는 모든 구성요소와 프레임워크 전반에 걸쳐 서버측 렌더링(SSR) 및 정적 사이트 생성(SSG)을 지원합니다. 이 기본 기능을 사용하면 추가 설정 없이 SSR 및 SSG의 이점을 활용할 수 있습니다.

다음은 Builder 및 Next.js를 사용하여 서버측에서 콘텐츠를 가져오고 렌더링하는 방법에 대한 기본 예입니다.
const express = require('express');
const React = require('react');
const ReactDOMServer = require('react-dom/server');
const App = require('./App');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
const html = ReactDOMServer.renderToString(<App />);
res.send(`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div>
<h2>
From server to browser with fully rendered pages
</h2>
<p>When we talk about SSR delivering "fully rendered pages," it's important to understand what that actually means. Let's break it down:</p>
<h3>
What is a fully rendered page?
</h3>
<p>A fully rendered page is an HTML document containing all the content users would get when they first load the page. This includes:</p>
<ol>
<li>The complete DOM structure</li>
<li>All text content</li>
<li>Image placeholders and other media elements</li>
<li>Initial styles</li>
</ol>
<p>Here's a basic example:<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My SSR Page</title>
<style>
/* Initial styles */
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>Welcome to My Site</h1>
<nav><!-- Fully populated navigation --></nav>
</header>
<main>
<article>
<h2>Article Title</h2>
<p>This is the full content of the article...</p>
</article>
</main>
<footer><!-- Fully populated footer --></footer>
<script src="hydration.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Builder for SSR을 활용하면 헤드리스 CMS의 유연성과 서버 측 렌더링의 성능 이점을 결합하는 동시에 사용하기 쉬운 시각적 편집 환경을 유지할 수 있습니다.
서버 측 렌더링(SSR)은 애플리케이션의 성능, SEO 및 사용자 경험을 크게 향상시킬 수 있는 웹 개발의 강력한 접근 방식입니다. 이 기사 전체에서 우리는 SSR이 무엇인지, 클라이언트 측 렌더링과 어떻게 다른지, 검색 엔진에 미치는 영향, Next.js와 같은 널리 사용되는 프레임워크를 사용한 실제 구현 전략을 살펴보았습니다.
또한 완전히 렌더링된 페이지의 개념에 대해 논의하고 다양한 생태계에 걸쳐 다양한 SSR 솔루션을 조사했습니다. SSR은 많은 이점을 제공하지만 구현 여부를 결정할 때 프로젝트의 구체적인 요구 사항을 고려하는 것이 중요합니다.
Q: SSR은 개발 작업 흐름에 어떤 영향을 미치나요?
A: SSR은 서버와 클라이언트 환경을 모두 고려해야 하기 때문에 개발을 더욱 복잡하게 만들 수 있습니다. 빌드 프로세스를 조정하고 브라우저별 API에 주의해야 할 수도 있습니다.
Q: SSR이 내 사이트의 TTI(Time to Interactive)에 어떤 영향을 미치나요
A: SSR은 초기 콘텐츠 가시성을 향상시킬 수 있지만 브라우저가 초기 HTML을 수신한 후 JavaScript를 로드하고 수화해야 하므로 TTI가 약간 지연될 수 있습니다.
Q: SSR과 관련된 보안 고려 사항이 있나요?
A: 네, SSR을 사용하면 민감한 데이터나 API가 서버 측에 노출되는 것에 대해 더 주의해야 합니다. 항상 사용자 입력을 삭제하고 초기 렌더링에 포함할 데이터에 주의하세요.
Q: SSR은 인증 및 개인화 콘텐츠와 어떻게 작동하나요?
A: SSR은 인증을 통해 작동할 수 있지만 주의 깊게 다루어야 합니다. 인증된 SSR 요청을 관리하려면 JWT 토큰이나 서버 측 세션과 같은 기술을 구현해야 할 수도 있습니다.
위 내용은 서버 측 렌더링 가이드의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!