큐 데이터 구조는 FIFO(선입선출) 원칙을 사용합니다. 처리할 개체를 도착 순서대로 보관하는 데 사용됩니다. 이것은 줄을 서 있는 사람들의 줄과 매우 유사합니다. Java는 Collection 인터페이스 형태로 데이터 구조에 대한 대규모 지원을 제공하므로 큐는 Collection 인터페이스에서 사용할 수 있는 인터페이스입니다. Collection 인터페이스를 확장합니다. Java.util 패키지에서 사용할 수 있으며 몇 가지 추가 추출, 삽입 및 검사 작업과 함께 Collection 인터페이스에서 사용할 수 있는 모든 작업을 지원합니다.
무료 소프트웨어 개발 과정 시작
웹 개발, 프로그래밍 언어, 소프트웨어 테스팅 등
구문:
Interface Queue<E>
큐는 클래스가 아닌 인터페이스이므로 직접 인스턴스화할 수 없습니다. 선언은 대기열이 컬렉션과 유사한 일반적인 값을 허용하며 모든 객체를 대기열에 전달할 수 있음을 보여줍니다. Java에는 대기열을 사용하는 동안 사용할 수 있는 대기열 인터페이스의 여러 구현이 있습니다. LinkedList와 PriorityQueue가 있습니다.
큐는 아래와 같이 선언할 수 있습니다.
Queue< Object > q = new LinkedList<>();
Queue< Object > q = new PriorityQueue<>();
Java의 대기열 구성원 유형
다음은 대기열에서 사용할 수 있는 모든 방법입니다.
| Returns special value | Throws exception | |
| Insert | offer(e) | add(e) |
| Remove | poll() | remove() |
| Examine | peek() | element() |
So as explained, two types of methods throw an exception and return a special value. There are three types of operation in this kind of operation: insertion, the second is removal, and the third is retrieval or examination. In the case of the remove operation, an object will be removed from the queue. Still, in the case of examination, the object will be returned without actually removing from the queue.
Given below are the different examples of Queue in Java:
Code:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
}
}Output:

Note here that the order of insertion is the same with output from left to write.
Code:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(q.remove() + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(q);
}
}Output:
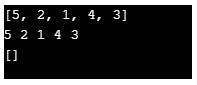
Here, we have used the function isEmpty() to check when the queue becomes empty after removing elements. The removal order is the same as per the insertion. After removing all the elements, we printed the queue and obtained an empty bracket at the end.
Code:
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(q.remove() + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(q);
}
}Output:

Here, we have used PriorityQueue, which will hold and return the elements depending upon the elements’ natural ordering or upon the comparator, if any passed. Note the insertion order and removal orders are not the same. The removal is based totally on the value of elements.
Code:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
System.out.println( q.peek() );
System.out.println(q);
}
}Output:

Note here that we have used the peek() function, which will return the head of the queue without actually removing it. We printed the queue after performing the peek operation, and you can observe that the head element, which is 5, remains unchanged in the queue.
Code:
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
System.out.println( q.peek() );
System.out.println(q);
}
}Output:

This is similar to the previous example’s LinkedList operation, but note the head element is 1 because it’s a PriorityQueue.
Java utilizes the Queue interface as a means to maintain elements in insertion order. It supports operations like insertion, retrieval, and removal. There are alternative methods available for all the methods. We have seen examples of the most commonly used methods in queue operation.
위 내용은 자바의 큐의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!