
This time I will show you how to use Vue.js calculated properties and listeners. What are theprecautionsfor using Vue.js calculated properties and listeners. The following is a practical case. Let’s take a look. take a look.
1. Overview
Calculated properties
Theexpressionin the template is very convenient, but They were originally designed for simple calculations. Putting too much logic into a template can make it overweight and difficult to maintain. For example:
{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}
Here, the template is no longer simple declarative logic. You have to watch for a while to realize that here you want to display the flippedStringof the variable message. It becomes more difficult to deal with when you want to reference the flipped string here multiple times in the template.
So, for any complex logic, you should use computed properties.
Basic example
Original message: "{{ message }}"
Computed reversed message: "{{ reversedMessage }}"
var vm = new Vue({ el: '#example', data: { message: 'Hello' }, computed: { // 计算属性的 getter reversedMessage: function () { // `this` 指向 vm 实例 return this.message.split('').reverse().join('') } } })
Result:
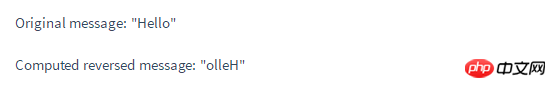
console.log(vm.reversedMessage) // => 'olleH' vm.message = 'Goodbye' console.log(vm.reversedMessage) // => 'eybdooG'
2. Computed property cache vs method
You may have noticed that we can achieve the same effect by calling methods in expressionsReversed message: "{{ reversedMessage() }}"
// 在组件中 methods: { reversedMessage: function () { return this.message.split('').reverse().join('') } }
computed: { now: function () { return Date.now() } }
3. Computed properties vs listening properties
Vue provides a more general way to observe and respond to data on Vue instances Changed: Listening properties. When you have some data that needs to change asotherdata changes, it's easy to abuse watches - especially if you've usedAngularJSbefore. However, it is often better to use computed properties instead of imperative watch callbacks.
Think about this example{{ fullName }}
var vm = new Vue({ el: '#demo', data: { firstName: 'Foo', lastName: 'Bar', fullName: 'Foo Bar' }, watch: { firstName: function (val) { this.fullName = val + ' ' + this.lastName }, lastName: function (val) { this.fullName = this.firstName + ' ' + val } } })
var vm = new Vue({ el: '#demo', data: { firstName: 'Foo', lastName: 'Bar' }, computed: { fullName: function () { return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName } } })
4. Computed property setters
Computed properties only have getters by default, but you can also provide a setter when needed// ... computed: { fullName: { // getter get: function () { return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName }, // setter set: function (newValue) { var names = newValue.split(' ') this.firstName = names[0] this.lastName = names[names.length - 1] } } } // ...
现在再运行 vm.fullName = 'John Doe' 时,setter 会被调用,vm.firstName 和 vm.lastName 也会相应地被更新。
五、侦听器
虽然计算属性在大多数情况下更合适,但有时也需要一个自定义的侦听器。这就是为什么 Vue 通过 watch 选项提供了一个更通用的方法,来响应数据的变化。当需要在数据变化时执行异步或开销较大的操作时,这个方式是最有用的。
例如:
Ask a yes/no question:
{{ answer }}
结果:当没有输入?号,那么显示如下:
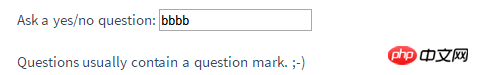
当有?时候会输出“yes”或者“no”
具体案例效果地址:侦听器

在这个示例中,使用 watch 选项允许我们执行异步操作 (访问一个 API),限制我们执行该操作的频率,并在我们得到最终结果前,设置中间状态。这些都是计算属性无法做到的。
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of How to use Vue.js computed properties with listeners. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




