
In actual development, there are usually dozens or even hundreds of routes, all written in index.js, which is bloated and difficult to maintain. In this case, express.Router can be used to implement a more elegant routing solution. This article mainly introduces the method of using Express.Router in Node.js in detail. It has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it. I hope it can help everyone.
The directory structure is as follows:
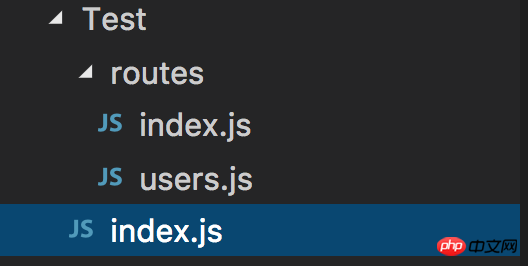
routes’ index.js code is as follows:
const express = require('express') const router = express.Router() router.get('/', function (req, res) { res.send('hello, express') }) module.exports = router
routes The users.js code is as follows:
const express = require('express') const router = express.Router() router.get('/:name', function (req, res) { res.send('hello, ' + req.params.name) }) module.exports = router
The main index.js code is as follows:
const express = require('express'); const app = express() const indexRouter = require('./routes/index'); const userRouter = require('./routes/users'); app.use('/', indexRouter); app.use('/users', userRouter); app.listen(3000);
Browser access request :
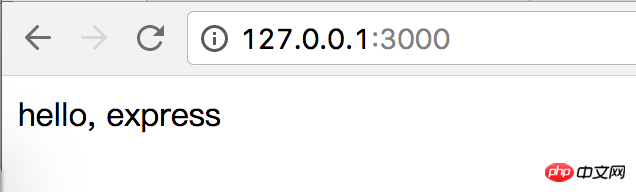
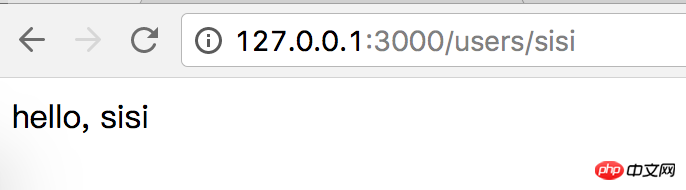
Each routing file generates an express.Router instance router and exports it, and mounts it to a different path through app.use .
In actual development, it is recommended to use express.Router to separate different routes into different routing files.
Related recommendations:
How to use the async function in Node.js
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Node.js using Express.Router. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




