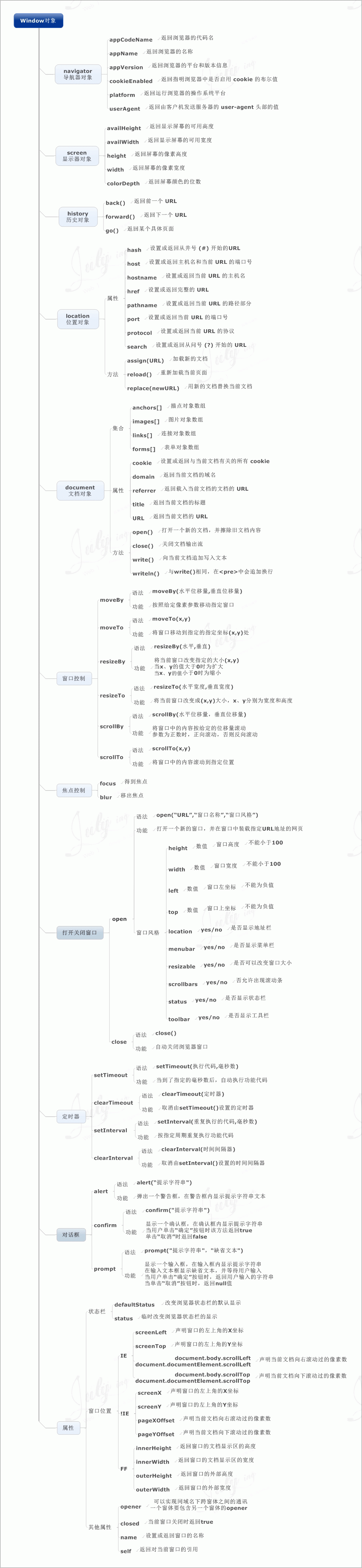
js composition
We all know that <font face="NSimsun">javascript</font> consists of three parts, <font face="NSimsun">ECMAScript</font>, <font face="NSimsun">DOM</font> and <font face="NSimsun">BOM</font>. The specific expressions vary depending on the host (browser), ie and other browsers Very different styles.
1. DOM is a standard of W3C; [a standard commonly observed by all browsers]
2. BOM is determined by each browser manufacturer according to DOM
Implementation on respective browsers; [shown as different browser definitions and different implementation methods]
3. window is a BOM object, not a js object;
<font face="NSimsun">DOM</font> (Document Object Model) is the application programming interface (<font face="NSimsun">HTML</font>) for <font face="NSimsun">XML</font> and <font face="NSimsun">API</font>.
<font face="NSimsun">BOM</font> mainly deals with browser windows and frames, but usually browser-specific <font face="NSimsun">JavaScript</font> extensions are considered part of the BOM. These extensions include:
弹出新的浏览器窗口 移动、关闭浏览器窗口以及调整窗口大小 提供 Web 浏览器详细信息的定位对象 提供用户屏幕分辨率详细信息的屏幕对象 对 cookie 的支持 IE 扩展了 BOM,加入了 ActiveXObject 类,可以通过 JavaScript 实例化 ActiveX 对象
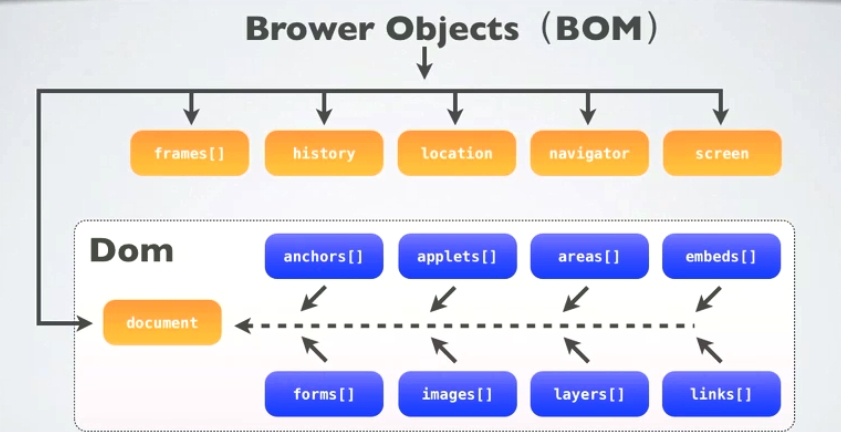
<font face="NSimsun">javacsript</font> accesses, controls, and modifies the client (browser) by accessing the <font face="NSimsun">BOM</font> (Browser Object Model) object. Since the <font face="NSimsun">BOM</font> of <font face="NSimsun">window</font> contains <font face="NSimsun">document</font>, the properties of the window object and The method is directly available and perceived, so you can directly use the <font face="NSimsun">window</font> attribute of the <font face="NSimsun">document</font> object. Through the <font face="NSimsun">document</font> attribute, you can access, retrieve, and modify the content and structure of the XHTML document. Because the <font face="NSimsun">document</font> object is the root node of the DOM (Document Object Model) model. It can be said that BOM contains <font face="NSimsun">DOM</font> (object). What the browser provides for access is the BOM object. From the BOM object to the <font face="NSimsun">DOM</font> object, js can operate the browser and the documents read by the browser. Among them
DOM contains: <font face="NSimsun">window</font>
Window对象包含属性:document、location、navigator、screen、history、frames Document根节点包含子节点:forms、location、anchors、images、links
As can be seen from <font face="NSimsun">window.document</font>, the most fundamental object of DOM is the sub-object of the window object of BOM.
Difference: DOM describes the methods and interfaces for processing web page content, and BOM describes the methods and interfaces for interacting with the browser.
Get to know DOM
Let’s take a look at the following code first:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8" />
<title>DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2><a href="http://www.baidu.com">javascript DOM</a></h2>
<p>对HTML元素进行操作,可添加、改变或移除css样式等</p>
<ul>
<li>Javascript</li>
<li>DOM</li>
<li>CSS</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
Decompose HTML code into DOM node hierarchy diagram:
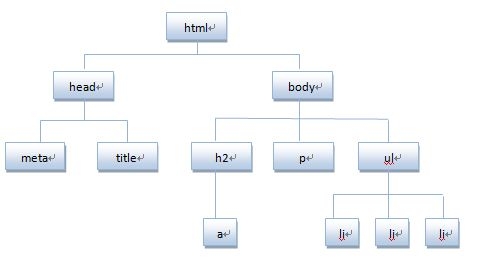
**HTML文档可以说由节点构成的集合,DOM节点有:** 1. 元素节点:上图中<html>、<body>、<p>等都是元素节点,即标签。 2. 文本节点:向用户展示的内容,如<li>...</li>中的JavaScript、DOM、CSS等文本。 3. 属性节点:元素属性,如<a>标签的链接属性href="http://www.baidu.com"。
Node attributesNode attributesnodeName returns a string whose content is the name of the nodenodeType returns an integer, this value represents the type of the given nodenodeValue returns the current value of the given node
Traverse the node treeTraverse the node treechildNodes returns an array consisting of the child nodes of a given element firstChild returns the first child node lastChild returns the last child node parentNode returns a given node Parent node nextSibling returns the next child node of the given node previousSibling returns the previous child node of the given node
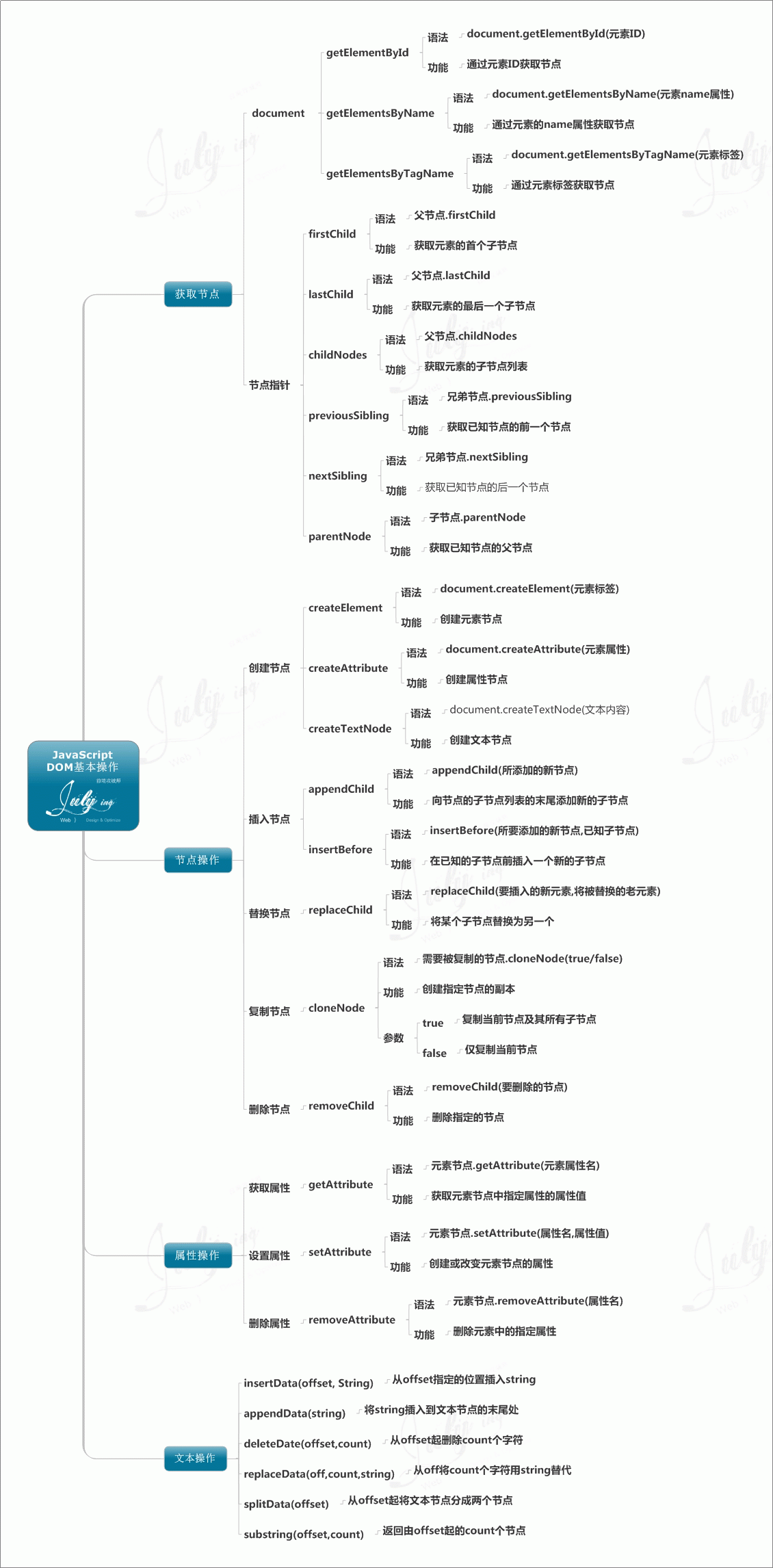
DOM OperationsDOM OperationscreatElement(element) creates a new element node creatTextNode() creates a new text node containing the given text appendChild() adds a new one after the last node list of the specified node insertBefore() inserts a given node in front of the given child node of a given element node removeChild() removes a child node from a given element replaceChild() replaces a child node of a given parent element Replace with another node
DOM represents documents by creating trees and describes methods and interfaces for processing web content, giving developers unprecedented control over the content and structure of documents. Nodes can be easily deleted, added and replaced using the DOM API.
1. Access node
`var oHtml = document.documentElement;` //返回存在于 XML 以及 HTML 文档中的文档根节点,oHtml包含了一个表示<html />的HTMLElement对象
`document.body` //是对 HTML 页面的特殊扩展,提供了对 <body> 标签的直接访问</span><span></span></span>
`document.getElementById("ID")` //通过指定的 ID 来返回元素,getElementById() 无法工作在 XML 中,IE6还会返回name为指定ID的元素
`document.getElementByName("name")`//获取所有name特性等于指定值的元素,不过在IE6和Opera7.5上还会返回id为给定名称的元素且仅检查<input/>和<img/>
`var x=document.getElementsByTagName("p");` //使用指定的标签名返回所有的元素列表NodeList,索引号从0开始。当参数是一个星号的时候,IE6并不返回所有的元素,必须用document.all来替代
2. Characteristics and methods of Node nodes
firstChild //Node,指向在childNodes列表中的第一个节点 lastChild //Node,指向在childNodes列表中的最后一个节点 parentNode //Node,指向父节 ownerDocument //Document,指向这个节点所属的文档 firstChild //Node,指向在childNodes列表中的第一个节点 lastChild //Node,指向在childNodes列表中的最后一个节点 parentNode //Node,指向父节点 childNodes //NodeList,所有子节点的列表 previousSibling /Node,/指向前一个兄弟节点:如果这个节点就是第一个节点,那么该值为 null `nextSibling` //Node,指向后一个兄弟节点:如果这个节点就是最后一个节点,那么该值为null `hasChildNodes()` //Boolean,当childNodes包含一个或多个节点时,返回真值
3.DOM events
DOM同时两种事件模型:冒泡型事件和捕获型事件
冒泡型事件:事件按照从最特定的事件目标到最不特定的事件目标的顺序触发
<body onclick="handleClick()">
<div onclick="handleClick()">Click Me</div>
</body>
触发的顺序是:div、body、html(IE 6.0和Mozilla 1.0)、document、window(Mozilla 1.0)
捕获型事件:与冒泡事件相反的过程,事件从最不精确的对象开始触发,然后到最精确
上面例子触发的顺序是:document、div
DOM事件模型最独特的性质是,文本节点也触发事件(在IE中不会)。
4. Event handling function/listening function
**事件处理函数/监听函数**
在JavaScript中:
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oDiv.onclick = function(){ //onclick只能用小写,默认为冒泡型事件
alert("Clicked!");
}
在HTML中:
<div onclick="javascript: alert("Clicked!")"></div> //onclick大小写任意
IE event handlers attachEvent() and detachEvent()
In IE, each element and window object has two methods: <font face="NSimsun">attachEvent()和detachEvent()</font>. These two methods accept the same two parameters, the event handler name and the event handler function, such as:
[object].attachEvent("name_of_event_handler","function_to_attach")
[object].detachEvent("name_of_event_handler","function_to_remove")
var fnClick = function(){
alert("Clicked!");
}
oDiv.attachEvent("onclick", fnClick); //添加事件处理函数
oDiv.attachEvent("onclick", fnClickAnother); // 可以添加多个事件处理函数
oDiv.detachEvent("onclick", fnClick); //移除事件处理函数
在使用<font face="NSimsun">attachEvent()</font>方法的情况下,事件处理程序会在全局作用域中运行,因此this等于window。
跨浏览器的事件处理程序
<code>addHandler()和removeHandler()</code>
<font face="NSimsun">addHandler()</font>方法属于一个叫EventUntil()的对象,这两个方法均接受三个相同的参数,要操作的元素,事件名称和事件处理程序函数。
事件类型
**事件类型** 鼠标事件:click、dbclick、mousedown、mouseup、mouseover、mouseout、mousemove 键盘事件:keydown、keypress、keyup HTML事件:load、unload、abort、error、select、change、submit、reset、 resize、scroll、focus、blur
事件处理器
执行JavaScript 代码的程序在事件发生时会对事件做出响应。为了响应一个特定事件
而被执行的代码称为事件处理器。
在HTML标签中使用事件处理器的语法是:
<code><HTML标签 事件处理器="JavaScript代码''> </code>
事件处理程序
事件就是用户或浏览器自身执行的某种动作。比如<font face="NSimsun">click,mouseup,keydown,mouseover</font>等都是事件的名字。而响应某个事件的函数就叫事件处理程序(事件监听器),事件处理程序以<font face="NSimsun">on</font>开头,因此<font face="NSimsun">click</font>的事件处理程序就是<font face="NSimsun">onclick</font>
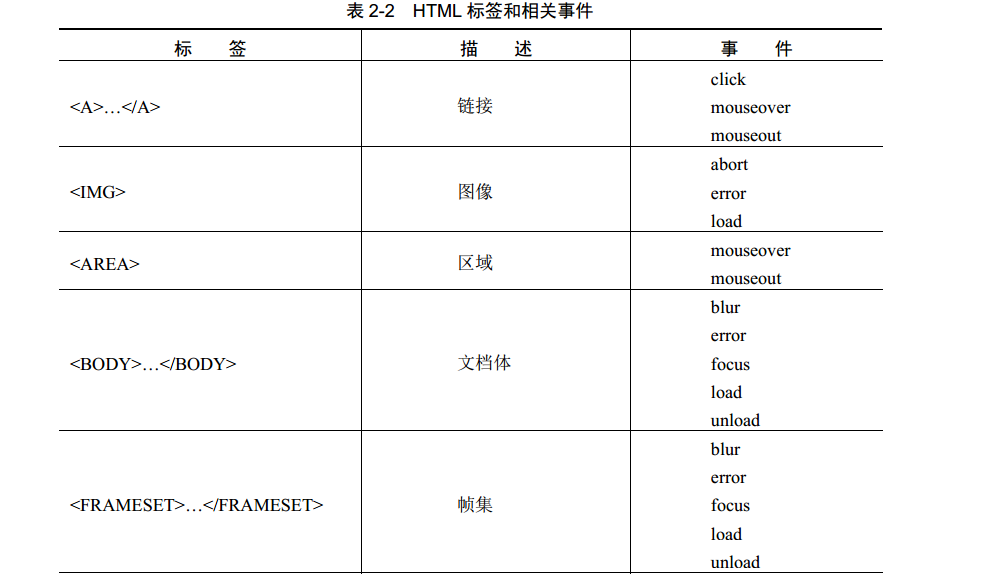
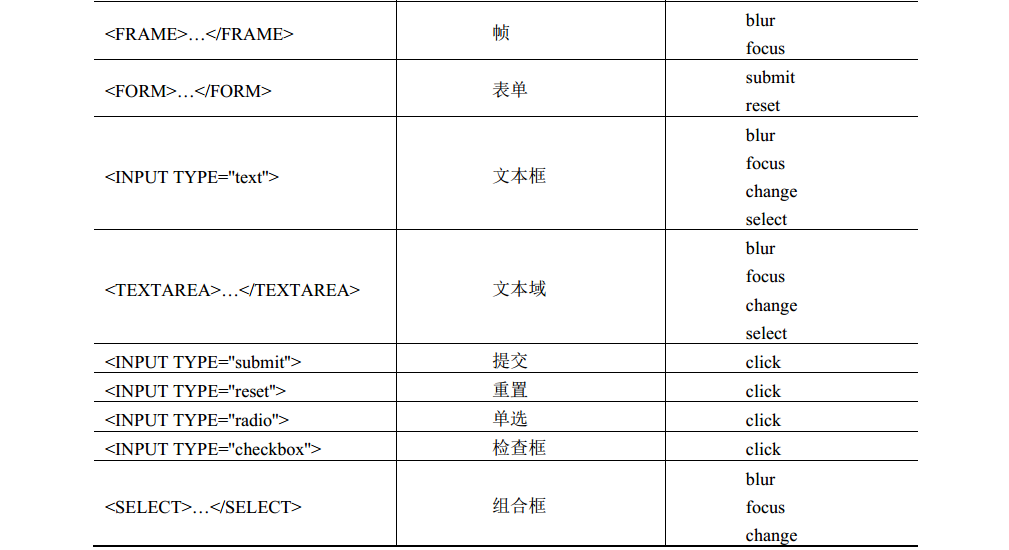
DOM 0级事件处理程序
DOM 0级事件处理程序:把一个函数赋值给一个事件的处理程序属性
<input type="button" value="按钮2" id="ben2"/>
var btn2=document.getElementById('btn2');获得btn2按钮对象
btn2.onclick //给btn2添加onclick属性,属性又触发了一个事件处理程序
btn2.onclick=function(){
} //添加匿名函数
btn2.onclick=null //删除onclick属性
如何阻止冒泡?
阻止冒泡有以下方法:
<code>e.cancelBubble=true; e.stopPropagation(); return false;</code>
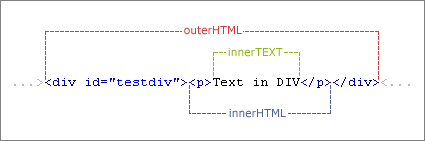
innerText、innerHTML、outerHTML、outerText
innerText、innerHTML、outerHTML、outerText innerText: 表示起始标签和结束标签之间的文本 innerHTML: 表示元素的所有元素和文本的HTML代码 如:<div><b>Hello</b> world</div>的innerText为Hello world,innerHTML为Hello world outerText: 与前者的区别是替换的是整个目标节点,问题返回和innerText一样的内容 outerHTML: 与前者的区别是替换的是整个目标节点,返回元素完整的HTML代码,包括元素本身
DOM 2级事件处理程序
DOM 2级事件定义了两个方法,用于指定和删除事件处理程序的操作。<font face="NSimsun">addEventListener()</font>和<font face="NSimsun">removeEventListener()</font>
addEventListener()和removeEventListener()
在DOM中,addEventListener()和removeEventListener()用来分配和移除事件处理函数,与IE不同的是,这些方法需要三个参数:事件名称,要分配的函数和处理函数是用于冒泡阶段(false)还是捕获阶段(true),默认为冒泡阶段false
[object].addEventListener("name_of_event",fnhander,bcapture)
[object].removeEventListener("name_of_event",fnhander,bcapture)
var fnClick = function(){
alert("Clicked!");
}
oDiv.addEventListener("onclick", fnClick, false); //添加事件处理函数
oDiv.addEventListener("onclick", fnClickAnother, false); // 与IE一样,可以添加多个事件处理函数
oDiv.removeEventListener("onclick", fnClick, false); //移除事件处理函数
如果使用addEventListener()将事件处理函数加入到捕获阶段,则必须在removeEventListener()中指明是捕获阶段,才能正确地将这个事件处理函数删除
oDiv.onclick = fnClick;
oDiv.onclick = fnClickAnother; //使用直接赋值,后续的事件处理函数会覆盖前面的处理函数
oDiv.onclick = fnClick;
oDiv.addEventListener("onclick", fnClickAnother, false); //会按顺序进行调用,不会覆盖
一张图了解OUTHTML和innerText、innerHTML:
DOM基本操作思维导图
更详细的XML DOM - Element 对象的属性和方法请访问w3cshool
BOM 部分
<font face="NSimsun">BOM</font>的核心是<font face="NSimsun">window</font>,而<font face="NSimsun">window</font>对象又具有双重角色,它既是通过js访问浏览器窗口的一个接口,又是一个<font face="NSimsun">Global</font>(全局)对象。这意味着在网页中定义的任何对象,变量和函数,都以window作为其<font face="NSimsun">global</font>对象。
window.close(); //关闭窗口
window.alert("message"); //弹出一个具有OK按钮的系统消息框,显示指定的文本
window.confirm("Are you sure?"); //弹出一个具有OK和Cancel按钮的询问对话框,返回一个布尔值
window.prompt("What's your name?", "Default"); //提示用户输入信息,接受两个参数,即要显示给用户的文本和文本框中的默认值,将文本框中的值作为函数值返回
window.status //可以使状态栏的文本暂时改变
window.defaultStatus //默认的状态栏信息,可在用户离开当前页面前一直改变文本
window.setTimeout("alert('xxx')", 1000); //设置在指定的毫秒数后执行指定的代码,接受2个参数,要执行的代码和等待的毫秒数
window.clearTimeout("ID"); //取消还未执行的暂停,将暂停ID传递给它
window.setInterval(function, 1000); //无限次地每隔指定的时间段重复一次指定的代码,参数同setTimeout()一样
window.clearInterval("ID"); //取消时间间隔,将间隔ID传递给它
window.history.go(-1); //访问浏览器窗口的历史,负数为后退,正数为前进
window.history.back(); //同上
window.history.forward(); //同上
window.history.length //可以查看历史中的页面数
document对象
document对象:实际上是window对象的属性,document == window.document为true,是唯一一个既属于BOM又属于DOM的对象 document.lastModified //获取最后一次修改页面的日期的字符串表示 document.referrer //用于跟踪用户从哪里链接过来的 document.title //获取当前页面的标题,可读写 document.URL //获取当前页面的URL,可读写 document.anchors[0]或document.anchors["anchName"] //访问页面中所有的锚 document.forms[0]或document.forms["formName"] //访问页面中所有的表单 document.images[0]或document.images["imgName"] // 访问页面中所有的图像 document.links [0]或document.links["linkName"] //访问页面中所有的链接 document.applets [0]或document.applets["appletName"] //访问页面中所有的Applet document.embeds [0]或document.embeds["embedName"] //访问页面中所有的嵌入式对象 document.write(); 或document.writeln(); //将字符串插入到调用它们的位置
location对象
location对象:表示载入窗口的URL,也可用window.location引用它
location.href //当前载入页面的完整URL,如http://www.somewhere.com/pictures/index.htm
location.portocol //URL中使用的协议,即双斜杠之前的部分,如http
location.host //服务器的名字,如www.wrox.com
location.hostname //通常等于host,有时会省略前面的www
location.port //URL声明的请求的端口,默认情况下,大多数URL没有端口信息,如8080
location.pathname //URL中主机名后的部分,如/pictures/index.htm
location.search //执行GET请求的URL中的问号后的部分,又称查询字符串,如?param=xxxx
location.hash //如果URL包含#,返回该符号之后的内容,如#anchor1
location.assign("http:www.baidu.com"); //同location.href,新地址都会被加到浏览器的历史栈中
location.replace("http:www.baidu.com"); //同assign(),但新地址不会被加到浏览器的历史栈中,不能通过back和forward访问
location.reload(true | false); //重新载入当前页面,为false时从浏览器缓存中重载,为true时从服务器端重载,默认为false
navigator对象
`navigator`对象:包含大量有关Web浏览器的信息,在检测浏览器及操作系统上非常有用,也可用window.navigator引用它 `navigator.appCodeName` //浏览器代码名的字符串表示 navigator.appName //官方浏览器名的字符串表示 navigator.appVersion //浏览器版本信息的字符串表示 navigator.cookieEnabled //如果启用cookie返回true,否则返回false navigator.javaEnabled //如果启用java返回true,否则返回false navigator.platform //浏览器所在计算机平台的字符串表示 navigator.plugins //安装在浏览器中的插件数组 navigator.taintEnabled //如果启用了数据污点返回true,否则返回false navigator.userAgent //用户代理头的字符串表示
screen对象
screen对象:用于获取某些关于用户屏幕的信息,也可用window.screen引用它 screen.width/height //屏幕的宽度与高度,以像素计 screen.availWidth/availHeight //窗口可以使用的屏幕的宽度和高度,以像素计 screen.colorDepth //用户表示颜色的位数,大多数系统采用32位 window.moveTo(0, 0); window.resizeTo(screen.availWidth, screen.availHeight); //填充用户的屏幕
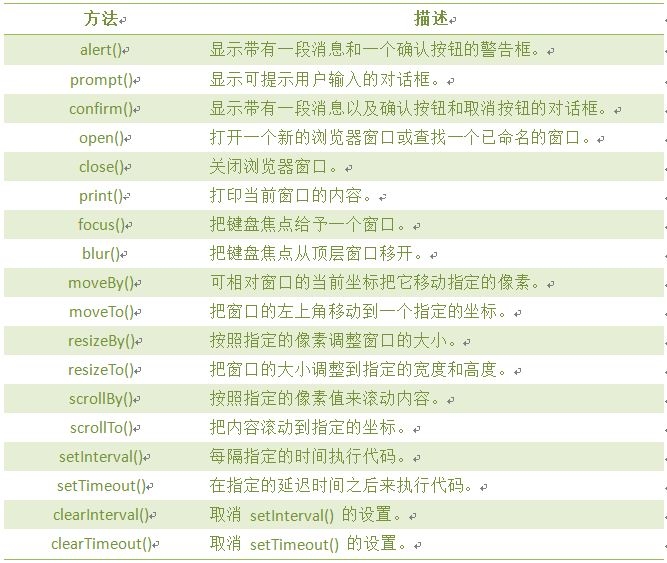
window对象方法
BOM和DOM的结构关系示意图
window对象思维导图