
这篇文章主要分享了Java异常简介和架构,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考一下
Java异常简介
Java异常是Java提供的一种识别及响应错误的一致性机制。
Java异常机制可以使程序中异常处理代码和正常业务代码分离,保证程序代码更加优雅,并提高程序健壮性。在有效使用异常的情况下,异常能清晰的回答what, where, why这3个问题:异常类型回答了“什么”被抛出,异常堆栈跟踪回答了“在哪“抛出,异常信息回答了“为什么“会抛出。
Java异常机制用到的几个关键字:try、catch、finally、throw、throws。
• try -- 用于监听。将要被监听的代码(可能抛出异常的代码)放在try语句块之内,当try语句块内发生异常时,异常就被抛出。
• catch -- 用于捕获异常。catch用来捕获try语句块中发生的异常。
• finally -- finally语句块总是会被执行。它主要用于回收在try块里打开的物力资源(如数据库连接、网络连接和磁盘文件)。只有finally块,执行完成之后,才会回来执行try或者catch块中的return或者throw语句,如果finally中使用了return或者throw等终止方法的语句,则就不会跳回执行,直接停止。
• throw -- 用于抛出异常。
• throws -- 用在方法签名中,用于声明该方法可能抛出的异常。
下面通过几个示例对这几个关键字进行简单了解。
示例一: 了解try和catch基本用法
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int i = 10/0;
System.out.println("i="+i);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Caught Exception");
System.out.println("e.getMessage(): " + e.getMessage());
System.out.println("e.toString(): " + e.toString());
System.out.println("e.printStackTrace():");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}运行结果:
Caught Exception
e.getMessage(): / by zero
e.toString(): java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
e.printStackTrace():
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at Demo1.main(Demo1.java:6)
结果说明:在try语句块中有除数为0的操作,该操作会抛出java.lang.ArithmeticException异常。通过catch,对该异常进行捕获。
观察结果我们发现,并没有执行System.out.println("i="+i)。这说明try语句块发生异常之后,try语句块中的剩余内容就不会再被执行了。
示例二: 了解finally的基本用法
在"示例一"的基础上,我们添加finally语句。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int i = 10/0;
System.out.println("i="+i);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Caught Exception");
System.out.println("e.getMessage(): " + e.getMessage());
System.out.println("e.toString(): " + e.toString());
System.out.println("e.printStackTrace():");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("run finally");
}
}
}运行结果:
Caught Exception
e.getMessage(): / by zero
e.toString(): java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
e.printStackTrace():
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at Demo2.main(Demo2.java:6)
run finally
结果说明:最终执行了finally语句块。
示例三: 了解throws和throw的基本用法
throws是用于声明抛出的异常,而throw是用于抛出异常。
class MyException extends Exception {
public MyException() {}
public MyException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test();
} catch (MyException e) {
System.out.println("Catch My Exception");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void test() throws MyException{
try {
int i = 10/0;
System.out.println("i="+i);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
throw new MyException("This is MyException");
}
}
}运行结果:
Catch My Exception
MyException: This is MyException
at Demo3.test(Demo3.java:24)
at Demo3.main(Demo3.java:13)
结果说明:
MyException是继承于Exception的子类。test()的try语句块中产生ArithmeticException异常(除数为0),并在catch中捕获该异常;接着抛出MyException异常。main()方法对test()中抛出的MyException进行捕获处理。
Java异常框架
Java异常架构图
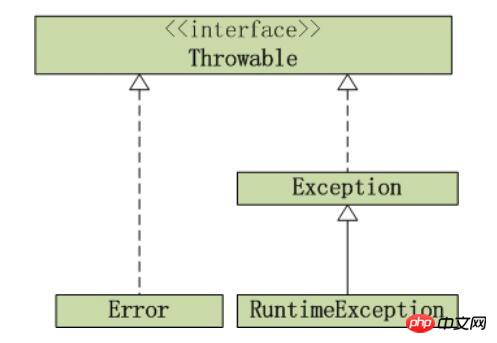
1. Throwable
Throwable是 Java 语言中所有错误或异常的超类。
Throwable包含两个子类: Error 和 Exception。它们通常用于指示发生了异常情况。
Throwable包含了其线程创建时线程执行堆栈的快照,它提供了printStackTrace()等接口用于获取堆栈跟踪数据等信息。
2. Exception
Exception及其子类是 Throwable 的一种形式,它指出了合理的应用程序想要捕获的条件。
3. RuntimeException
RuntimeException是那些可能在 Java 虚拟机正常运行期间抛出的异常的超类。
编译器不会检查RuntimeException异常。例如,除数为零时,抛出ArithmeticException异常。RuntimeException是ArithmeticException的超类。当代码发生除数为零的情况时,倘若既"没有通过throws声明抛出ArithmeticException异常",也"没有通过try...catch...处理该异常",也能通过编译。这就是我们所说的"编译器不会检查RuntimeException异常"!
如果代码会产生RuntimeException异常,则需要通过修改代码进行避免。例如,若会发生除数为零的情况,则需要通过代码避免该情况的发生!
4. Error
和Exception一样,Error也是Throwable的子类。它用于指示合理的应用程序不应该试图捕获的严重问题,大多数这样的错误都是异常条件。
和RuntimeException一样,编译器也不会检查Error。
Java将可抛出(Throwable)的结构分为三种类型:被检查的异常(Checked Exception),运行时异常(RuntimeException)和错误(Error)。
(01) 运行时异常
定义: RuntimeException及其子类都被称为运行时异常。
特点: Java编译器不会检查它。也就是说,当程序中可能出现这类异常时,倘若既"没有通过throws声明抛出它",也"没有用try-catch语句捕获它",还是会编译通过。例如,除数为零时产生的ArithmeticException异常,数组越界时产生的IndexOutOfBoundsException异常,fail-fail机制产生的ConcurrentModificationException异常等,都属于运行时异常。
虽然Java编译器不会检查运行时异常,但是我们也可以通过throws进行声明抛出,也可以通过try-catch对它进行捕获处理。
如果产生运行时异常,则需要通过修改代码来进行避免。例如,若会发生除数为零的情况,则需要通过代码避免该情况的发生!
(02) 被检查的异常
定义: Exception类本身,以及Exception的子类中除了"运行时异常"之外的其它子类都属于被检查异常。
特点: Java编译器会检查它。此类异常,要么通过throws进行声明抛出,要么通过try-catch进行捕获处理,否则不能通过编译。例如,CloneNotSupportedException就属于被检查异常。当通过clone()接口去克隆一个对象,而该对象对应的类没有实现Cloneable接口,就会抛出CloneNotSupportedException异常。
被检查异常通常都是可以恢复的。
(03) 错误
定义: Error类及其子类。
特点: 和运行时异常一样,编译器也不会对错误进行检查。
当资源不足、约束失败、或是其它程序无法继续运行的条件发生时,就产生错误。程序本身无法修复这些错误的。例如,VirtualMachineError就属于错误。
按照Java惯例,我们是不应该是实现任何新的Error子类的!
对于上面的3种结构,我们在抛出异常或错误时,到底该哪一种?《Effective Java》中给出的建议是:对于可以恢复的条件使用被检查异常,对于程序错误使用运行时异常。
The above is the detailed content of 简单介绍Java的异常和架构. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!