
数学では、ガウス ノイズは、平均 0 と標準偏差 (σ) の正規分布したランダム値を入力データに追加することによって生成されるノイズの一種です。ガウス分布としても知られる正規分布は、確率密度関数 (PDF) によって定義される連続確率分布です。は確率変数、μ は平均、σ は標準偏差です。
正規分布でランダムな値を生成し、入力データに追加します。たとえば、ガウス ノイズを画像に追加する場合、画像をピクセル値の 2 次元行列として表現し、numpy ライブラリ np.random.randn(rows,cols) を使用してランダムな値を生成できます。正規分布を取得し、ピクセル値で画像に追加します。これにより、ガウス ノイズが追加された新しい画像が生成されます。
ガウス ノイズはホワイト ノイズとも呼ばれ、正規分布に従うランダム ノイズの一種です。深層学習では、モデルの堅牢性と汎化能力を向上させるために、トレーニング中に入力データにガウス ノイズが追加されることがよくあります。これはデータ拡張と呼ばれます。入力データにノイズを追加することにより、モデルは入力の小さな変化に対して堅牢な特徴を学習することを強制され、新しい未知のデータに対するパフォーマンスの向上に役立ちます。トレーニング中にニューラル ネットワークの重みにガウス ノイズを追加して、パフォーマンスを向上させることもできます。これはドロップアウトと呼ばれる手法です。 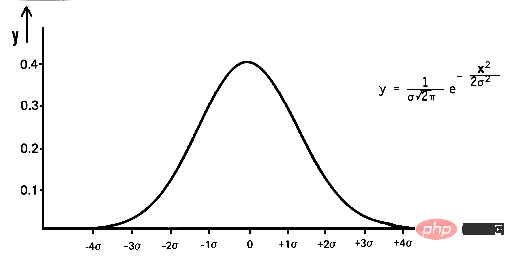
pdf(x) = (1 / (σ * sqrt(2 * π))) * e^(- (x — μ)² / (2 * σ²))
ガウス ノイズをディープ ラーニングで使用する方法の例をいくつか示します。
データ拡張: 深層学習におけるガウス ノイズの一般的な使用法は、トレーニング中に入力データにガウス ノイズを追加することです。たとえば、各画像がモデルに渡される前にガウス ノイズを追加できます。これにより、モデルは、画像内の汚れやわずかな欠落を表す可能性のある、入力の小さな変化に対して堅牢な特徴を学習するように強制されます。したがって、画像がトレーニング データとわずかに異なる場合でも、モデルは画像を正確に識別する可能性が高くなります。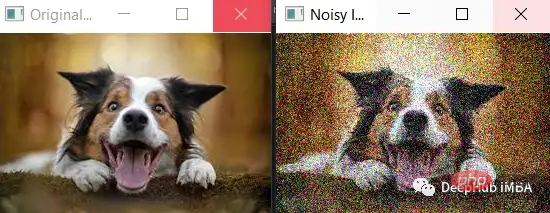 ドロップアウト: 深層学習におけるガウス ノイズのもう 1 つの用途は、トレーニング中にニューラル ネットワークの重みにガウス ノイズを追加することです。これをドロップアウトと呼びます。トレーニング中に、ドロップアウトはネットワーク内の一部の重みを特定の確率 (例: 0.5) でランダムにゼロに設定します。これにより、ネットワークはデータの複数の冗長表現を学習することになり、モデルがより堅牢になり、過学習が起こりにくくなります。
ドロップアウト: 深層学習におけるガウス ノイズのもう 1 つの用途は、トレーニング中にニューラル ネットワークの重みにガウス ノイズを追加することです。これをドロップアウトと呼びます。トレーニング中に、ドロップアウトはネットワーク内の一部の重みを特定の確率 (例: 0.5) でランダムにゼロに設定します。これにより、ネットワークはデータの複数の冗長表現を学習することになり、モデルがより堅牢になり、過学習が起こりにくくなります。
正則化: モデルのパラメーターにガウス ノイズを追加することも、正則化手法とみなすことができます。これにより、モデルの重み値がより小さくなるように強制され、その結果、モデルがより一般的になり、過学習が起こりにくくなります。
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator # Define the data generator datagen = ImageDataGenerator( featurewise_center=False,# set input mean to 0 over the dataset samplewise_center=False,# set each sample mean to 0 featurewise_std_normalization=False,# divide inputs by std of the dataset samplewise_std_normalization=False,# divide each input by its std zca_whitening=False,# apply ZCA whitening rotation_range=0,# randomly rotate images in the range (degrees, 0 to 180) width_shift_range=0.1,# randomly shift images horizontally (fraction of total width) height_shift_range=0.1,# randomly shift images vertically (fraction of total height) horizontal_flip=False,# randomly flip images vertical_flip=False,# randomly flip images noise_std=0.5# add gaussian noise to the data with std of 0.5 ) # Use the generator to transform the data during training model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32), steps_per_epoch=len(x_train) / 32, epochs=epochs)
Keras 的 ImageDataGenerator 类用于定义一个数据生成器,该数据生成器将指定的数据增强技术应用于输入数据。 我们将 noise_std 设置为 0.5,这意味着标准偏差为 0.5 的高斯噪声将添加到输入数据中。 然后在调用 model.fit_generator 期间使用生成器在训练期间将数据扩充应用于输入数据。
至于Dropout,可以使用Keras中的Dropout层,设置dropout的rate,如果设置rate为0.5,那么dropout层会drop掉50%的权重。 以下是如何向模型添加 dropout 层的示例:
from keras.layers import Dropout model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(64, input_dim=64, activation='relu')) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
需要注意的是,标准差、Dropout的实际值将取决于具体问题和数据的特征。使用不同的值进行试验并监视模型的性能通常是一个好主意。
下面我们介绍使用Keras 在训练期间将高斯噪声添加到输入数据和权重。为了向输入数据添加噪声,我们可以使用 numpy 库生成随机噪声并将其添加到输入数据中。 这是如何执行此操作的示例:
import numpy as np # Generate some random input data x_train = np.random.rand(1000, 64) y_train = np.random.rand(1000, 10) # Add Gaussian noise to the input data noise_std = 0.5 x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_std * np.random.randn(*x_train.shape) # Train the model model.fit(x_train_noisy, y_train, epochs=10)
我们输入数据 x_train 是形状为 (1000, 64) 的二维数组,噪声是使用 np.random.randn(*x_train.shape) 生成的,它将返回具有相同形状的正态分布均值为 0,标准差为 1的随机值数组。然后将生成的噪声与噪声的标准差 (0.5) 相乘,并将其添加到输入数据中,从而将其添加到输入数据中。
为了给权重添加噪声,我们可以使用 Keras 中的 Dropout 层,它会在训练过程中随机丢弃一些权重。 高斯噪声是深度学习中广泛使用的技术,在图像分类训练时可以在图像中加入高斯噪声,提高图像分类模型的鲁棒性。 这在训练数据有限或具有很大可变性时特别有用,因为模型被迫学习对输入中的小变化具有鲁棒性的特征。
以下是如何在训练期间向图像添加高斯噪声以提高图像分类模型的鲁棒性的示例:
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator # Define the data generator datagen = ImageDataGenerator( featurewise_center=False,# set input mean to 0 over the dataset samplewise_center=False,# set each sample mean to 0 featurewise_std_normalization=False,# divide inputs by std of the dataset samplewise_std_normalization=False,# divide each input by its std zca_whitening=False,# apply ZCA whitening rotation_range=0,# randomly rotate images in the range (degrees, 0 to 180) width_shift_range=0,# randomly shift images horizontally (fraction of total width) height_shift_range=0,# randomly shift images vertically (fraction of total height) horizontal_flip=False,# randomly flip images vertical_flip=False,# randomly flip images noise_std=0.5# add gaussian noise to the data with std of 0.5 ) # Use the generator to transform the data during training model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32), steps_per_epoch=len(x_train) / 32, epochs=epochs)
目标检测:在目标检测模型的训练过程中,可以将高斯噪声添加到输入数据中,以使其对图像中的微小变化(例如光照条件、遮挡和摄像机角度)更加鲁棒。
def add_noise(image, std): """Add Gaussian noise to an image.""" noise = np.random.randn(*image.shape) * std return np.clip(image + noise, 0, 1) # Add noise to the training images x_train_noisy = np.array([add_noise(img, 0.1) for img in x_train]) # Train the model model.fit(x_train_noisy, y_train, epochs=10)
语音识别:在训练过程中,可以在音频数据中加入高斯噪声,这可以帮助模型更好地处理音频信号中的背景噪声和其他干扰,提高语音识别模型的鲁棒性。
def add_noise(audio, std): """Add Gaussian noise to an audio signal.""" noise = np.random.randn(*audio.shape) * std return audio + noise # Add noise to the training audio x_train_noisy = np.array([add_noise(audio, 0.1) for audio in x_train]) # Train the model model.fit(x_train_noisy, y_train, epochs=10)
生成模型:在 GAN、Generative Pre-training Transformer (GPT) 和 VAE 等生成模型中,可以在训练期间将高斯噪声添加到输入数据中,以提高模型生成新的、看不见的数据的能力。
# Generate random noise noise = np.random.randn(batch_size, 100) # Generate fake images fake_images = generator.predict(noise) # Add Gaussian noise to the fake images fake_images_noisy = fake_images + 0.1 * np.random.randn(*fake_images.shape) # Train the discriminator discriminator.train_on_batch(fake_images_noisy, np.zeros((batch_size, 1)))
在这个例子中,生成器被训练为基于随机噪声作为输入生成新的图像,并且在生成的图像传递给鉴别器之前,将高斯噪声添加到生成的图像中。这提高了生成器生成新的、看不见的数据的能力。
对抗训练:在对抗训练时,可以在输入数据中加入高斯噪声,使模型对对抗样本更加鲁棒。
下面的对抗训练使用快速梯度符号法(FGSM)生成对抗样本,高斯噪声为 在训练期间将它们传递给模型之前添加到对抗性示例中。 这提高了模型对对抗性示例的鲁棒性。
# Generate adversarial examples x_adv = fgsm(model, x_train, y_train, eps=0.01) # Add Gaussian noise to the adversarial examples noise_std = 0.05 x_adv_noisy = x_adv + noise_std * np.random.randn(*x_adv.shape) # Train the model model.fit(x_adv_noisy, y_train, epochs=10)
去噪:可以将高斯噪声添加到图像或信号中,模型的目标是学习去除噪声并恢复原始信号。下面的例子中输入图像“x_train”首先用标准的高斯噪声破坏 0.1 的偏差,然后将损坏的图像通过去噪自动编码器以重建原始图像。 自动编码器学习去除噪声并恢复原始信号。
# Add Gaussian noise to the images noise_std = 0.1 x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_std * np.random.randn(*x_train.shape) # Define the denoising autoencoder input_img = Input(shape=(28, 28, 1)) x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(input_img) x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x) x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) encoded = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x) # at this point the representation is (7, 7, 32) x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(encoded) x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x) x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x) decoded = Conv2D(1, (3, 3), activation='sigmoid', padding='same')(x) autoencoder = Model(input_img, decoded) autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary
异常检测:高斯噪声可以添加到正常数据中,模型的目标是学习将添加的噪声作为异常检测。
# Add Gaussian noise to the normal data noise_std = 0.1 x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_std * np.random.randn(*x_train.shape) # Concatenate the normal and the noisy data x_train_concat = np.concatenate((x_train, x_train_noisy)) y_train_concat = np.concatenate((np.zeros(x_train.shape[0]), np.ones(x_train_noisy.shape[0]))) # Train the anomaly detection model model.fit(x_train_concat, y_train_concat, epochs=10)
稳健优化:在优化过程中,可以将高斯噪声添加到模型的参数中,使其对参数中的小扰动更加稳健。
Define the loss function def loss_fn(params): model.set_weights(params) return model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=32)[0] # Define the optimizer optimizer = optimizers.Adam(1e-3) # Define the step function def step_fn(params): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: loss = loss_fn(params) grads = tape.gradient(loss, params) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, params)) return params + noise_std * np.random.randn(*params.shape) # Optimize the model params = model.get_weights()
高斯噪声是深度学习中用于为输入数据或权重添加随机性的一种技术。 它是一种通过将均值为零且标准差 (σ) 正态分布的随机值添加到输入数据中而生成的随机噪声。 向数据中添加噪声的目的是使模型对输入中的小变化更健壮,并且能够更好地处理看不见的数据。 高斯噪声可用于广泛的应用,例如图像分类、对象检测、语音识别、生成模型和稳健优化。
以上が深層学習におけるガウス ノイズ: その理由と使用方法の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。