

[関連する学習の推奨事項: python チュートリアル]
あなたも私と同じように、暗号化されたデジタル通貨の基盤となるブロックチェーン テクノロジーに非常に興味がありますか?興味があり、特にどのように動作するかを知りたいです。
しかし、ブロックチェーン技術を学ぶのは簡単ではありません。たくさんのビデオチュートリアルやさまざまなコースを見てきましたが、最終的に感じたのは、実際に利用できる実践的なコースが少なすぎるということです。
私は実際に学ぶのが好きで、特に 1 つのコードに基づいて動作メカニズム全体を理解するのが好きです。私と同じようにこの学習方法が好きなら、このチュートリアルを終える頃には、ブロックチェーン技術がどのように機能するかを理解しているでしょう。
ブロックチェーンは、ブロックと呼ばれる 不変で順序付けられた レコードのチェーンであることを思い出してください。トランザクション、ファイル、または任意のデータを含めることができます。ただし、重要なことは、これらが hash を使用してリンクされていることです。
ハッシュに詳しくない場合は、ここで説明します。
このガイドの目的は何ですか?
HTTP を介したブロックチェーンの操作について説明するため、基本的な Python を安心して読み書きできるようになります。 HTTP の仕組み。
何を準備する必要がありますか?
Python 3.6 (および pip) がインストールされていることを確認してください。また、Flask と Requests もインストールする必要がありますlibrary:
pip install Flask==0.12.2 requests==2.18.4
ちなみに、Postman や cURL などの HTTP をサポートするクライアントも必要ですが、その他のクライアントも使用できます。
ソース コードはどこですか?
ここをクリックできます
お気に入りのテキスト エディターまたは IDE を開きます, 個人的には PyCharm の方が良いので、blockchain.py という名前の新しいファイルを作成します。この 1 つのファイルだけを使用します。ただし、まだよくわからない場合は、ソース コードを参照することもできます。
Blockchain クラスとそのコンストラクターを作成します。 (ブロックチェーンを保存するために) 初期化するための空のリストと、トランザクションを保存するための別のリストを作成します。以下はクラスの例です:
blockchain.py
class Blockchain(object): def __init__(self): self.chain = [] self.current_transactions = [] def new_block(self): # Creates a new Block and adds it to the chain pass def new_transaction(self): # Adds a new transaction to the list of transactions pass @staticmethod def hash(block): # Hashes a Block pass @property def last_block(self): # Returns the last Block in the chain pass
私たちの Blockchain クラスは連鎖データの管理を担当し、データを保存します。トランザクション そして、連鎖されたデータに新しいブロックを追加するメソッドもあります。さらにメソッドを拡張してみましょう。
各ブロックには、index、タイムスタンプ (Unix タイムスタンプ) 、トランザクション リストがあります。 、 チェックサム (これについては後で詳しく説明します)、および 前のブロックのハッシュ 。
ブロックの例は次のとおりです:
blockchain.py
block = {
'index': 1,
'timestamp': 1506057125.900785,
'transactions': [
{
'sender': "8527147fe1f5426f9dd545de4b27ee00",
'recipient': "a77f5cdfa2934df3954a5c7c7da5df1f",
'amount': 5,
}
],
'proof': 324984774000,
'previous_hash': "2cf24dba5fb0a30e26e83b2ac5b9e29e1b161e5c1fa7425e73043362938b9824"
}この時点で、ブロックチェーンの概念明らかなはずです。各新しいブロックには、その中に前のブロックの ハッシュ が含まれています。これは、blockchain を不変にするものであるため、非常に重要です。攻撃者が blockchain 内の以前のブロックを破損した場合、後続のすべてのブロックには正しいハッシュ値が含まれなくなります。
これは意味がありますか?まだ理解していない場合は、少し考えてください。これがブロックチェーンの背後にある中心的な考え方です。
トランザクションをブロックに追加する方法が必要になります。 new_transaction() メソッドの役割は次のとおりで、非常に簡単です:
blockchain.py
class Blockchain(object):
...
def new_transaction(self, sender, recipient, amount):
"""
Creates a new transaction to go into the next mined Block
:param sender: <str> Address of the Sender
:param recipient: <str> Address of the Recipient
:param amount: <int> Amount
:return: <int> The index of the Block that will hold this transaction
"""
self.current_transactions.append({
'sender': sender,
'recipient': recipient,
'amount': amount,
})
return self.last_block['index'] + 1</int></int></str></str> new_transaction( ) メソッドはトランザクションをリストに追加し、トランザクションが追加されるブロックの インデックスを返します。 --- 次の ペアをマイニングして送信する方法について話します。トランザクションは後でユーザーにとって役立ちます。
ブロックチェーンがインスタンス化されたら、Genesisブロック(ブロックの先頭領域ブロックのないブロック)を追加する必要があります。で。また、マイニング (またはプルーフ オブ ワーク) の結果である proof をオリジン ブロックに追加する必要もあります。マイニングについては後で詳しく説明します。
コンストラクターで genesis ブロックを作成することに加えて、 new_block() 、 new_transaction() および も完了します。 hash() 関数:
blockchain.py
import hashlib
import json
from time import time
class Blockchain(object):
def __init__(self):
self.current_transactions = []
self.chain = []
# 创建创世区块
self.new_block(previous_hash=1, proof=100)
def new_block(self, proof, previous_hash=None):
"""
创建一个新的区块到区块链中
:param proof: <int> 由工作证明算法生成的证明
:param previous_hash: (Optional) <str> 前一个区块的 hash 值
:return: <dict> 新区块
"""
block = {
'index': len(self.chain) + 1,
'timestamp': time(),
'transactions': self.current_transactions,
'proof': proof,
'previous_hash': previous_hash or self.hash(self.chain[-1]),
}
# 重置当前交易记录
self.current_transactions = []
self.chain.append(block)
return block
def new_transaction(self, sender, recipient, amount):
"""
创建一笔新的交易到下一个被挖掘的区块中
:param sender: <str> 发送人的地址
:param recipient: <str> 接收人的地址
:param amount: <int> 金额
:return: <int> 持有本次交易的区块索引
"""
self.current_transactions.append({
'sender': sender,
'recipient': recipient,
'amount': amount,
})
return self.last_block['index'] + 1
@property
def last_block(self):
return self.chain[-1]
@staticmethod
def hash(block):
"""
给一个区块生成 SHA-256 值
:param block: <dict> Block
:return: <str>
"""
# 我们必须确保这个字典(区块)是经过排序的,否则我们将会得到不一致的散列
block_string = json.dumps(block, sort_keys=True).encode()
return hashlib.sha256(block_string).hexdigest()</str></dict></int></int></str></str></dict></str></int>上記のコードは簡単です --- コードを明確にするために、いくつかのコメントとコメントを追加しました。ドキュメンテーション。ブロックチェーンはほぼ完成しました。しかしこの時点で、新しいブロックがどのように作成、鍛造、または採掘されるのか疑問に思っているはずです。
Proof-of-Work (PoW) アルゴリズムを使用して、ブロックチェーン上で新しいブロックがどのように作成またはマイニングされるかを証明します。 PoW の目標は、特定の条件を満たす数値を計算することです。これを検証するのは計算的には難しくても、検証するのは簡単です。これが、proof of work の背後にある中心的な考え方です。
理解を助けるために簡単な例を見てみましょう:
假设一个整数 x 乘以另一个整数 y 的积的 Hash 值必须以 0 结尾,即 hash(x * y) = ac23dc...0。设 x = 5,求y 。
用 Python 实现:
from hashlib import sha256
x = 5
y = 0 # We don't know what y should be yet...
while sha256(f'{x*y}'.encode()).hexdigest()[-1] != "0":
y += 1
print(f'The solution is y = {y}')结果是:y = 21。因为,生成的 Hash 值结尾必须为 0。
hash(5 * 21) = 1253e9373e...5e3600155e860
在比特币中,工作量证明算法被称为 Hashcash ,它和上面的问题很相似,只不过计算难度非常大。这就是矿工们为了争夺创建区块的权利而争相计算的问题。 通常,计算难度与目标字符串需要满足的特定字符的数量成正比,矿工算出结果后,就会获得一定数量的比特币奖励(通过交易)。
验证结果,当然非常容易。
实现工作量证明
让我们来实现一个相似 PoW 算法。规则类似上面的例子:
找到一个数字 P ,使得它与前一个区块的 Proof 拼接成的字符串的 Hash 值以 4 个零开头。
blockchain.py
import hashlib
import json
from time import time
from uuid import uuid4
class Blockchain(object):
...
def proof_of_work(self, last_proof):
"""
Simple Proof of Work Algorithm:
- Find a number p' such that hash(pp') contains leading 4 zeroes, where p is the previous p'
- p is the previous proof, and p' is the new proof
:param last_proof: <int>
:return: <int>
"""
proof = 0
while self.valid_proof(last_proof, proof) is False:
proof += 1
return proof
@staticmethod
def valid_proof(last_proof, proof):
"""
Validates the Proof: Does hash(last_proof, proof) contain 4 leading zeroes?
:param last_proof: <int> Previous Proof
:param proof: <int> Current Proof
:return: <bool> True if correct, False if not.
"""
guess = f'{last_proof}{proof}'.encode()
guess_hash = hashlib.sha256(guess).hexdigest()
return guess_hash[:4] == "0000"</bool></int></int></int></int>衡量算法复杂度的办法是修改零开头的个数。使用 4 个来用于演示,你会发现多一个零都会大大增加计算出结果所需的时间。
现在 Blockchain 类基本已经完成了,接下来使用 HTTP Requests 来进行交互。
我们将使用 Python Flask 框架,这是一个轻量 Web 应用框架,它方便将网络请求映射到 Python 函数,现在我们来让 Blockchain 运行在基于 Flask web 上。
我们将创建三个接口:
/transactions/new 创建一个交易并添加到区块/mine 告诉服务器去挖掘新的区块/chain 返回整个区块链我们的 Flask 服务器 将扮演区块链网络中的一个节点。我们先添加一些框架代码:
blockchain.py
import hashlib
import json
from textwrap import dedent
from time import time
from uuid import uuid4
from flask import Flask
class Blockchain(object):
...
# Instantiate our Node(实例化我们的节点)
app = Flask(__name__)
# Generate a globally unique address for this node(为这个节点生成一个全球唯一的地址)
node_identifier = str(uuid4()).replace('-', '')
# Instantiate the Blockchain(实例化 Blockchain类)
blockchain = Blockchain()
@app.route('/mine', methods=['GET'])
def mine():
return "We'll mine a new Block"
@app.route('/transactions/new', methods=['POST'])
def new_transaction():
return "We'll add a new transaction"
@app.route('/chain', methods=['GET'])
def full_chain():
response = {
'chain': blockchain.chain,
'length': len(blockchain.chain),
}
return jsonify(response), 200
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)简单的说明一下以上代码:
发送到节点的交易数据结构如下:
{
"sender": "my address",
"recipient": "someone else's address",
"amount": 5
}因为我们已经有了添加交易的方法,所以基于接口来添加交易就很简单了。让我们为添加事务写函数:
blockchain.py
import hashlib
import json
from textwrap import dedent
from time import time
from uuid import uuid4
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
...
@app.route('/transactions/new', methods=['POST'])
def new_transaction():
values = request.get_json()
# Check that the required fields are in the POST'ed data
required = ['sender', 'recipient', 'amount']
if not all(k in values for k in required):
return 'Missing values', 400
# Create a new Transaction
index = blockchain.new_transaction(values['sender'], values['recipient'], values['amount'])
response = {'message': f'Transaction will be added to Block {index}'}
return jsonify(response), 201挖矿正是神奇所在,它很简单,做了一下三件事:
blockchain.py
import hashlib
import json
from time import time
from uuid import uuid4
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
...
@app.route('/mine', methods=['GET'])
def mine():
# We run the proof of work algorithm to get the next proof...
last_block = blockchain.last_block
last_proof = last_block['proof']
proof = blockchain.proof_of_work(last_proof)
# We must receive a reward for finding the proof.
# The sender is "0" to signify that this node has mined a new coin.
blockchain.new_transaction(
sender="0",
recipient=node_identifier,
amount=1,
)
# Forge the new Block by adding it to the chain
previous_hash = blockchain.hash(last_block)
block = blockchain.new_block(proof, previous_hash)
response = {
'message': "New Block Forged",
'index': block['index'],
'transactions': block['transactions'],
'proof': block['proof'],
'previous_hash': block['previous_hash'],
}
return jsonify(response), 200注意交易的接收者是我们自己的服务器节点,我们做的大部分工作都只是围绕 Blockchain 类方法进行交互。到此,我们的区块链就算完成了,我们来实际运行下。
你可以使用 cURL 或 Postman 去和 API 进行交互
启动 Server:
$ python blockchain.py * Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
让我们通过请求 http://localhost:5000/mine ( GET )来进行挖矿:
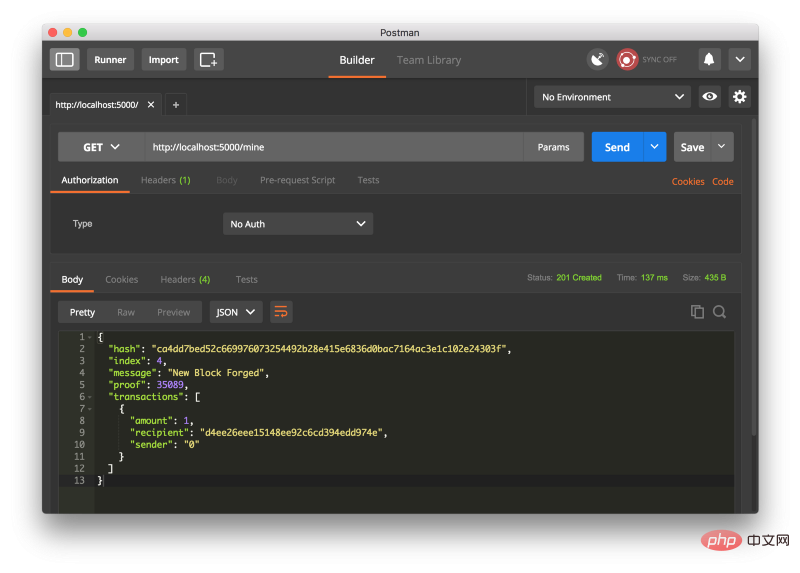
用 Postman 发起一个 GET 请求.
创建一个交易请求,请求 http://localhost:5000/transactions/new (POST),如图
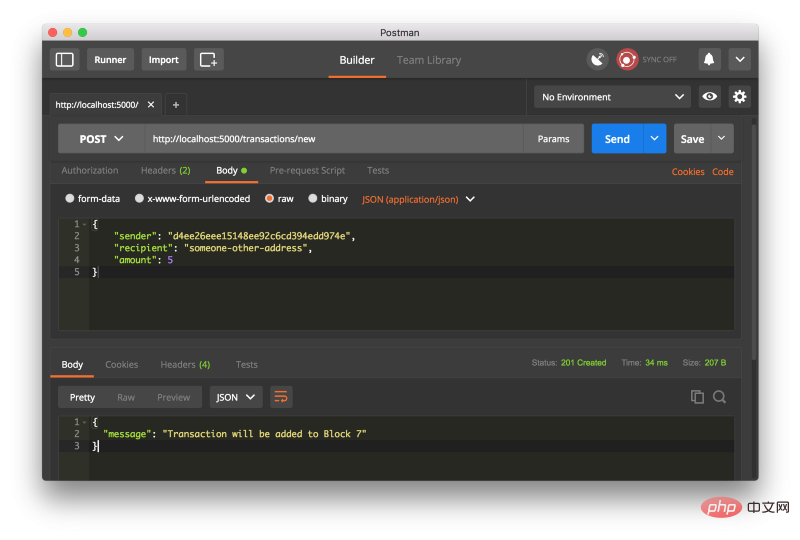
如果不是使用 Postman,则用一下的 cURL 语句也是一样的:
$ curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"sender": "d4ee26eee15148ee92c6cd394edd974e",
"recipient": "someone-other-address",
"amount": 5
}' "http://localhost:5000/transactions/new"在挖了两次矿之后,就有 3 个块了,通过请求 http://localhost:5000/chain 可以得到所有的块信息
{
"chain": [
{
"index": 1,
"previous_hash": 1,
"proof": 100,
"timestamp": 1506280650.770839,
"transactions": []
},
{
"index": 2,
"previous_hash": "c099bc...bfb7",
"proof": 35293,
"timestamp": 1506280664.717925,
"transactions": [
{
"amount": 1,
"recipient": "8bbcb347e0634905b0cac7955bae152b",
"sender": "0"
}
]
},
{
"index": 3,
"previous_hash": "eff91a...10f2",
"proof": 35089,
"timestamp": 1506280666.1086972,
"transactions": [
{
"amount": 1,
"recipient": "8bbcb347e0634905b0cac7955bae152b",
"sender": "0"
}
]
}
],
"length": 3
}我们已经有了一个基本的区块链可以接受交易和挖矿。但是区块链系统应该是分布式的。既然是分布式的,那么我们究竟拿什么保证所有节点有同样的链呢?这就是一致性问题,我们要想在网络上有多个节点,就必须实现一个一致性的算法。
在实现一致性算法之前,我们需要找到一种方式让一个节点知道它相邻的节点。每个节点都需要保存一份包含网络中其它节点的记录。因此让我们新增几个接口:
/nodes/register 接收 URL 形式的新节点列表./nodes/resolve 执行一致性算法,解决任何冲突,确保节点拥有正确的链.我们修改下 Blockchain 的 init 函数并提供一个注册节点方法:
blockchain.py
... from urllib.parse import urlparse ... class Blockchain(object): def __init__(self): ... self.nodes = set() ... def register_node(self, address): """ Add a new node to the list of nodes :param address: <str> Address of node. Eg. 'http://192.168.0.5:5000' :return: None """ parsed_url = urlparse(address) self.nodes.add(parsed_url.netloc)</str>
我们用 set 来储存节点,这是一种避免重复添加节点的简单方法.
就像先前讲的那样,当一个节点与另一个节点有不同的链时,就会产生冲突。 为了解决这个问题,我们将制定最长的有效链条是最权威的规则。换句话说就是:在这个网络里最长的链就是最权威的。 我们将使用这个算法,在网络中的节点之间达成共识。
blockchain.py
...
import requests
class Blockchain(object)
...
def valid_chain(self, chain):
"""
Determine if a given blockchain is valid
:param chain: <list> A blockchain
:return: <bool> True if valid, False if not
"""
last_block = chain[0]
current_index = 1
while current_index True if our chain was replaced, False if not
"""
neighbours = self.nodes
new_chain = None
# We're only looking for chains longer than ours
max_length = len(self.chain)
# Grab and verify the chains from all the nodes in our network
for node in neighbours:
response = requests.get(f'http://{node}/chain')
if response.status_code == 200:
length = response.json()['length']
chain = response.json()['chain']
# Check if the length is longer and the chain is valid
if length > max_length and self.valid_chain(chain):
max_length = length
new_chain = chain
# Replace our chain if we discovered a new, valid chain longer than ours
if new_chain:
self.chain = new_chain
return True
return False</bool></list>第一个方法 valid_chain() 负责检查一个链是否有效,方法是遍历每个块并验证散列和证明。
resolve_conflicts() 是一个遍历我们所有邻居节点的方法,下载它们的链并使用上面的方法验证它们。 如果找到一个长度大于我们的有效链条,我们就取代我们的链条。
我们将两个端点注册到我们的API中,一个用于添加相邻节点,另一个用于解决冲突:
blockchain.py
@app.route('/nodes/register', methods=['POST'])
def register_nodes():
values = request.get_json()
nodes = values.get('nodes')
if nodes is None:
return "Error: Please supply a valid list of nodes", 400
for node in nodes:
blockchain.register_node(node)
response = {
'message': 'New nodes have been added',
'total_nodes': list(blockchain.nodes),
}
return jsonify(response), 201
@app.route('/nodes/resolve', methods=['GET'])
def consensus():
replaced = blockchain.resolve_conflicts()
if replaced:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain was replaced',
'new_chain': blockchain.chain
}
else:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain is authoritative',
'chain': blockchain.chain
}
return jsonify(response), 200在这一点上,如果你喜欢,你可以使用一台不同的机器,并在你的网络上启动不同的节点。 或者使用同一台机器上的不同端口启动进程。 我在我的机器上,不同的端口上创建了另一个节点,并将其注册到当前节点。 因此,我有两个节点:http://localhost:5000 和 http://localhost:5001。 注册一个新节点:
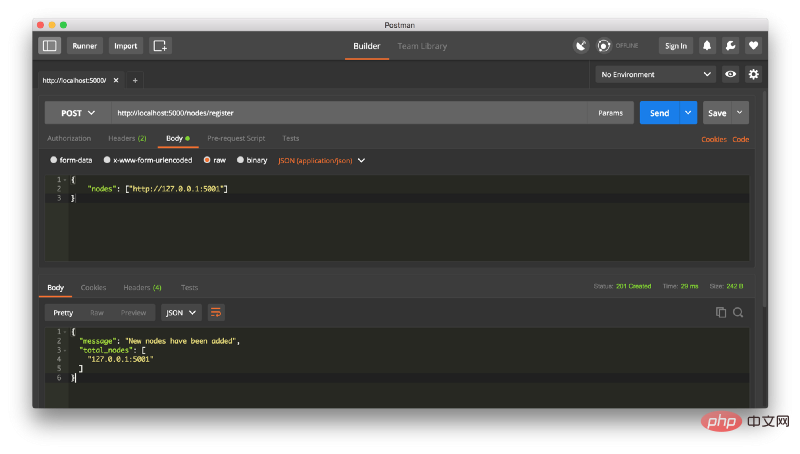
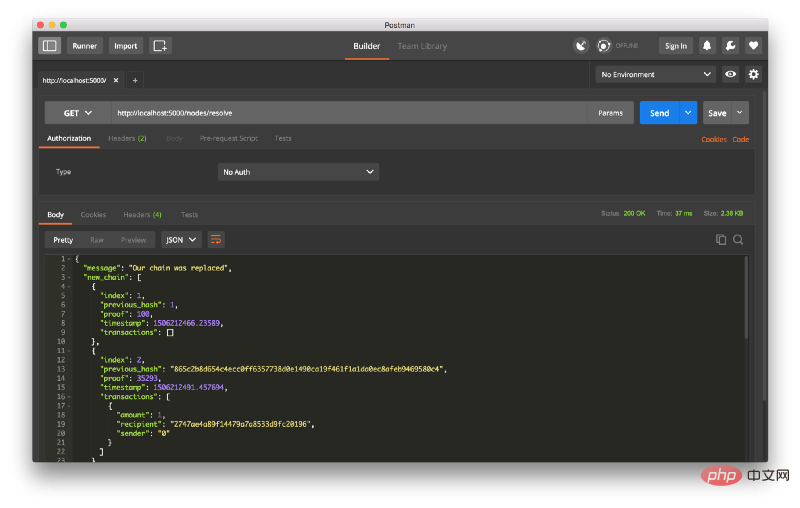
然后我在节点 2 上挖掘了一些新的块,以确保链条更长。 之后,我在节点1上调用 GET /nodes/resolve,其中链由一致性算法取代:
这是一个包,去找一些朋友一起,以帮助测试你的区块链。
我希望本文能激励你创造更多新东西。我之所以对数字货币入迷,是因为我相信区块链会很快改变我们看待事物的方式,包括经济、政府、档案管理等。
更新:我计划在接下来的第2部分中继续讨论区块链交易验证机制,并讨论一些可以让区块链进行生产的方法。
相关推荐:编程视频课程
以上がPython を使用して独自のブロックチェーンを構築するの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。