
PHP にファイルをインポートするにはどのような方法がありますか? PHP インポート ファイルには 4 つのステートメントがあります: include、require、include_once、require_once PHP インポート ファイルの具体的な例を見てみましょう。
基本構文
require: require 関数は通常、PHP スクリプトの先頭に配置され、実行されます。 PHP の前に まず、require で指定されたインポートされたファイルを読み込み、インポートされたスクリプト ファイルをインクルードして実行してみます。 require の仕組みは PHP の実行効率を高めるためのもので、同じ Web ページ内で一度解釈されると、2 回目は解釈されなくなります。ただし、同様に、インポートされたファイルを繰り返し解釈しないため、PHP でファイルを導入するためにループまたは条件ステートメントを使用する場合は include を使用する必要があります。
include: は、PHP スクリプト内のどこにでも (通常はプロセス コントロールの処理部分に) 配置できます。 include で指定したファイルに対して PHP スクリプトを実行すると、インクルードされて実行が試行されます。この方法により、プログラムの実行プロセスを簡略化できます。同じファイルに 2 回目に遭遇した場合でも、PHP は再度それを再解釈します。 include の実行効率は、require の実行効率よりもはるかに低くなります。同時に、インポートされたファイルにユーザー定義関数が含まれている場合、 PHP では、解釈プロセス中に関数定義が繰り返されるという問題が発生します。
require_once/include_once: これらの関数は、それぞれ require/include と同じです。違いは、実行時に、ターゲット コンテンツが以前にインポートされているかどうかを最初にチェックすることです。インポートされているため、同じコンテンツが再度導入されることはありません。
#お互いの違い
//test1.php
<?php
include './tsest.php';
echo 'this is test1';
?>
//test2.php
<?php
echo 'this is test2\n';
function test() {
echo 'this is test\n';
}
?>
//结果:
this is test1//test1.php
<?php
require './tsest.php';
echo 'this is test1';
?>
//test2.php
<?php
echo 'this is test2\n';
function test() {
echo 'this is test\n';
}
?>
//test1.php <?php include './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1this is test2 //test1.php <?php include './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include_once './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1 //test1.php <?php include_once './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1this is test2 //test1.php <?php include_once './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include_once './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1
require と require_once: include と include_once と同じ違いです。
読み込み時の実行処理
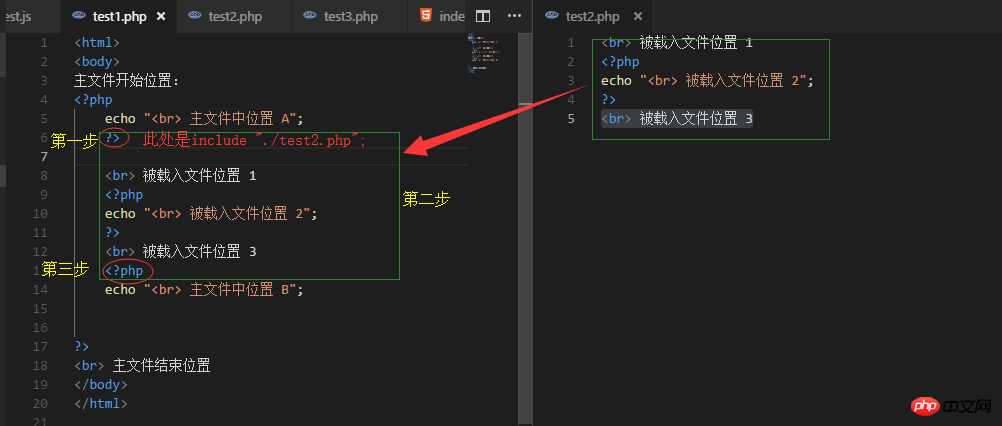
1. include(require)文からphpスクリプトモードを終了(htmlコードモードに入る)2. include ステートメントで設定したファイル内のコードを読み込み、実行してみます3. html モードを終了し、php スクリプト モードに再度入り、後続のスクリプトの実行を続行しますプログラム
//test1.php
<html>
<body>
主文件开始位置:
<?php
echo "<br> 主文件中位置 A";
include "./test2.php"; //要载入的文件
echo "<br> 主文件中位置 B";
?>
<br> 主文件结束位置
</body>
</html>
//test2.php
<br> 被载入文件位置 1
<?php
echo "<br> 被载入文件位置 2";
?>
<br> 被载入文件位置 3 #分析:
#分析:
#相対パス:
./ 表示表示当前位置,即当前网页文件所在的目录 . . / 表示上一级位置,即当前网页文件所在目录的上一级目录 //例如: include "./test2.php"; require "../../test3.html";
絶対パス:
include "C:/PHP/test/test2.php";
<?php define('DS') or define('DS',DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR); echo "使用绝对路径引入(方法一)"; include __DIR__ . DS . 'test2.php'; echo "使用绝对路径载入方法(方法二)"; $root = $_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT']; // 获得当前站点的根目录 include $root.DS.'node_test'.DS.'inAndRe'.DS. 'test2.php'; ?>
include "http://www.lishnli/index.php"
需要注意:无论采用哪种路径,必须要加上文件后缀名,这四种文件载入方式不能识别无后缀的文件。
//test1.php include "./test2.php"; //结果:this is test2 //test1.php include "./test2"; //结果:
返回值的比较
上文说道include有返回值,而require无返回值
对于include,如果载入成功,有返回值,返回值为1;如果载入失败,则返回false.
对于require,如果载入成功,有返回值,返回值为1;如果载入失败,无返回值。
//test1.php <?php $a = include "./test2.php"; var_dump($a); echo "<br>"; $b = include "./test2.phps"; var_dump($b); echo "<br>"; $c = require "./test2.php"; var_dump($c); echo "<br>"; $d = require "./test2.phps"; var_dump($d); ?>
输出:

当被载入文件中有return语句时,会有另外的机制,此时return语句的作用是终止载入过程,即被载入文件中return语句的后续代码不再载入。return语句也可以用于被载入文件载入时返回一个数据。
//test1.php <?php $a = include "./test2.php"; echo "<br>"; var_dump($a); ?> //test2.php //该文件中有return语句 <?php $b = 'test2'; echo "被载入的文件:A 位置"; return $b; echo "<br 被载入的文件: B 位置"; ?>
结果:

相关推荐:
php 字符串写入文件或追加入文件(file_put_contents)
以上がPHPにファイルをインポートするにはどのような方法がありますか? PHPでファイルを導入する4つの方法(コード)を紹介の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。