
1. はじめに
ファイルのアップロードは比較的一般的な機能ですが、最初にアップロード ボタンをクリックしてからファイルのパスを見つけてアップロードする必要があります。それはユーザーエクスペリエンスに大きな問題をもたらします。 HTML5 は、ドラッグ アンド ドロップ アップロードに必要な API のサポートを開始します。 Nodejs も最近人気が高まっているテクノロジであり、これが私が nodejs に初めて触れたきっかけでもあります。nodejs 開発で最もよく使用される開発フレームワークの 1 つは、mvc モデルに似たフレームワークです。 HTML5とnodejs Expressを組み合わせて、ドラッグ&ドロップアップロード機能を実装しました。
2. 基礎知識の普及
1. NodeJsの基礎知識
Nodejsは単純にサーバー上でjsを実行できる開発プラットフォームであり、多くの国内企業でも使用され始めています。タオバオなどの待機。従来の Web アプリケーション開発プラットフォームは、同時実行性の高いリクエストに応答するためにマルチスレッドに依存しています。 Nodejs は、シングルスレッド、非同期 IO、およびイベント駆動型の設計モデルを採用しており、これにより、nodejs のパフォーマンスが大幅に向上します。これは、nodejs の最大の機能でもあり、nodejs では、すべての IO 操作がコールバックを通じて実行されます。nodejs が IO 操作を実行すると、IO リクエストがイベント キューにプッシュされ、プログラムが処理するのを待ちます。処理されてから呼び出します。コールバック関数は結果を返します。 たとえば、クエリ データベースの操作は次のとおりです。mysql.query("SELECT * FROM myTable",function(res){
callback(res);
});その中で: 
function uploader(url, data, files) {
this._files = files;
this._data = data;
this._url = url;
this._xhr = null;
this.onloadstart = {};
this.onload = {};
this.onloadend = {};
this.onprogress = {};
this.onerror = {};
this.ontimeout = {};
this.callback = {};//请求完成后回调
_self = this;
}
uploader.prototype = {
init: function () {
if (!isValid()) {
throw e;
}
this._xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
this._bindEvents();
},
send: function () {
if (this._xhr == null) {
this.init();
}
var formData = this._createFormData();
this._xhr.open('post', this._url, true);
this._xhr.send(formData);
},
_bindEvents: function () {
_self = this;
this._xhr.upload.loadstart = function (e) {
evalFunction(_self.onloadstart, e);
}
this._xhr.upload.onload = function (e) {
evalFunction(_self.onload, e);
};
this._xhr.upload.onloadend = function (e) {
evalFunction(_self.onloadend, e);
}
this._xhr.upload.onprogress = function (e) {
evalFunction(_self.onprogress, e)
};
this._xhr.upload.onerror = function (e) {
evalFunction(_self.onerror, e);
};
this._xhr.upload.ontimeout = function (e) {
evalFunction(_self.ontimeout, e);
}
this._xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (_self._xhr.readyState == 4) {
if (typeof _self.callback === 'function') {
var status = _self._xhr.status;
var data = _self._xhr.responseText;
_self.callback(status, data);
}
}
}
},
_createFormData: function () {
var formData = new FormData();
this._addDataToFormData(formData);
this._addFileToFormData(formData);
return formData;
},
_addDataToFormData: function (formData) {
if (this._data) {
for (var item in this._data) {
formData.append(item, this._data[item]);
}
}
},
_addFileToFormData: function (formData) {
if (this._files) {
for (var i = 0; i < this._files.length; i++) {
var file = this._files[i];
formData.append('file[' + i + ']', this._files[i]);
}
}
}
};
View Code
var uploaderFactory = {
send: function (url, data, files, callback) {
var insUploader = new uploader(url, data, files);
insUploader.callback = function (status, resData) {
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
callback(status, resData);
}
}
insUploader.send();
return insUploader;
}
};(function (upladerQueue) {
var Status = {
Ready: 0,
Uploading: 1,
Complete: 2
}
var _self = null;
var instance = null;
function Queue() {
this._datas = [];
this._curSize = 0;//当前长度
_self = this;
}
Queue.prototype = {
add: function (data) {
var key = new Date().getTime();
this._datas.push({key: key, data: data, status: Status.Ready});
this._curSize = this._datas.length;
return key;
},
remove: function (key) {
var index = this._getIndexByKey(key);
this._datas.splice(index, 1);
this._curSize = this._datas.length;
},
get: function (key) {
var index = this._getIndexByKey(key);
return index != -1 ? this._datas[index].data : null;
},
clear: function () {
this._datas = [];
this._curSize = this._datas.length;
},
size: function () {
return this._curSize;
},
setItemStatus: function (key, status) {
var index = this._getIndexByKey(key);
if (index != -1) {
this._datas[index].status = status;
}
},
nextReadyingIndex: function () {
for (var i = 0; i < this._datas.length; i++) {
if (this._datas[i].status == Status.Ready) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
},
getDataByIndex: function (index) {
if (index < 0) {
return null;
}
return this._datas[index];
},
_getIndexByKey: function (key) {
for (var i = 0; i < this._datas.length; i++) {
if (this._datas[i].key == key) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
function getInstace() {
if (instance === null) {
instance = new Queue();
return instance;
} else {
return instance;
}
}
upladerQueue.Queue = getInstace();
upladerQueue.UploadStatus = Status;
})(window.uploaderQueue);(function (upladerQueue) {
var instance = null;
var _self;
function uploadEngine() {
this._url = null;
this._curUploadingKey = -1;//标志
this.uploadStatusChanged = {};
this.uploadItemProgress={};
_self = this;
}
uploadEngine.prototype = {
setUrl: function (url) {
this._url = url;
},
run: function () {
if (this._curUploadingKey === -1 && this._url) {
this._startUpload();
}
},
_startUpload: function () {
_self = this;
var index = upladerQueue.Queue.nextReadyingIndex();
if (index != -1) {
this._uploadItem(index);
} else {
this._curUploadingKey = -1;
return null;
}
},
_uploadItem: function (index) {
var data = upladerQueue.Queue.getDataByIndex(index).data;
_self = this;
this._readyUploadItem(index);
var upload = uploaderFactory.send(this._url, null, data.files, function (status, data) {
_self._completedUploadItem.call(_self, status, data);
});
this._uploadItemProgress(upload);
},
_uploadItemProgress: function (upload) {
upload.onprogress = function (e) {
_self.uploadItemProgress(_self._curUploadingKey,e);
}
},
_readyUploadItem: function (index) {
this._curUploadingKey = upladerQueue.Queue.getDataByIndex(index).key;
if (typeof this.uploadStatusChanged === 'function') {
this.uploadStatusChanged(this._curUploadingKey, upladerQueue.UploadStatus.Uploading);
}
upladerQueue.Queue.setItemStatus(this._curUploadingKey, upladerQueue.UploadStatus.Uploading);
},
_completedUploadItem: function (status, data) {
if (typeof this.uploadStatusChanged === 'function') {
this.uploadStatusChanged(this._curUploadingKey, upladerQueue.UploadStatus.Complete);
}
upladerQueue.Queue.setItemStatus(this._curUploadingKey, upladerQueue.UploadStatus.Complete);
this._startUpload();
}
};
function getInstace() {
if (instance === null) {
instance = new uploadEngine();
}
return instance;
}
upladerQueue.Engine = getInstace();
})(window.uploaderQueue);该对象比较简单主要提供一个run以及setUrl方法,用于启动上传引擎,以及设置上传路径的功能。内部使用递归的方法把文件队列中的方法全部上传到服务端。使用uploadItemProgress通知外部上传的进度,使用uploadStatusChanged通知文件上传状态,以便更新UI.
uploaderApp.js中主要包括三个对象,一个是类似jquery的一个简单的jquery对象(App$)。主要用于绑定事件。一个是uploaderArea对象,是拖曳上传的窗口区域,另一个是入口对象uploaderMain对象。主要用于初始化对象,对外部提供一个init方法,来初始化整个对象。
了解关于App$以及uploaderArea对象的代码请下载 源代码 ,下面仅对uploaderMain对象做简单的说明。
(function (app) {
var _self;
function uploaderMain(id) {
this._id = id;
this._area = null;
this.uploaders = [];
this._URL = 'file/uploader';
}
uploaderMain.prototype = {
init: function () {
_self = this;
this._initArea();
this._initQueueEng();
},
_initQueueEng: function () {
uploaderQueue.Engine.setUrl(this._URL);
uploaderQueue.Engine.uploadStatusChanged = function (key, status) {
if (status === uploaderQueue.UploadStatus.Uploading) {
_self._area.hideItemCancel(key);
} else if (status === uploaderQueue.UploadStatus.Complete) {
_self._area.completeItem(key);
_self._area.showItemCancel(key);
}
}
uploaderQueue.Engine.uploadItemProgress = function (key, e) {
var progress = e.position / e.total;
_self._area.changeItemProgress(key, Math.round(progress * 100));
}
},
_initArea: function () {
this._area = new app.area(this._id);
this._area.init();
this._area.drop = function (e) {
var key = uploaderQueue.Queue.add({files: e.dataTransfer.files});
uploaderQueue.Engine.run();
return key;
}
this._area.cancelItem = function (key) {
uploaderQueue.Queue.remove(key);
}
}
};
app.main = uploaderMain;
})(window.uploaderApp);在uploaderMain对象,相当于各个对象之间的中介,主要就是做对象的初始化功能、以及对象之间相互调用。使各个对象之间相互协作完成整个模块的功能。对外提供一个init方法来初始化整个程序,在html页面中只需如下代码:
<script type="text/javascript"> var main=new uploaderApp.main('container'); main.init(); </script>
以上代码就是创建一个入口对象,然后使用init方法来启动整个程序。
以上是对前端js的主要方法做的简单解释,如果想详细了解请下载源代码。下面简单看下后端js(nodejs)端实现的主要代码。
在express基础知识时,已经讲过在express已经对文件上传功能做了完整的封装,当路由到action时,文件已经完成上传只是文件上传到了一个临时目录,这个临时目录我们可以在app.js中配置的,配置方式如下:
app.use(express.bodyParser({
uploadDir:__dirname+'/public/temp'
}));这样在文件上传后文件就存放在/public/temp目录下,文件名也是express通过一定的算法随机获取的。在我们写的action中只需要把存在临时目录中的文件移动到服务端存放文件的目录下,然后删除临时目录下的文件即可。具体代码如下:
function uploader(req, res) {
if (req.files != 'undifined') {
console.dir(req.files);
utils.mkDir().then(function (path) {
uploadFile(req, res, path, 0);
});
}
}
function uploadFile(req, res, path, index) {
var tempPath = req.files.file[index].path;
var name = req.files.file[index].name;
if (tempPath) {
var rename = promise.denodeify(fs.rename);
rename(tempPath, path + name).then(function () {
var unlink = promise.denodeify(fs.unlink);
unlink(tempPath);
}).then(function () {
if (index == req.files.file.length - 1) {
var res = {
code: 1,
des: '上传成功'
};
res.send(res);
} else {
uploadFile(req, res, path, index + 1);
}
});
}
}2、实现效果
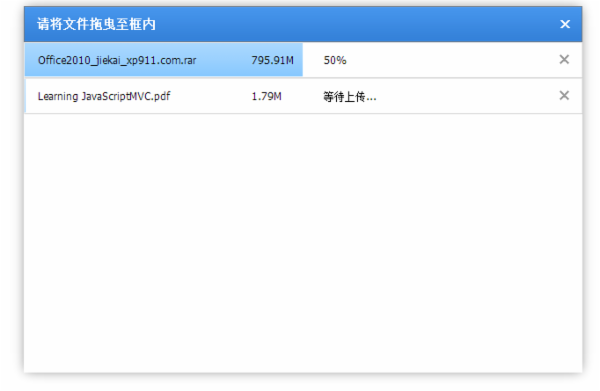
更多Nodejs+express+html5 实现拖拽上传相关文章请关注PHP中文网!