Redis vsデータベース:制限は何ですか?
Redis is limited by memory constraints and data persistence, while traditional databases struggle with performance in real-time scenarios. 1) Redis excels in real-time data processing and caching but may require complex sharding for large datasets. 2) Traditional databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL ensure strong consistency and ACID compliance, ideal for transactional integrity, but can be slower in high-speed applications.

When diving into the world of data storage and management, the choice between Redis and traditional databases often comes up. So, what are the limits of Redis compared to databases? Let's unpack this by exploring their capabilities, use cases, and where they shine or falter.
Redis, known for its blazing speed and in-memory data storage, excels in scenarios requiring real-time data processing and caching. On the other hand, traditional databases, like MySQL or PostgreSQL, are robust, offering strong consistency and ACID compliance, making them ideal for transactional data integrity. The limits of Redis are often around its memory constraints and data persistence, while databases might struggle with performance in high-speed, real-time scenarios.
Let's dive deeper into these aspects.
Redis is my go-to tool when I need lightning-fast data access. I've used it in projects where every millisecond counts, like real-time analytics or session management for high-traffic websites. Here's a little trick I've learned: if you're using Redis for caching, always set an expiration time on your keys to prevent memory bloat. It's like having a self-cleaning system that keeps your Redis instance running smoothly.
import redis
# Initialize Redis client
redis_client = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, db=0)
# Set a key with an expiration time of 3600 seconds (1 hour)
redis_client.setex('user_session:1234', 3600, 'user_data')On the flip side, Redis's reliance on memory can be a double-edged sword. Memory is expensive, and when you're dealing with large datasets, you might hit the wall of your server's capacity. I've seen projects where we had to implement complex sharding strategies to distribute data across multiple Redis instances. It's a bit like playing Tetris with your data—fitting everything just right to avoid crashing the system.
Contrast this with traditional databases, which offer a different set of trade-offs. I've worked on e-commerce platforms where data integrity and transaction safety were non-negotiable. Here, databases like PostgreSQL shine with their ACID properties. But, let's be real, they can feel sluggish compared to Redis. I remember optimizing a query on a large dataset and feeling the thrill of shaving off seconds from the response time, but it was still nowhere near the speed of Redis.
-- Example of a transaction in PostgreSQL BEGIN; UPDATE accounts SET balance = balance - 100 WHERE user_id = 1; UPDATE accounts SET balance = balance + 100 WHERE user_id = 2; COMMIT;
One of the pitfalls I've encountered with databases is the complexity of scaling. Vertical scaling is straightforward but hits a ceiling quickly. Horizontal scaling, while more flexible, can introduce complexities like data replication and consistency issues. I've spent sleepless nights debugging replication lag, only to realize that a simpler Redis setup might have solved the problem faster.
When it comes to data persistence, Redis offers some solutions like RDB and AOF, but they're not as robust as the backup and recovery mechanisms of traditional databases. I've had to implement custom backup strategies for Redis to ensure data safety, which adds another layer of complexity to the system.
In terms of performance optimization, both Redis and databases have their tricks. For Redis, I often use pipelining to batch commands and reduce network latency. It's like sending a bunch of letters in one go rather than one at a time.
# Example of Redis pipelining
with redis_client.pipeline() as pipe:
pipe.set('key1', 'value1')
pipe.set('key2', 'value2')
pipe.execute()For databases, indexing is your best friend. I've seen poorly indexed tables slow down queries to a crawl. It's like trying to find a book in a library without a catalog. Proper indexing can transform your database performance, making it almost feel like Redis in some scenarios.
-- Creating an index on a frequently queried column CREATE INDEX idx_user_id ON accounts(user_id);
In conclusion, the limits of Redis and traditional databases are shaped by their design philosophies. Redis is your speed demon, perfect for real-time applications but constrained by memory. Traditional databases are your reliable workhorses, ensuring data integrity at the cost of speed. The choice depends on your project's needs, and often, a hybrid approach can leverage the strengths of both. I've seen the best results when using Redis for caching and databases for persistent storage, creating a system that's both fast and reliable.
So, when you're faced with this decision, think about what matters most to your application. Are you chasing speed, or do you need the ironclad guarantees of data consistency? Sometimes, the answer lies in using both, and that's where the real magic happens.
以上がRedis vsデータベース:制限は何ですか?の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 1594
1594
 29
29
 1476
1476
 72
72
 267
267
 587
587
 125
125
 836
836
 21
21
 8
8
 Windows/LinuxにMySQL 8.0をインストールする方法は?
Jun 11, 2025 pm 03:25 PM
Windows/LinuxにMySQL 8.0をインストールする方法は?
Jun 11, 2025 pm 03:25 PM
MySQL 8.0をインストールするための鍵は、手順に従い、一般的な問題に注意を払うことです。 WindowsでMSIインストールパッケージを使用することをお勧めします。手順には、インストールパッケージのダウンロード、インストーラーの実行、インストールタイプの選択、ルートパスワードの設定、サービススタートアップの有効化、ポート競合に注意を払うか、ZIPバージョンの手動で構成することが含まれます。 Linux(Ubuntuなど)はAPTを通じてインストールされ、手順はソースを更新し、サーバーのインストール、セキュリティスクリプトの実行、サービスステータスの確認、ルート認証方法の変更を行います。どのプラットフォームに関係なく、デフォルトのパスワードを変更し、通常のユーザーを作成し、ファイアウォールを設定し、構成ファイルを調整して、セキュリティと通常の使用を確保するために文字セットやその他のパラメーターを最適化する必要があります。
 MongoDBのすべてのデータベースを表示する方法
Jun 04, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
MongoDBのすべてのデータベースを表示する方法
Jun 04, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
MongoDBのすべてのデータベースを表示する方法は、コマンド「showdbs」を入力することです。 1.このコマンドは、空でないデータベースのみを表示します。 2。データベースを「使用」コマンドを介して切り替えて、データを挿入して表示できます。 3.「ローカル」や「構成」などの内部データベースに注意してください。 4。ドライバーを使用する場合、詳細情報を取得するには、「listDatabase()」メソッドを使用する必要があります。 5。「db.stats()」コマンドは、詳細なデータベース統計を表示できます。
 Redisマスタースレーブレプリケーションの障害トラブルシューティングプロセス
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
Redisマスタースレーブレプリケーションの障害トラブルシューティングプロセス
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
Redisマスタースレーブの複製障害のトラブルシューティングと修復の手順には次のものがあります。1。ネットワーク接続を確認し、PingまたはTelnetを使用して接続をテストします。 2. Redis構成ファイルを確認して、レプリカと再生時間が正しく設定されていることを確認します。 3. Redisログファイルを確認し、エラー情報を見つけます。 4.ネットワークの問題の場合は、ネットワークデバイスを再起動するか、代替パスを切り替えてみてください。 5.構成問題の場合は、構成ファイルを変更します。 6.データの同期問題の場合は、Slaveofコマンドを使用してデータを再考します。
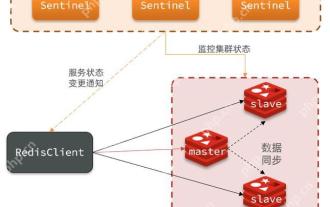 Redisクラスターノードの障害の迅速な場所と取り扱い
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Redisクラスターノードの障害の迅速な場所と取り扱い
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Redisクラスターノード障害の迅速な場所と処理手順は次のとおりです。1。障害を確認します。Clusternodesコマンドを使用して、ノードステータスを表示します。故障が表示された場合、ノードは失敗します。 2。原因を決定:ネットワーク、ハードウェア、および構成を確認します。一般的な問題には、メモリ制限を超えることが含まれます。 3。修理と復元:サービスの再起動、ハードウェアの交換、構成の変更など、理由に基づいて対策を講じます。 4。注:データの一貫性を確保し、適切なフェイルオーバーポリシーを選択し、監視およびアラームシステムを確立します。
 RedisとRabbitmqの間のパフォーマンス比較と共同アプリケーションシナリオ
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
RedisとRabbitmqの間のパフォーマンス比較と共同アプリケーションシナリオ
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
RedisとRabbitmqにはそれぞれ、パフォーマンスと共同アプリケーションのシナリオに独自の利点があります。 1.Redisは、高い並行性シナリオに適した最大マイクロ秒の遅延で、データの読み取りと書き込みで優れたパフォーマンスを発揮します。 2.RabbitMQは、メッセージング、ミリ秒での遅延に焦点を当て、マルチキューおよび消費者モデルをサポートします。 3。共同アプリケーションでは、Redisをデータストレージに使用でき、RabbitMQは非同期タスクを処理し、システムの応答速度と信頼性を向上させます。
 Redisクラスターの分割脳の問題を解決する方法と戦略
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Redisクラスターの分割脳の問題を解決する方法と戦略
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Redisクラスターにおけるスプリットブレインの問題に対する効果的な解決策には、次のものがあります。1)接続の安定性を確保するためのネットワーク構成の最適化。 2)ノード監視と障害検出、ツールを使用したリアルタイム監視。 3)フェールオーバーメカニズム、複数のマスターノードを回避するために高いしきい値を設定します。 4)データの一貫性保証、複製関数を使用してデータを同期させる。 5)手動の介入と回復、および必要に応じて手動処理。
 Eloquentを使用してデータベースに新しいレコードを作成するにはどうすればよいですか?
Jun 14, 2025 am 12:34 AM
Eloquentを使用してデータベースに新しいレコードを作成するにはどうすればよいですか?
Jun 14, 2025 am 12:34 AM
Eloquentを使用してデータベースに新しいレコードを作成するには、4つの主要な方法があります。1。ユーザー:: createなどの属性配列を渡すことにより、作成方法を迅速に作成します(['name' => 'johndoe' => 'john@example.com']); 2。保存方法を使用して、モデルを手動でインスタンス化し、値を1つずつ保存するために値を割り当てます。これは、条件付き割り当てまたは追加ロジックが必要なシナリオに適しています。 3. FirstOrCreateを使用して、データ条件に基づいてレコードを見つけたり作成したりして、データの重複を回避します。 4. updateorcreateを使用してレコードを見つけて更新しない場合は、それらを作成します。これは、繰り返しの可能性があるインポートされたデータなどを処理するのに適しています。
 Redis持続性パフォーマンスを改善するための構成提案
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
Redis持続性パフォーマンスを改善するための構成提案
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
構成を介してRedisの持続性パフォーマンスを改善する方法は次のとおりです。1。RDBの保存パラメーターを調整して、スナップショット生成周波数を減らします。 2。AOFのappendFSyncパラメーターをEverySecに設定します。 3. AOFとRDBを組み合わせて使用します。 4. AOF書き換えパフォーマンスを最適化するには、no-appendfsync-on-rewriteパラメーターを使用します。 5.ハイブリッド持続モードを有効にします。これらの構成は、データセキュリティを確保しながら、パフォーマンスを改善できます。





